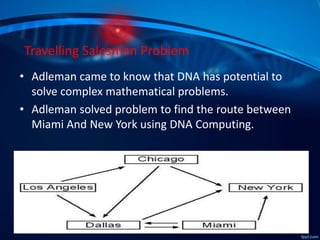
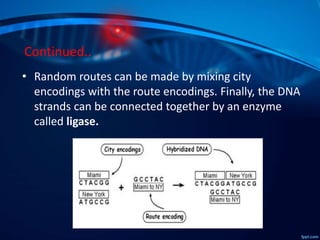
The document outlines the concept of DNA computing, highlighting DNA's uniqueness as a computational element due to its dense information storage, parallelism, and energy efficiency. It discusses Leonard Adleman's pioneering experiment in solving the Traveling Salesman Problem using DNA strands. While DNA computers exhibit significant advantages like massive data storage and low power requirements, they still face limitations and are not yet widely available for traditional computing applications.