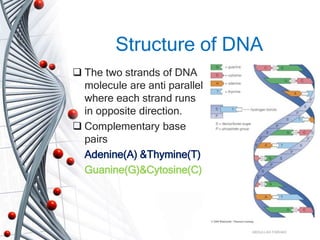
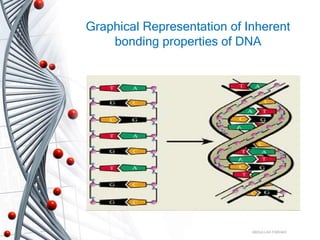
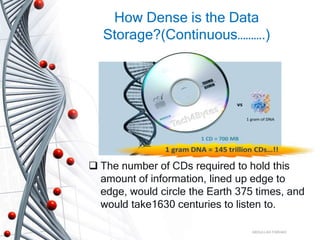
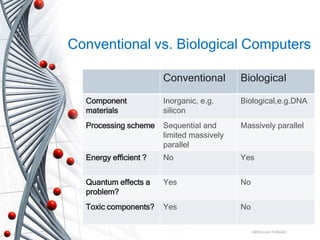
Bio computing uses DNA and biochemical processes to store and manipulate data similarly to human biology. DNA can store vast amounts of data densely due to its structure of paired bases. DNA computers use enzymes and chain reactions to compute solutions to problems in massively parallel processing, offering greater efficiency than conventional computers. While DNA computing shows potential for medical and data applications, it still requires further development to improve accuracy and stability before being a fully realized technology.