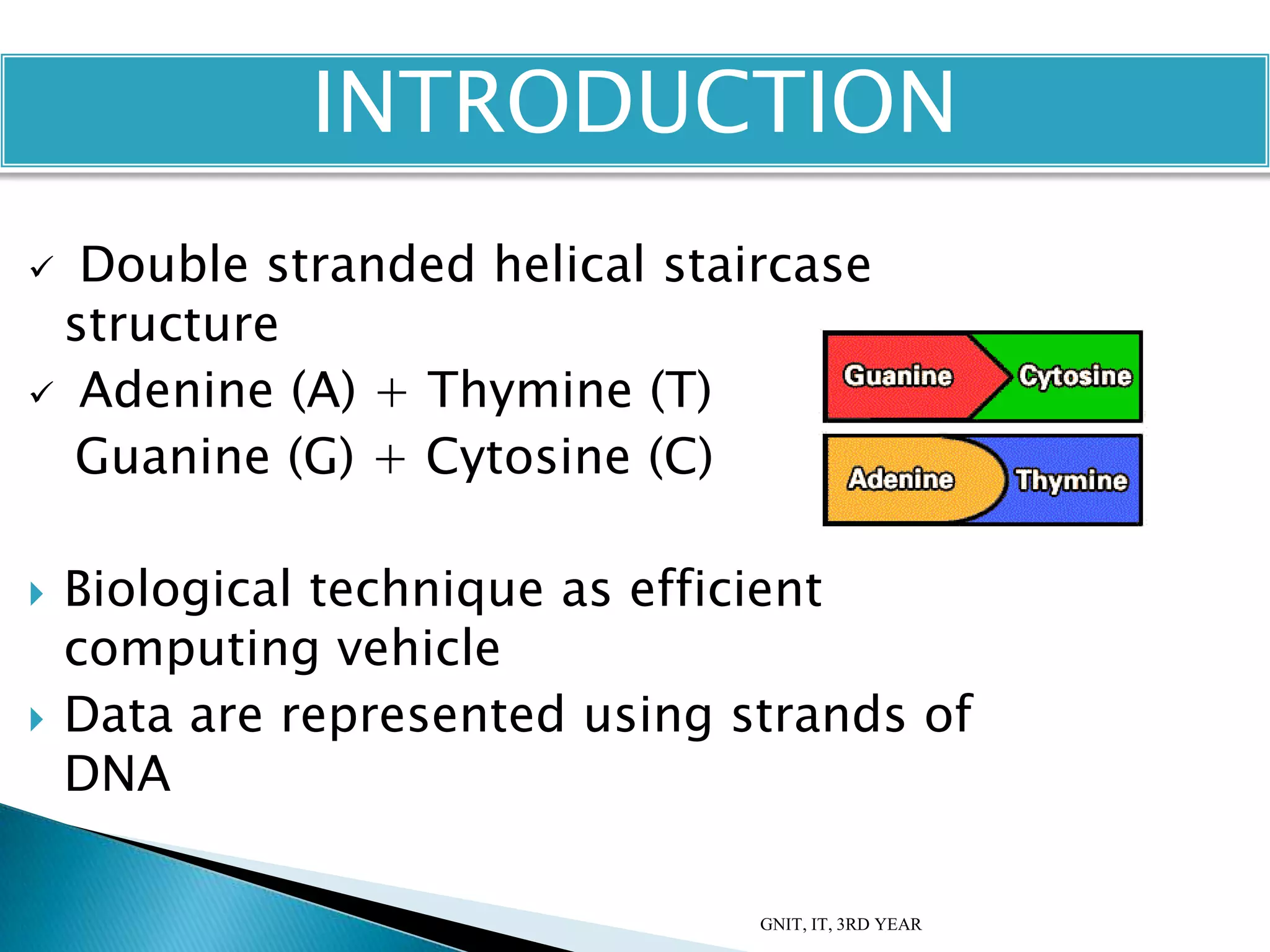
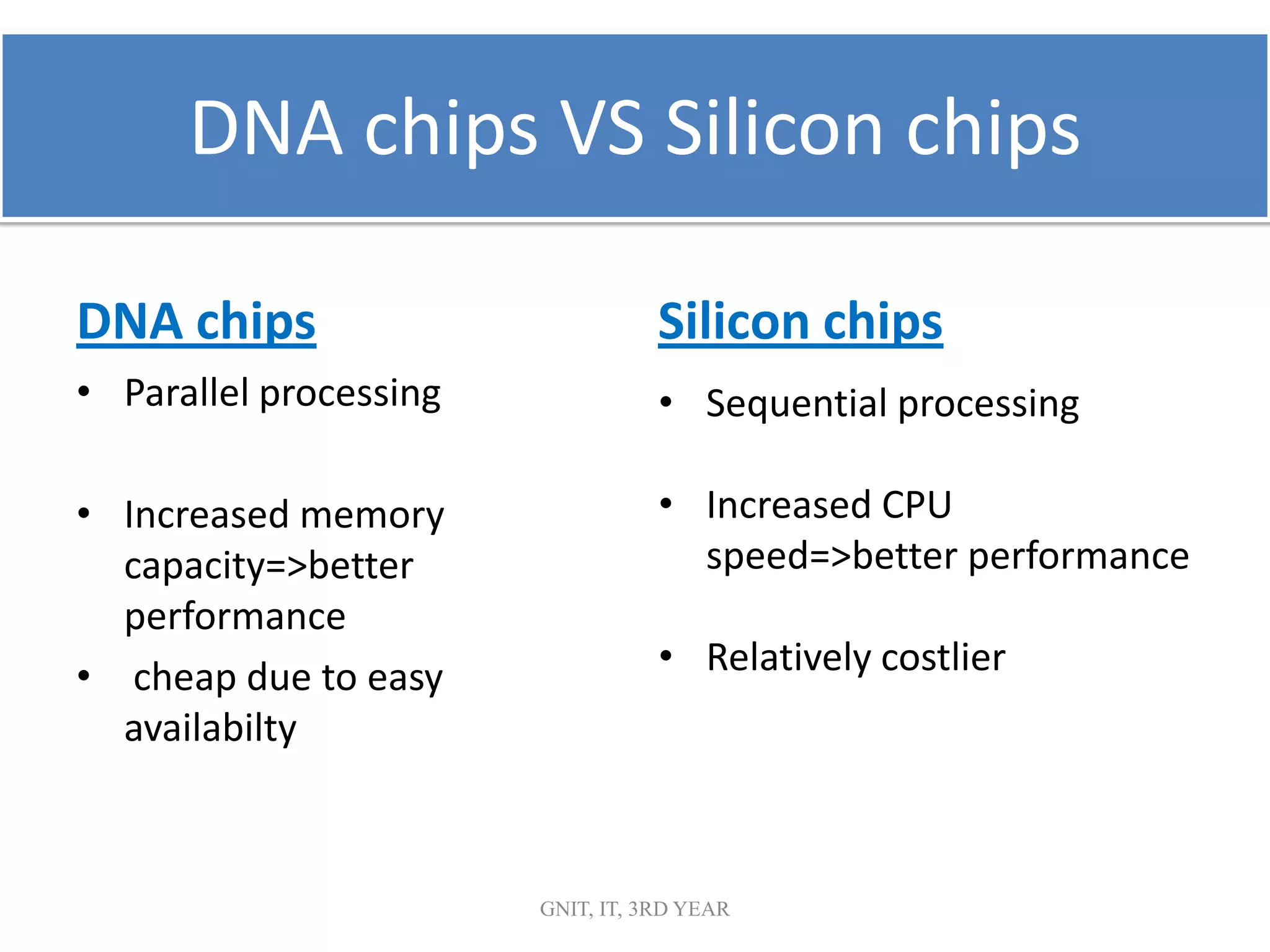
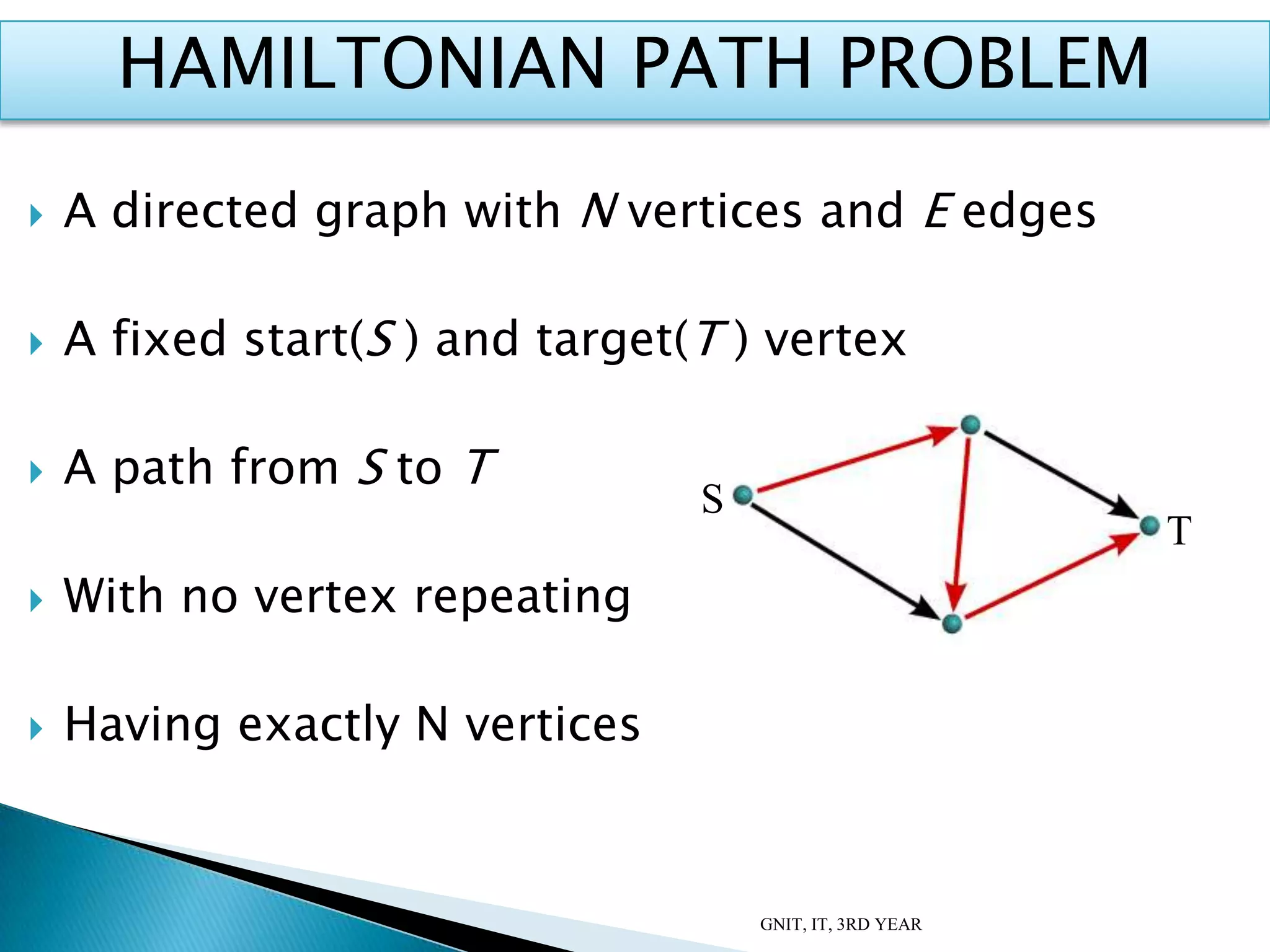
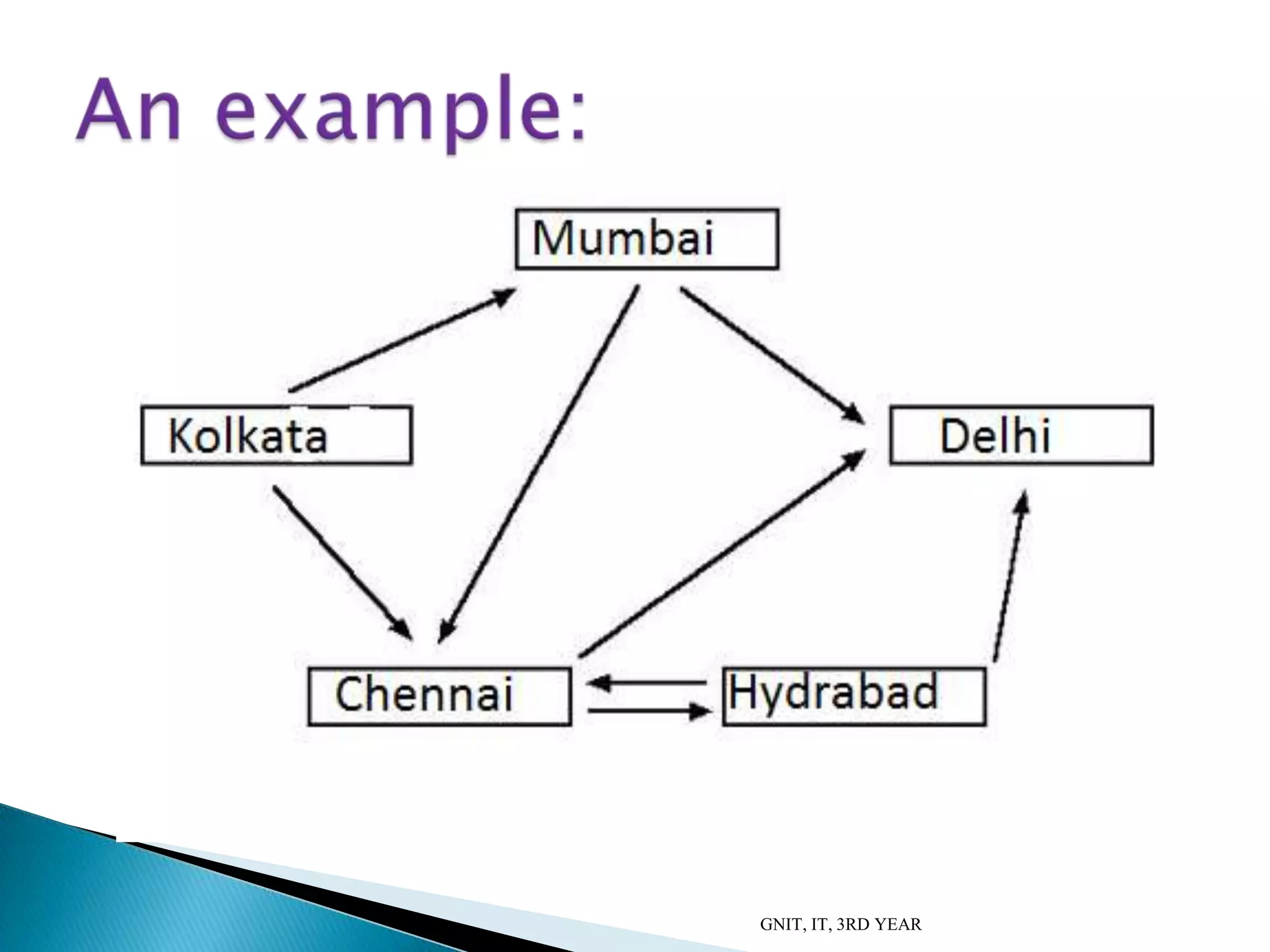
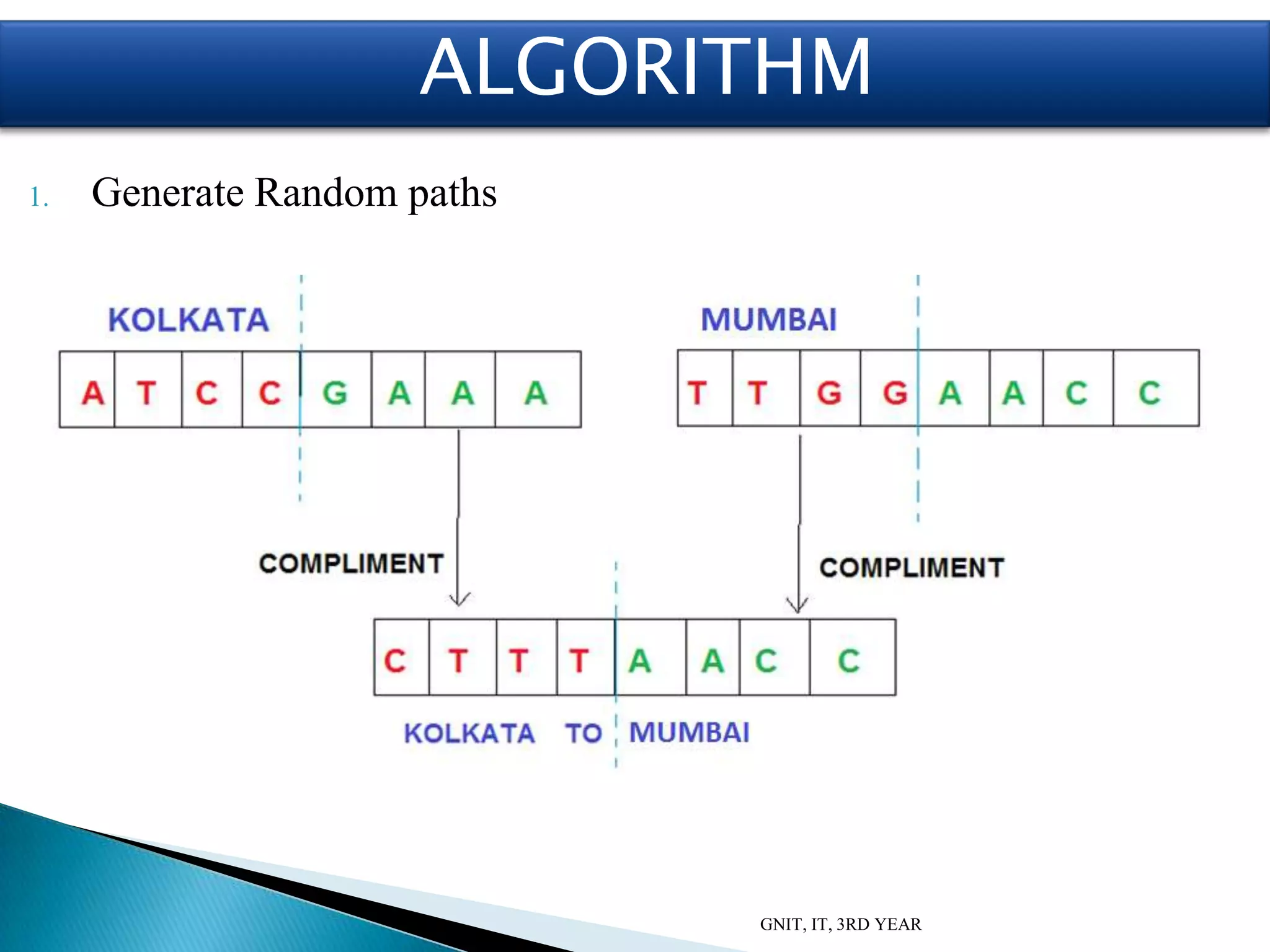
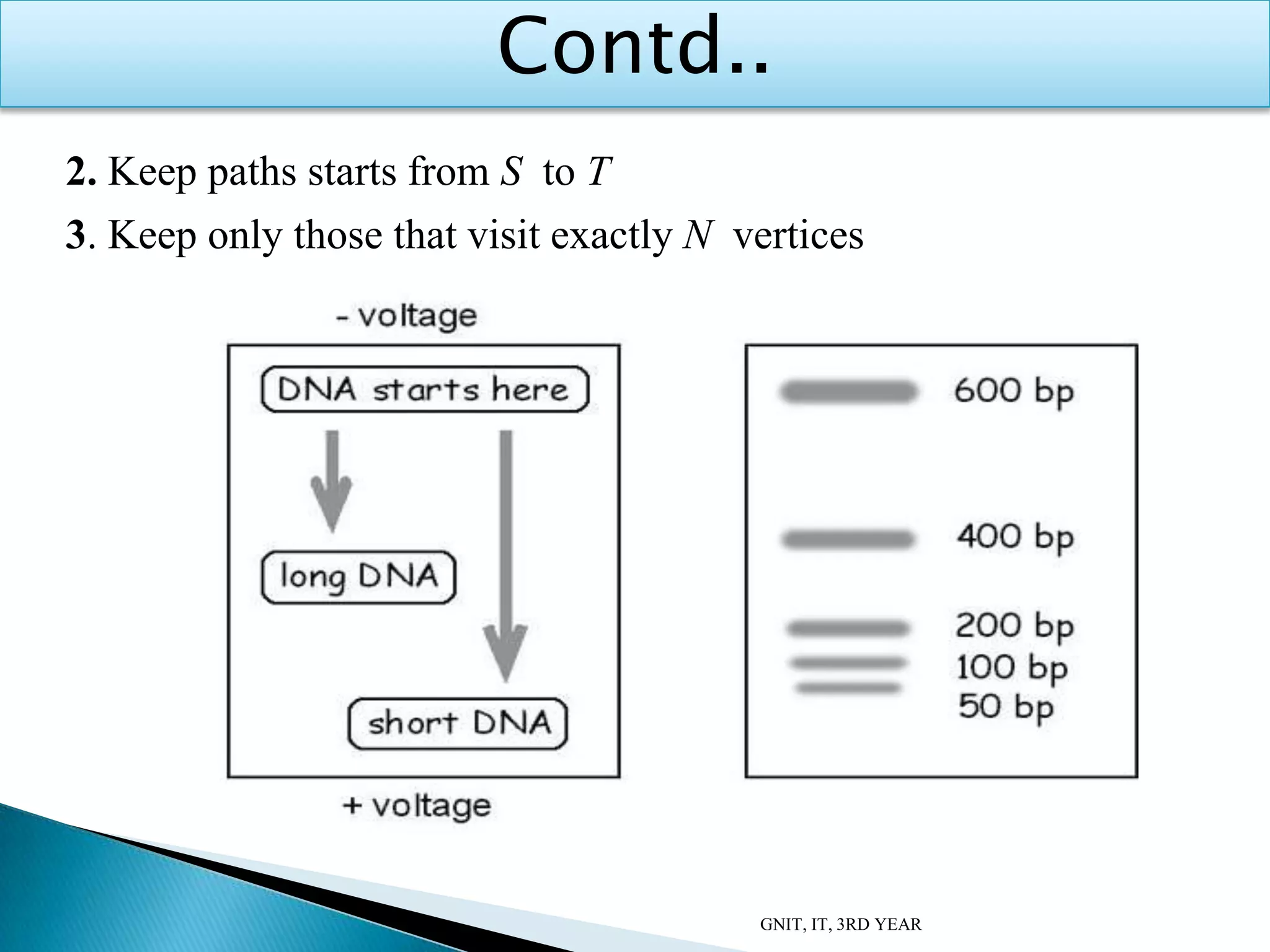
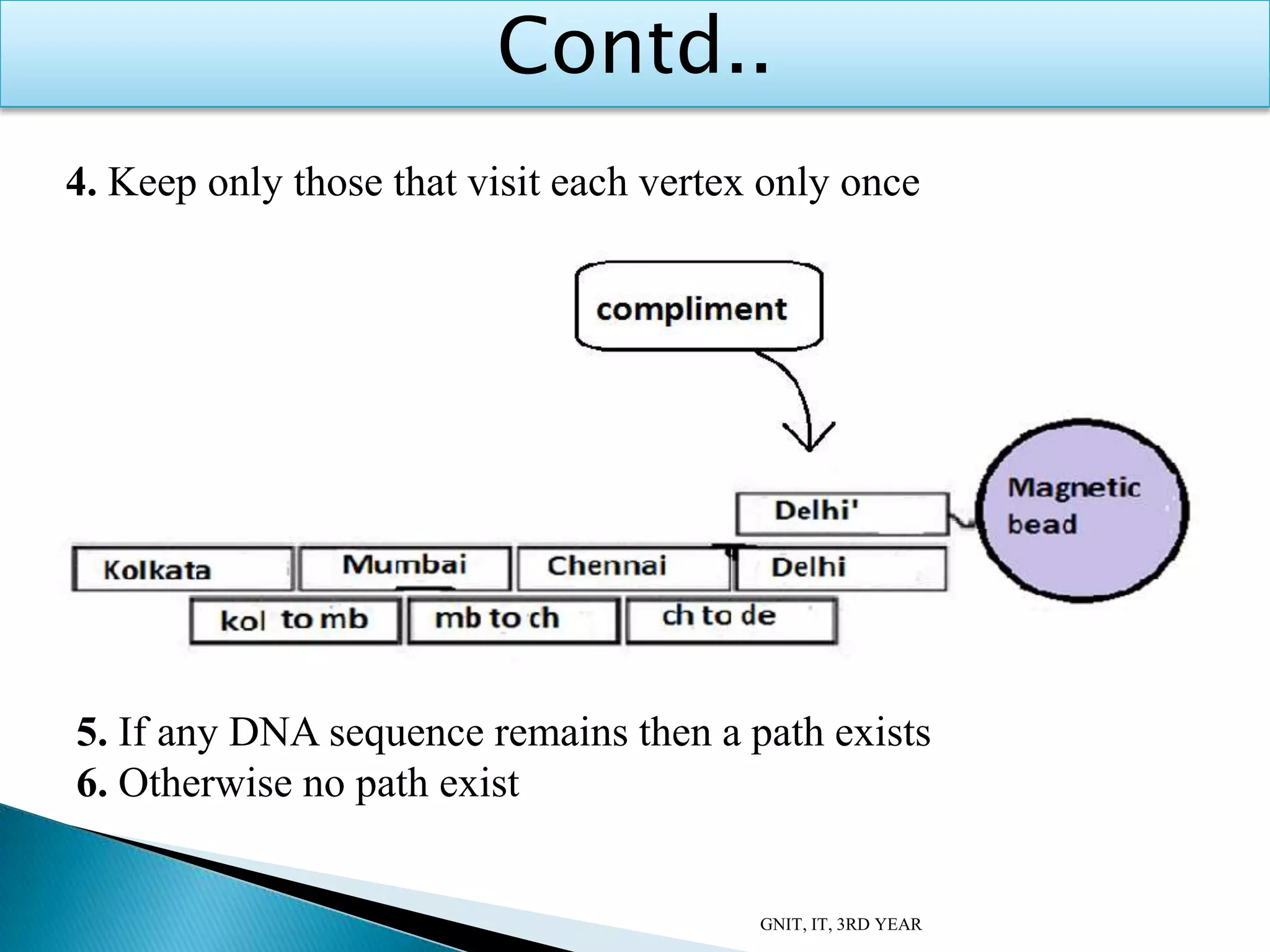
This document summarizes a presentation on DNA computing. It begins with an introduction to DNA and DNA computing, explaining how biological techniques can be used for efficient computing. It then discusses logical operations in DNA computers and Adleman's solution to the Hamiltonian path problem. The document compares DNA chips to silicon chips and outlines some advantages and applications of DNA computing, as well as its limitations and future prospects. It concludes by discussing potential applications like cryptography and planning efficient routes.





![[1] Intelligent Computing Everywhere Schuster, Alfons (Ed.), ISBN 978-1-
84628-943-9,2007
[2] Adleman, L. M. (1994). "Molecular computation of solutions to
combinatorial problems". Science 266 (5187): 1021–1024
[3] www.cdn-5.freeclipartnow.com
[4] www.idmarching.com
[5] NPTEL Videos
GNIT, IT, 3RD YEAR
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnacomputing-140429093407-phpapp01/75/Dna-computing-16-2048.jpg)