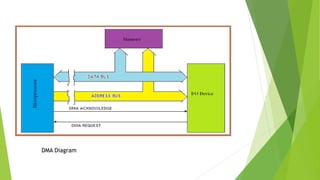
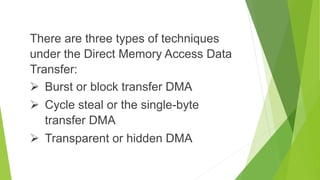
DMA data transfer involves transferring large amounts of data between I/O devices and memory without involving the CPU. There are three types of DMA transfer techniques: burst/block transfer DMA transfers all data at once, cycle steal/single-byte transfer DMA transfers one byte at a time alternating with the CPU, and transparent/hidden DMA transfers data during times when the CPU floats the buses so it is transparent to the CPU.