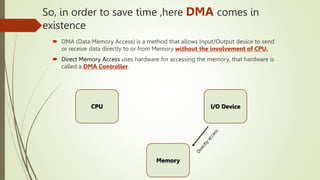
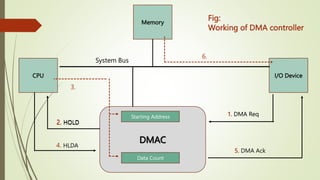
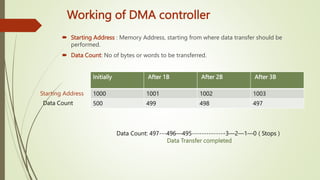
The document discusses Direct Memory Access (DMA), which allows peripherals to transfer data directly to and from memory without CPU intervention, thereby saving time. It describes the operation of a DMA controller, including the modes of transfer: burst mode, cycle stealing mode, and interleaving mode, each with varying implications for CPU access and efficiency. Overall, DMA enhances data transfer efficiency but can block CPU access depending on the mode used.