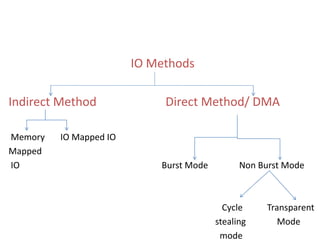
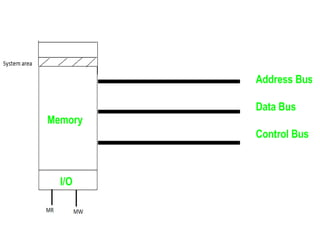
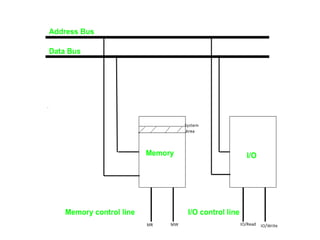
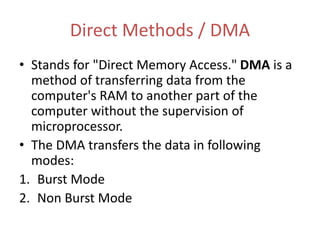
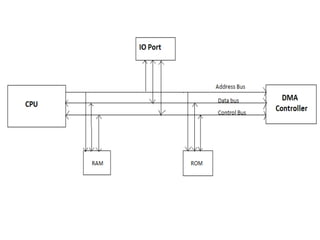
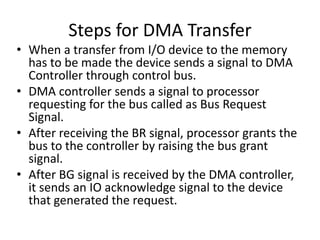
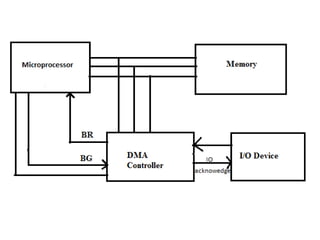
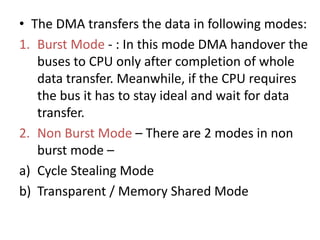
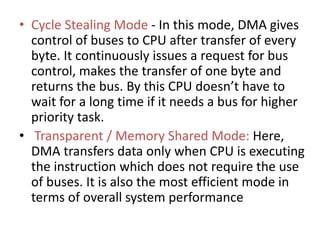
This document discusses indirect and direct I/O methods. Indirect methods include memory mapped I/O and I/O mapped I/O. Memory mapped I/O allows the CPU and I/O devices to share the same memory space, while I/O mapped I/O gives them separate memory spaces. Direct I/O uses DMA to transfer data without CPU involvement. DMA can operate in burst mode or non-burst modes like cycle stealing or transparent mode.