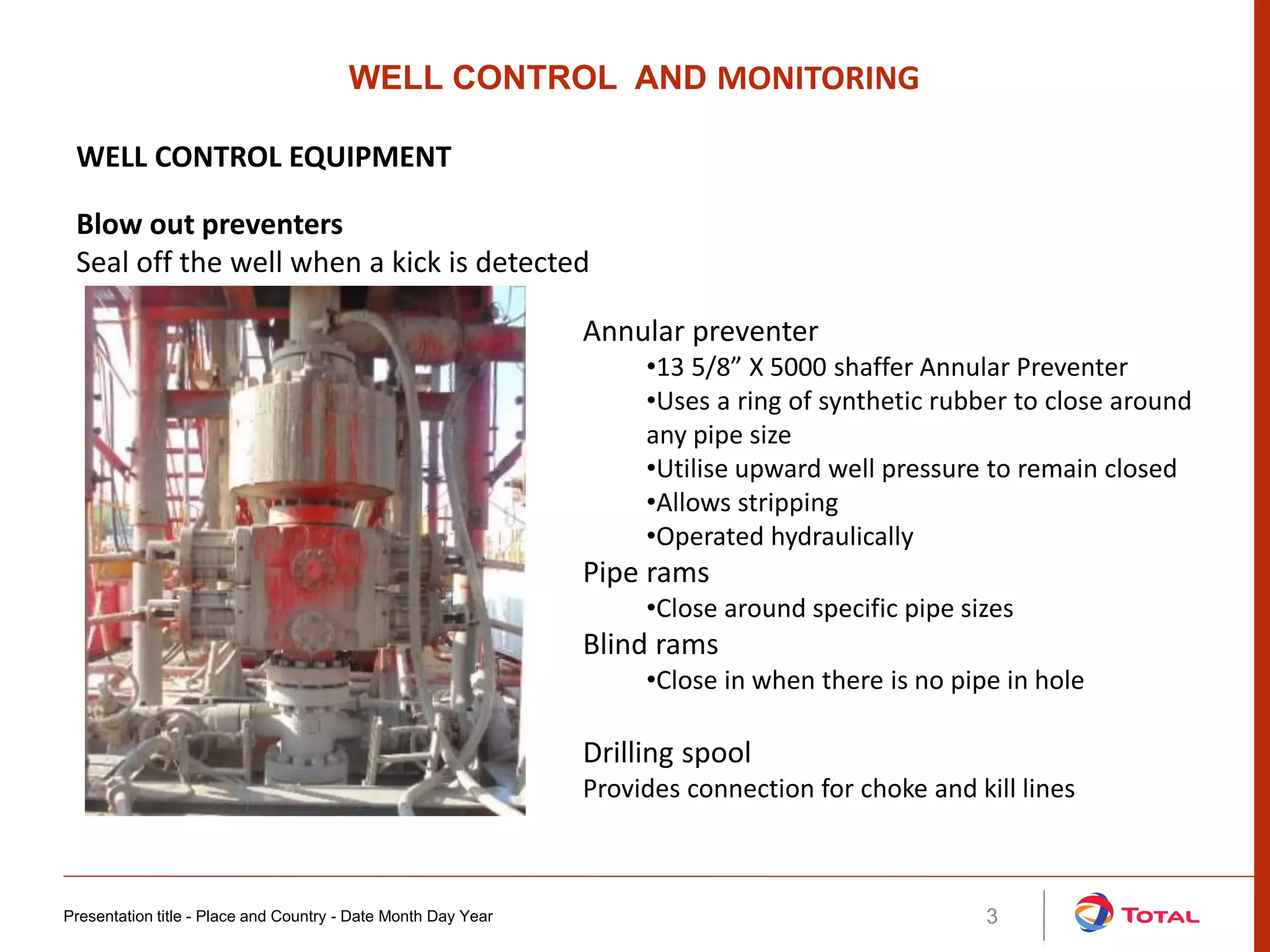
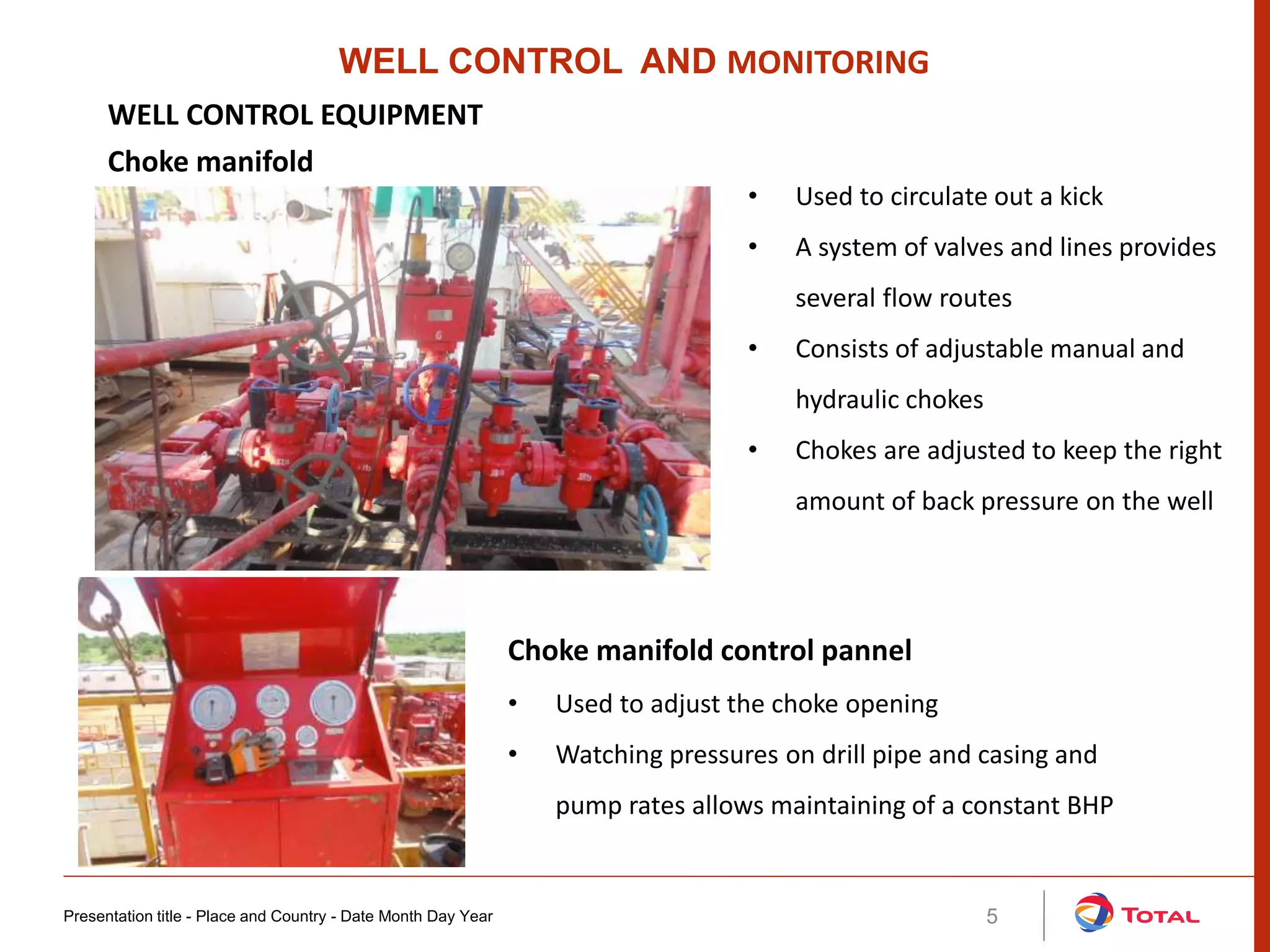
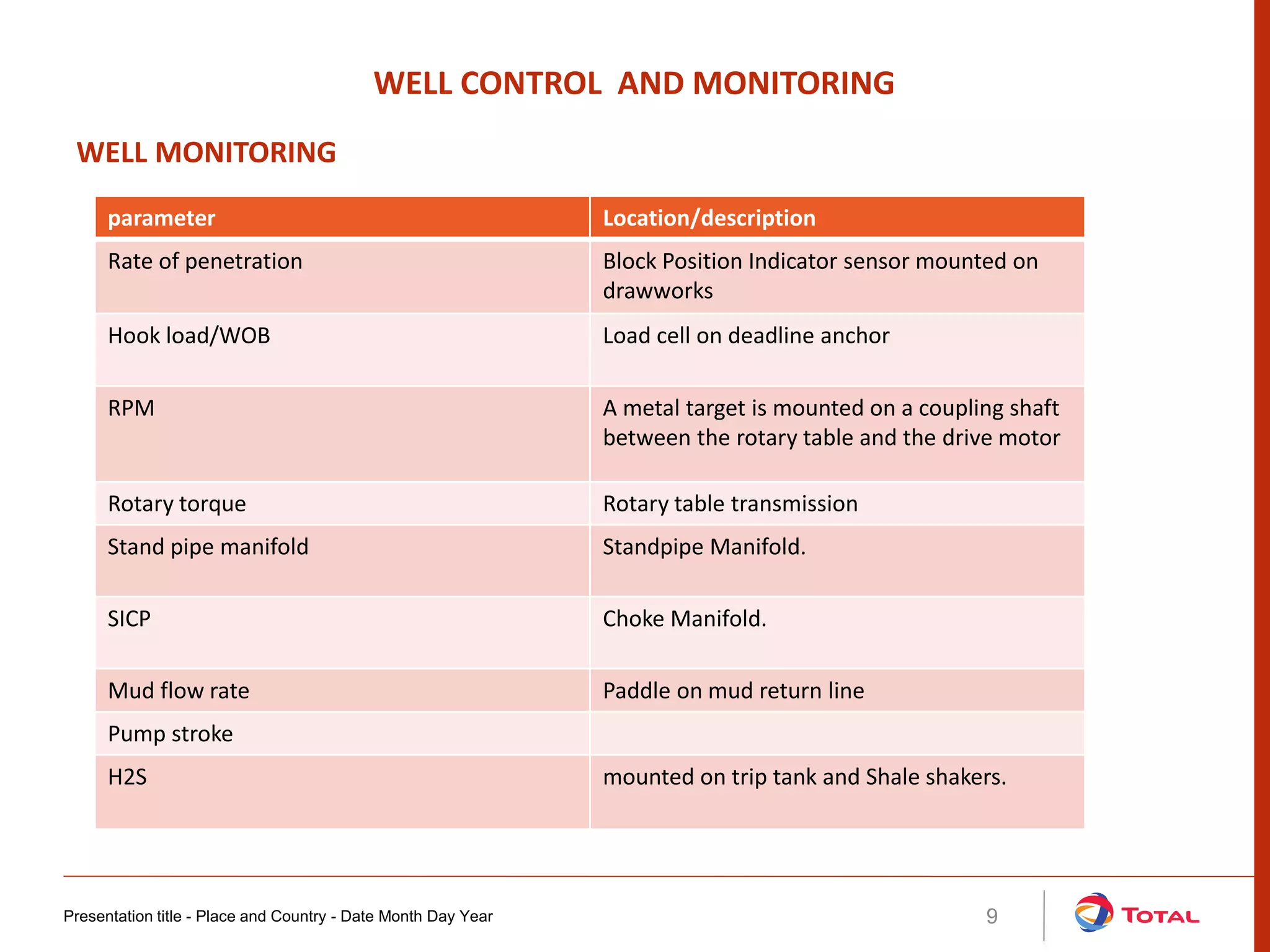
Kicks occur when formation pressures exceed the hydrostatic pressure of the drilling mud, allowing formation fluids to enter the wellbore. This can lead to a blowout if not controlled. Common causes of kicks include failing to keep the hole full, using insufficient mud density, swabbing during trips, lost circulation, and incorrect fill-up. Detecting kicks involves monitoring for increases in pit volume, return flow, drilling break, circulating pressure, shows of oil/gas/water, and hook load. Well control equipment like blowout preventers, choke manifolds, and degassers are used to safely circulate out kicks without allowing a blowout. Key parameters for well monitoring include rate of penetration, hook load, RPM, rot