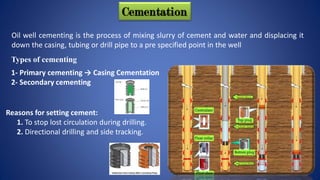
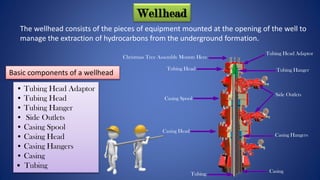
This document provides an overview of oil drilling and production processes. It discusses the key components of drilling rigs including the derrick, hoisting system, rotary system, and blowout preventer. It also describes well completion processes like casing, cementing, and installing the christmas tree and wellhead. The document is intended as part of a graduation project on the oil and gas industry.