This document discusses well control systems used in drilling operations. It describes:
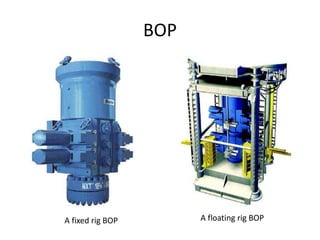
1) The key components of a well control system, including sensors to detect fluid flows, a blowout preventer (BOP) to shut off the well, and pressure control equipment like chokes.
2) Causes of "kicks" where formation fluids enter the borehole unexpectedly, and "blowouts" where kicks are not controlled and fluids reach the surface.
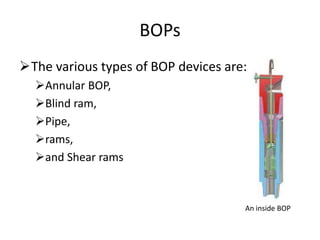
3) The different types of equipment in a BOP stack, including annular, blind, pipe, and shear rams, used to seal the annulus in various situations.