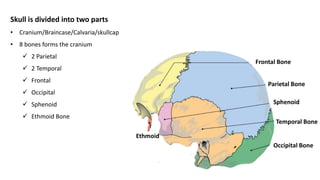
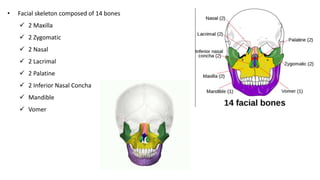
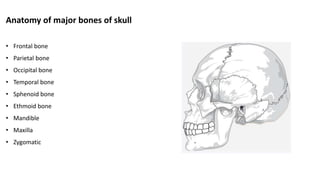
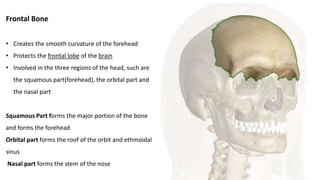
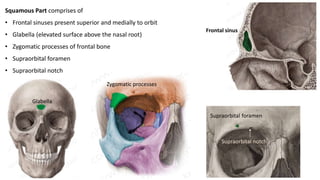
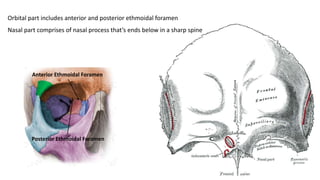
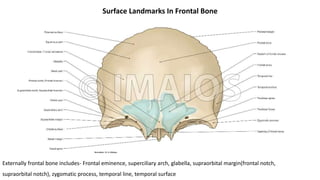
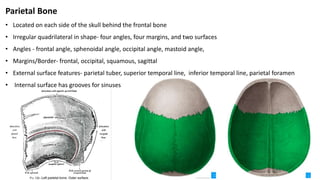
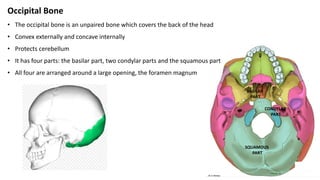
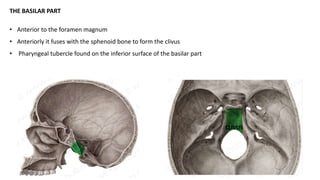
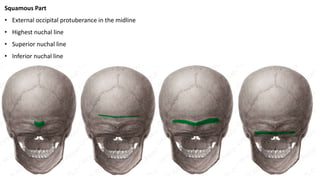
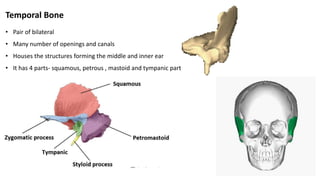
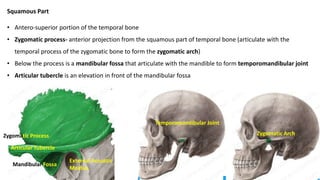
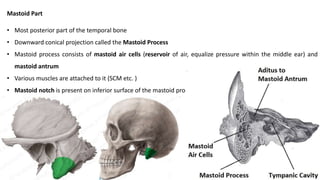
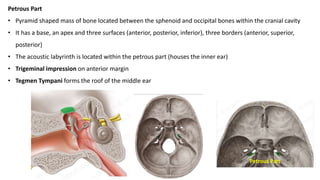
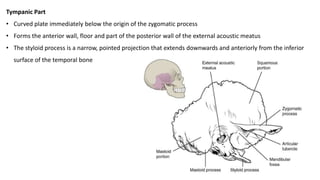
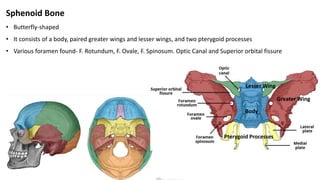
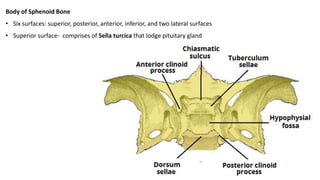
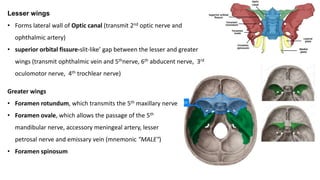
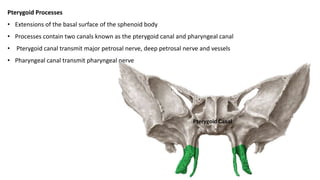
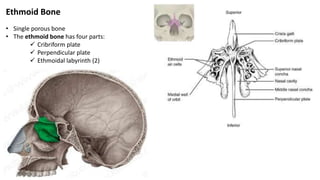
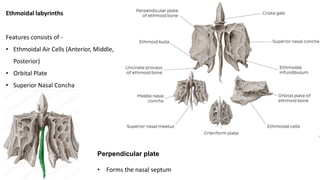
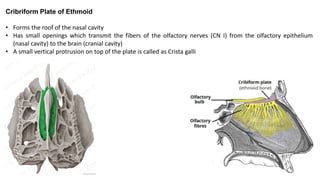
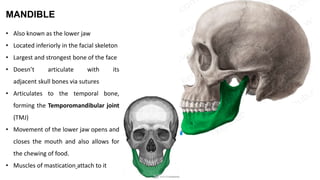
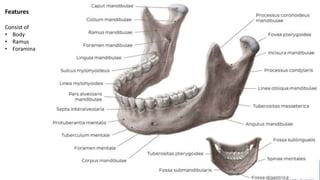
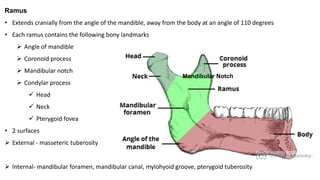
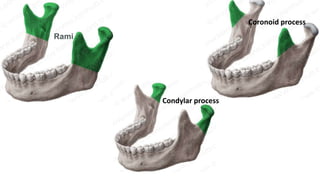
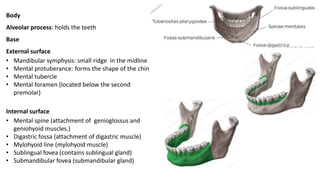
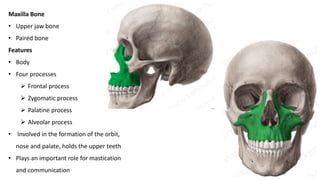
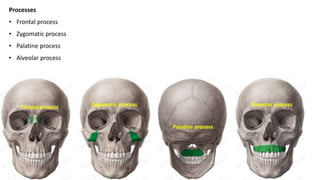
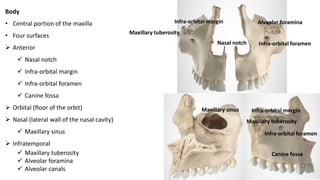
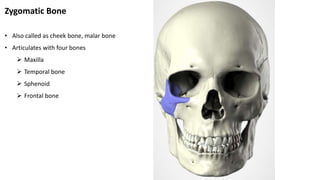
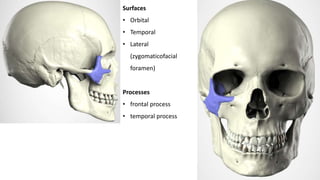
The skull is a bony structure that protects the brain and supports facial features, comprised of 22 fused flat bones. It is divided into the cranium, containing 8 bones, and the facial skeleton with 14 bones, with joints primarily formed by sutures and one synovial joint, the temporomandibular joint. Each bone has specific functions and structures, such as housing sensory organs and facilitating mastication.