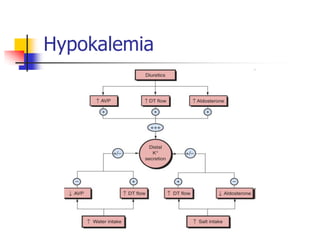
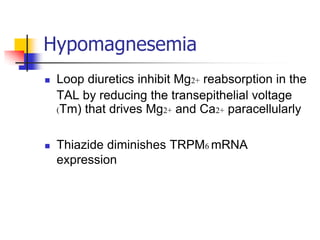
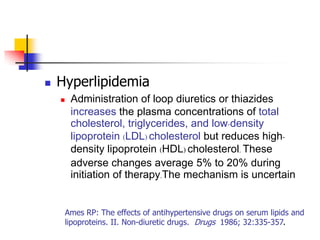
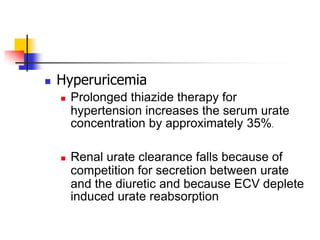
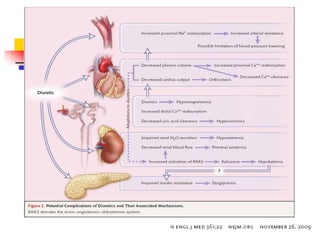
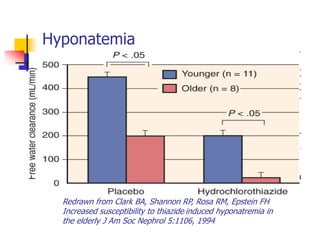
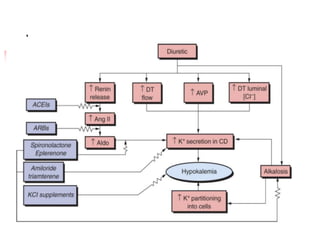
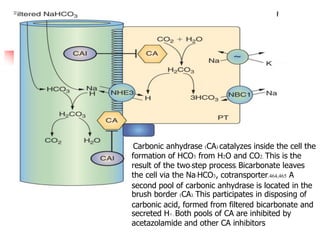
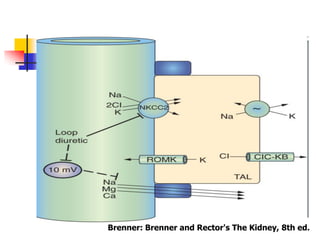
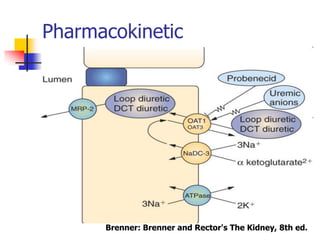
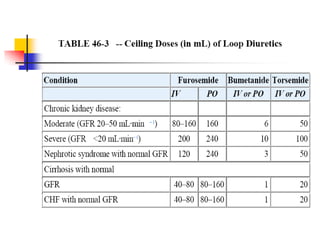
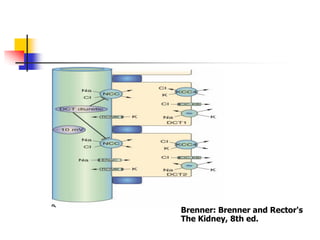
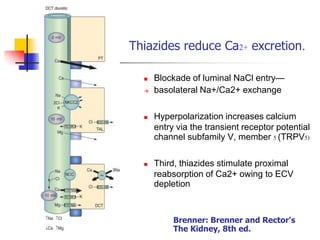
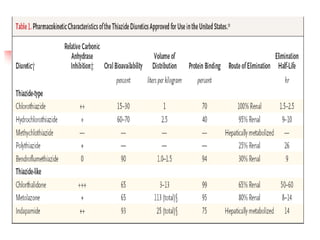
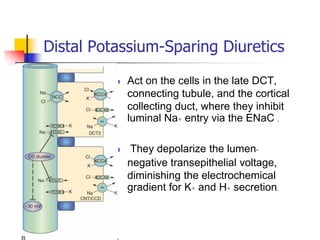
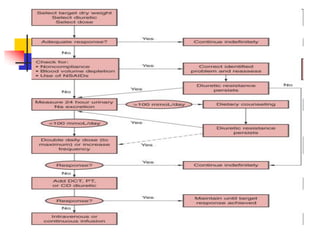
Loop diuretics, thiazides, and other diuretic classes are summarized. Loop diuretics act in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop by inhibiting the Na-K-2Cl transporter. Thiazides act in the distal convoluted tubule by blocking coupled Na and Cl reabsorption. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors inhibit bicarbonate absorption in the proximal tubule. Osmotic diuretics like mannitol are filtered but not reabsorbed, drawing water out of cells. Potassium-sparing diuretics like amiloride act late in the distal nephron to inhibit Na reabsorption. Diuretic combinations can have synergistic effects.


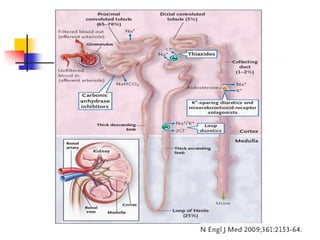
















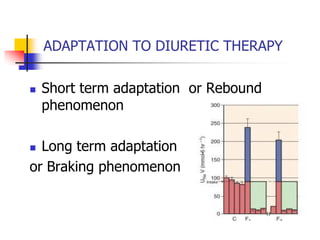



![Diuretic Combination
Diuretics acting on a separate
mechanism may be synergistic.
Ellison DH: The physiologic basis of diuretic synergism: Its role in treating
diuretic resistance [see comments]. Ann Intern Med 1991; 114:886-894.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diuretics2-111127100852-phpapp01/85/Diuretics2-37-320.jpg)