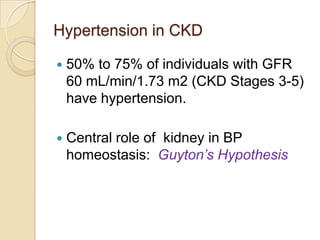
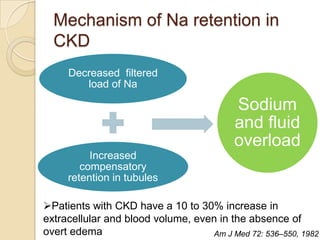
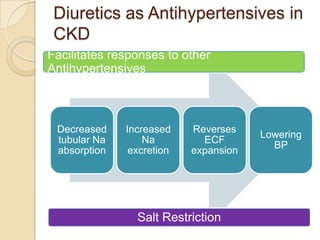
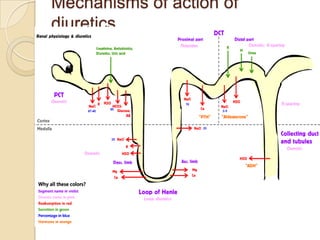
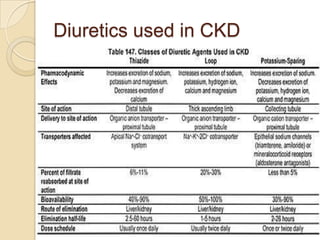
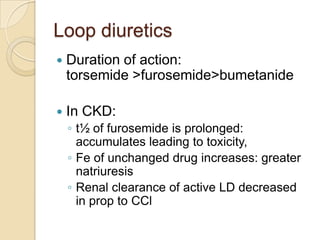
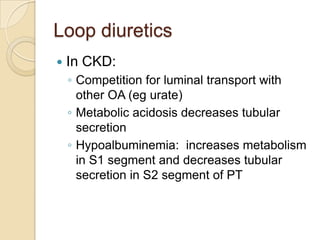
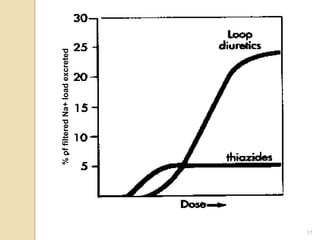
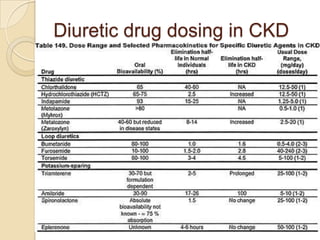
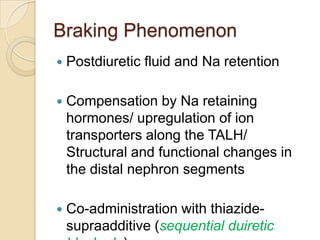
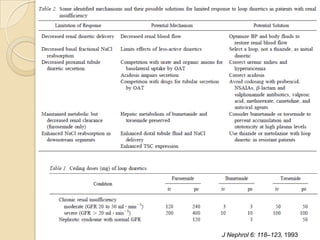
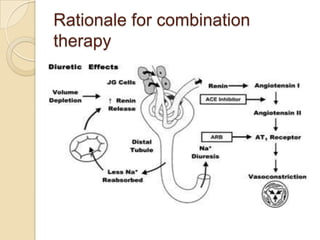
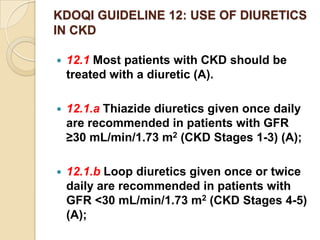
Diuretics are commonly used to treat hypertension in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). The ALLHAT trial found thiazide-type diuretics were superior to other antihypertensives in preventing cardiovascular disease and were less expensive. In CKD, loop diuretics are recommended for patients with a GFR <30 mL/min, while thiazide diuretics can be used for those with a GFR ≥30 mL/min. Combination diuretic therapy may be needed to overcome diuretic resistance seen in CKD. Close monitoring is required due to risks of electrolyte abnormalities and dehydration.



![ALLHAT trial
Intervention: Randomised to receive
◦ chlorthalidone, 12.5 to 25 mg/d (n=15255);
◦ amlodipine, 2.5 to 10 mg/d (n=9048);
◦ lisinopril, 10 to 40 mg/d (n=9054)
Doxazosin arm was prematurely terminated
Follow-up of approximately 4 to 8 years.
Primary outcome: combined fatal CHD or
nonfatal MI
Secondary outcomes: all cause
mortality, stroke, combined CHD (primary
outcome, coronary revascularization, or
angina with hospitalization), and combined
CVD (combined CHD, stroke, treated angina
without hospitalization, heart failure [HF], and
peripheral arterial disease).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-diureticsinckd-111031142924-phpapp02/85/Diuretics-in-CKD-4-320.jpg)