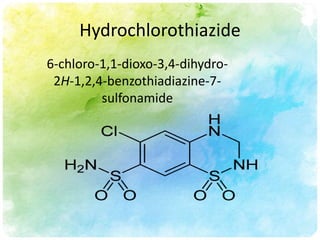
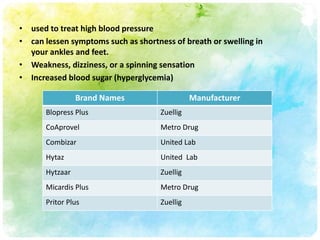
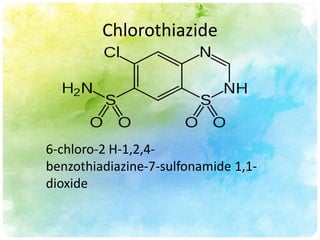
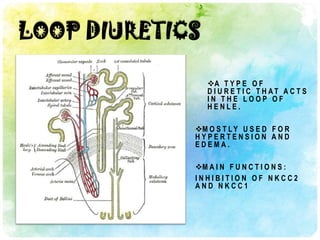
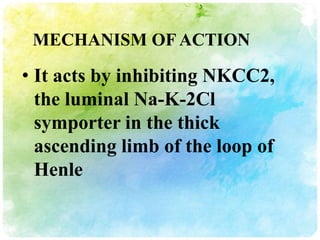
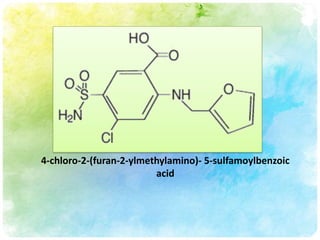
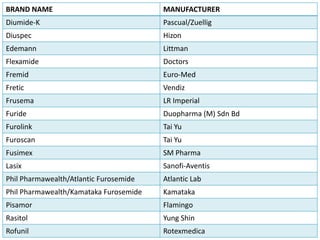
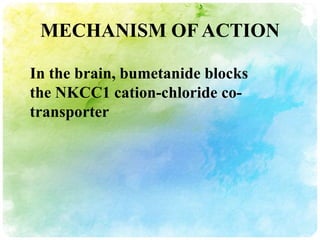
This document summarizes diuretic drugs. It discusses how diuretics work by increasing urine output through inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the kidneys. The main types of diuretics covered are loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, and osmotic diuretics. Specific diuretic drugs discussed include furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, and mannitol. The document also reviews the mechanisms and side effects of different classes of diuretic medications.























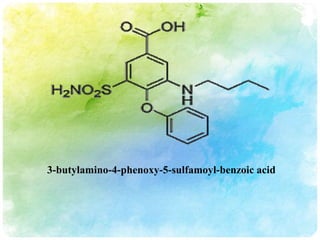


![[2,3-dichloro-4-(2-
methylenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diureticdrugs-120901222831-phpapp01/85/Diuretic-drugs-41-320.jpg)