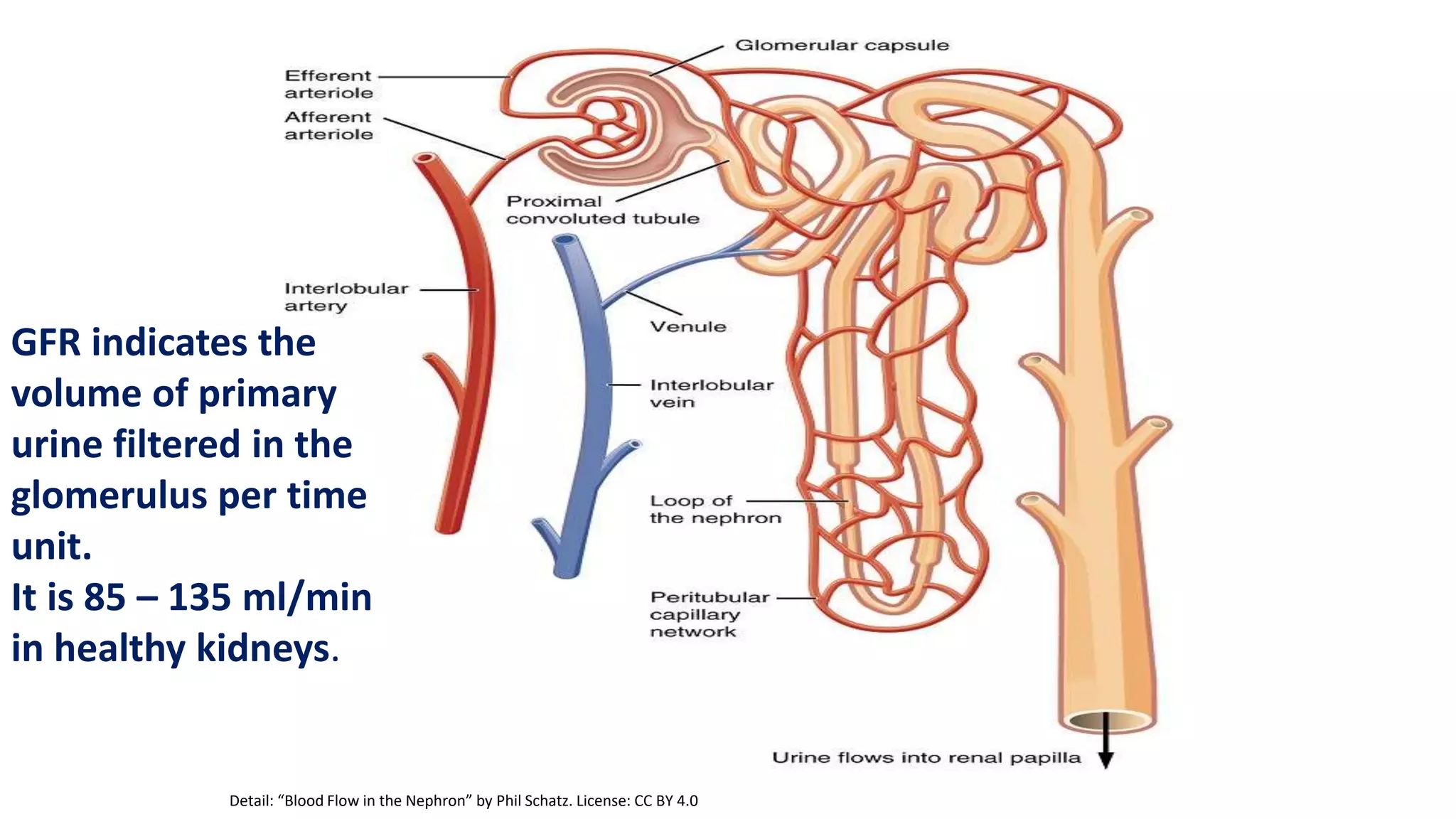
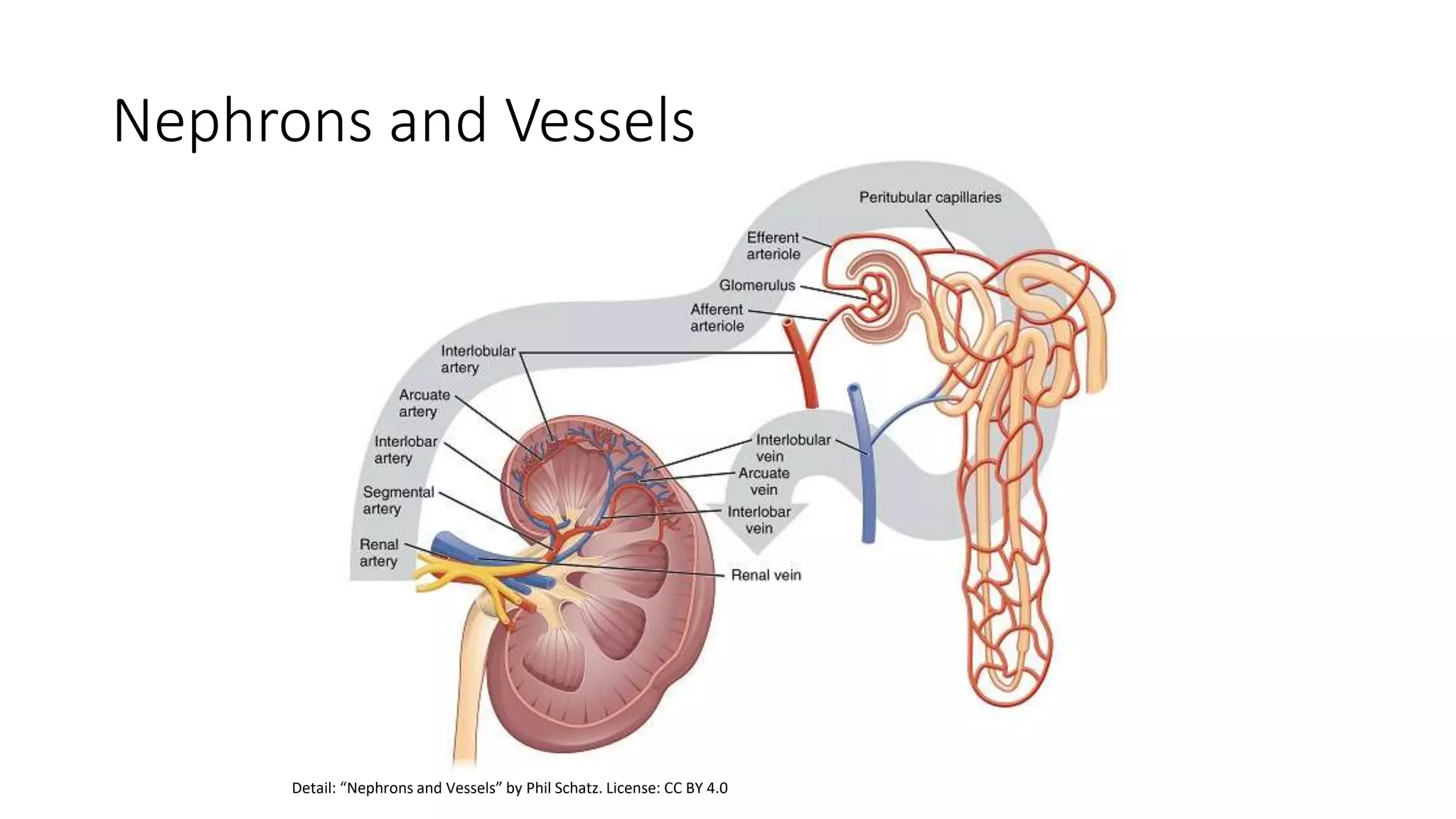
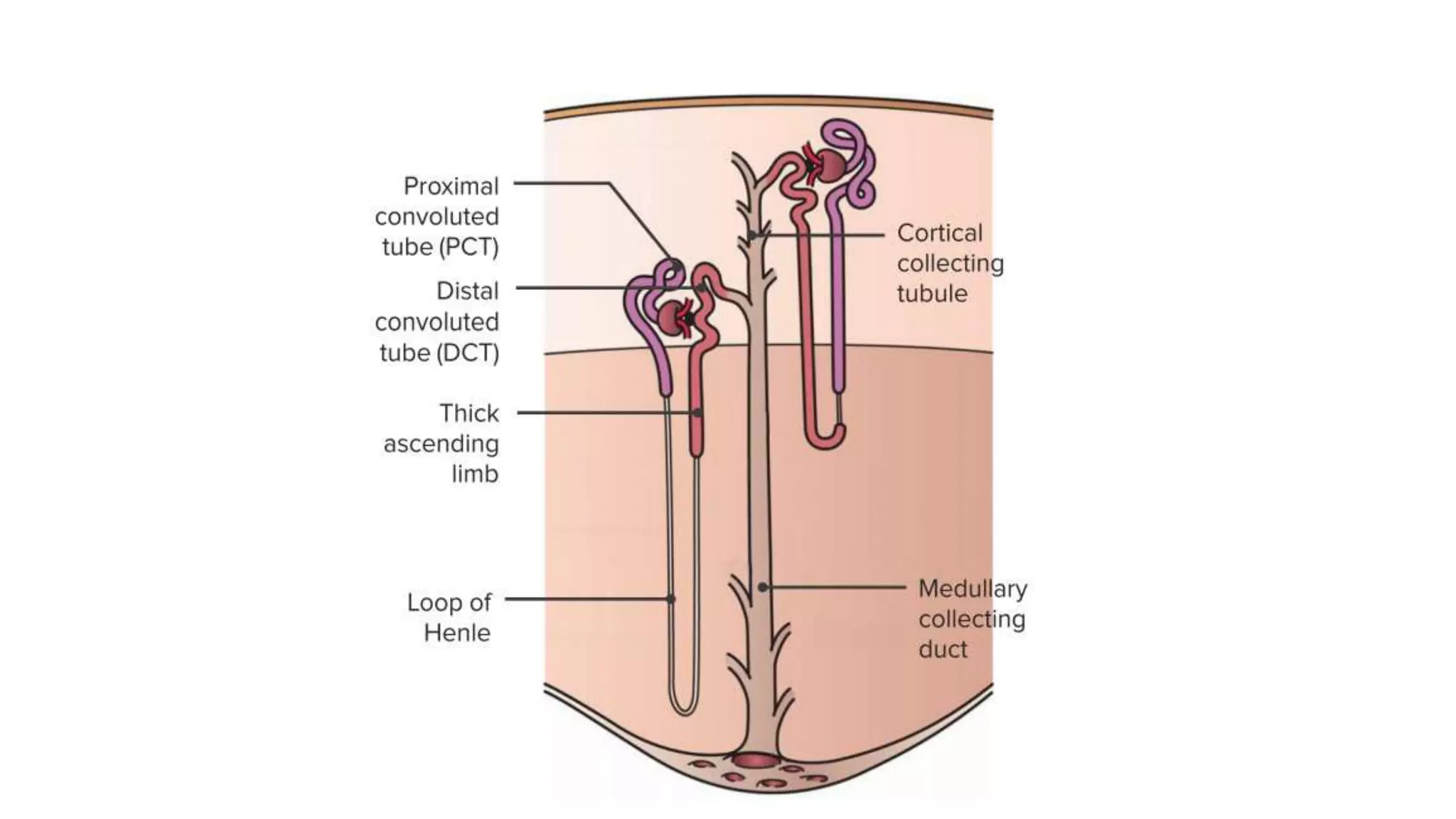
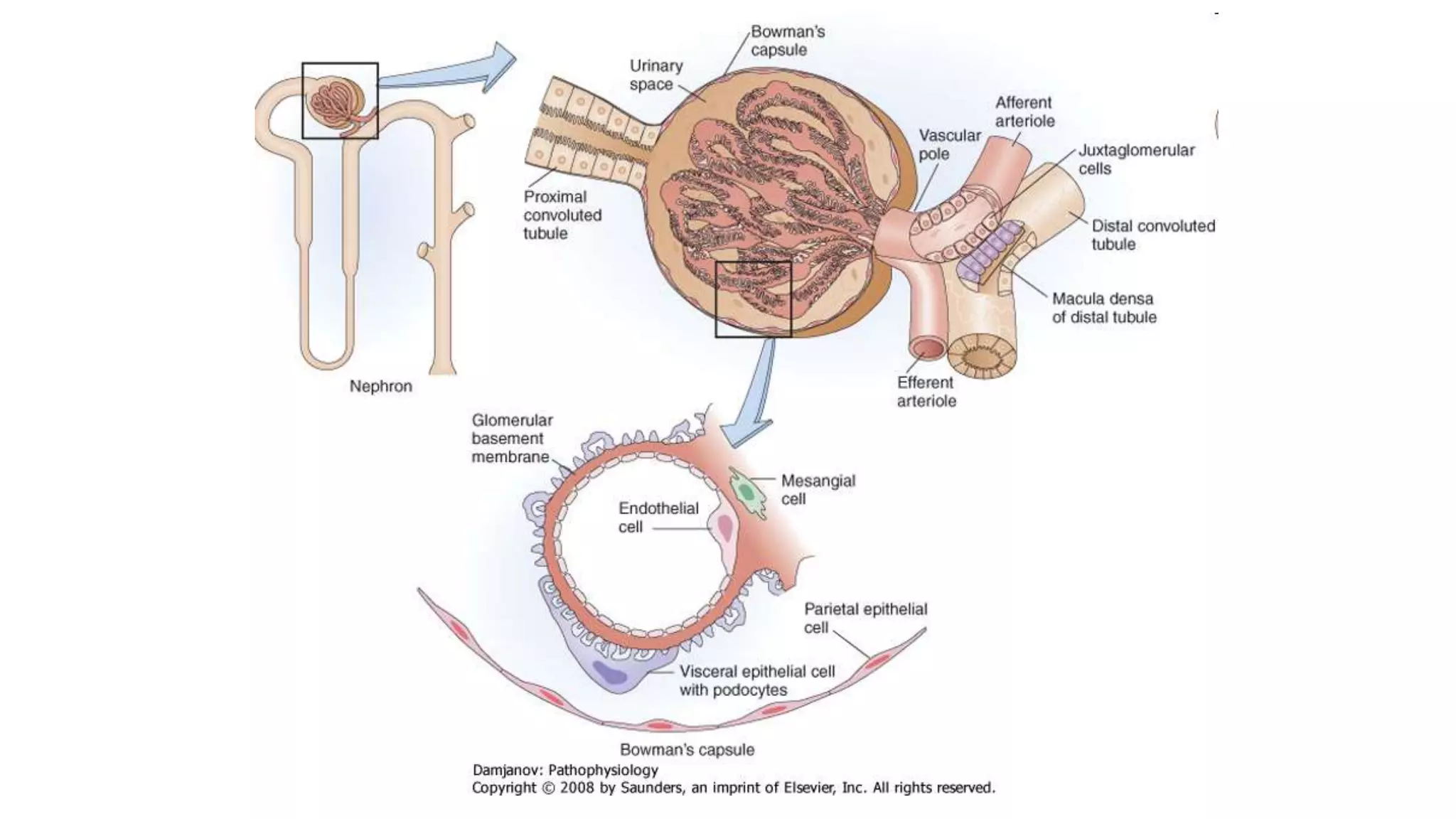
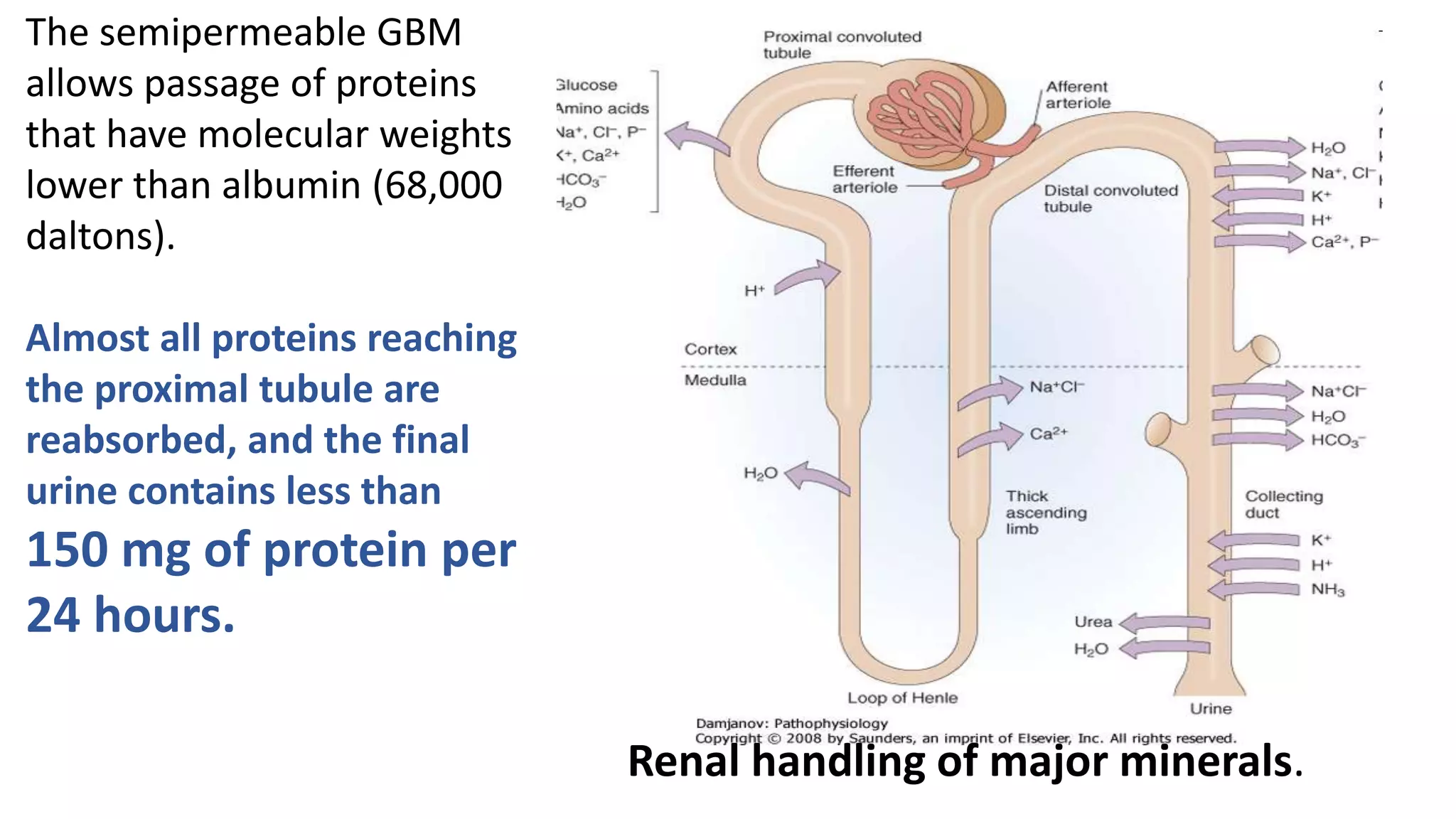
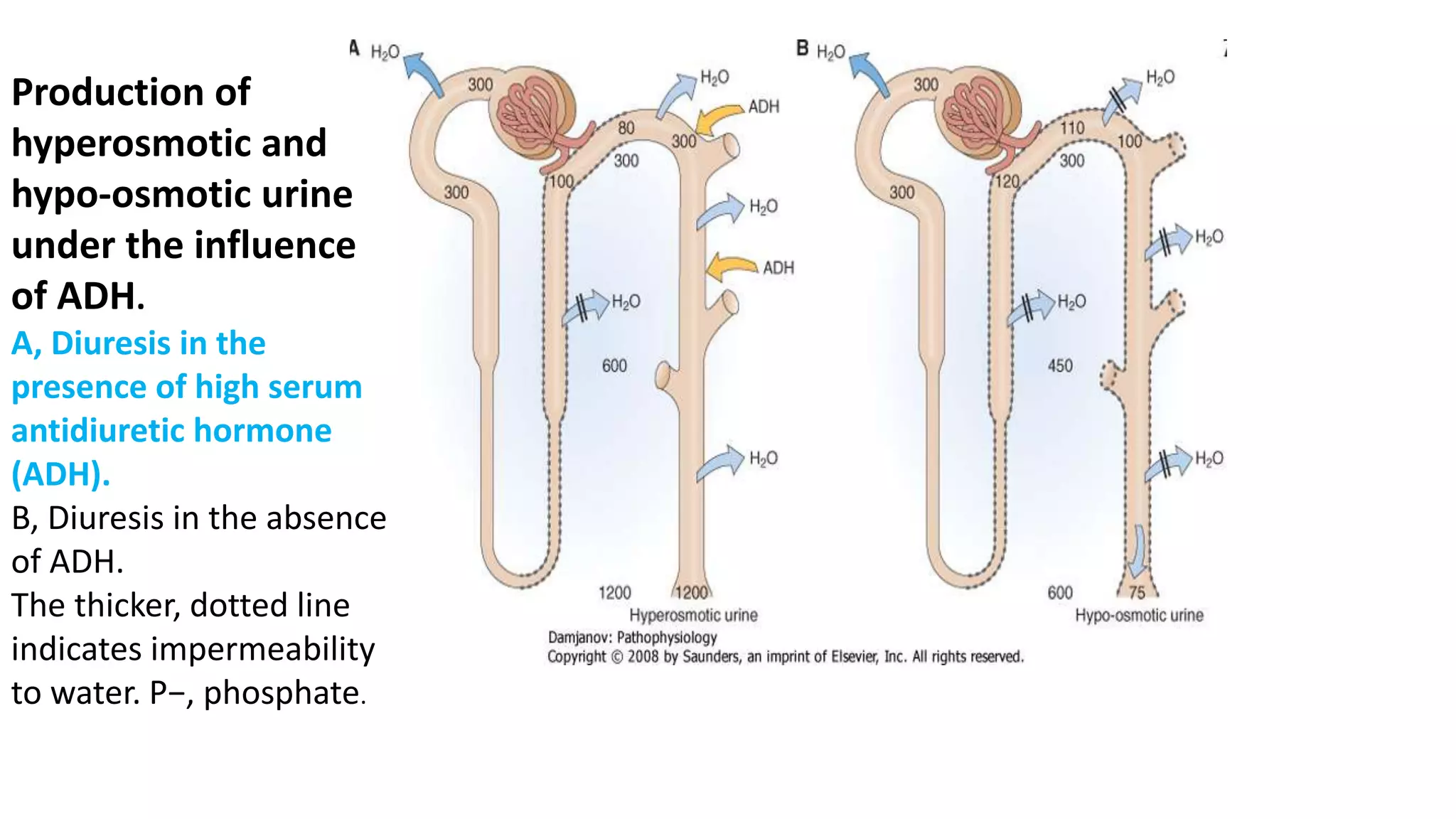
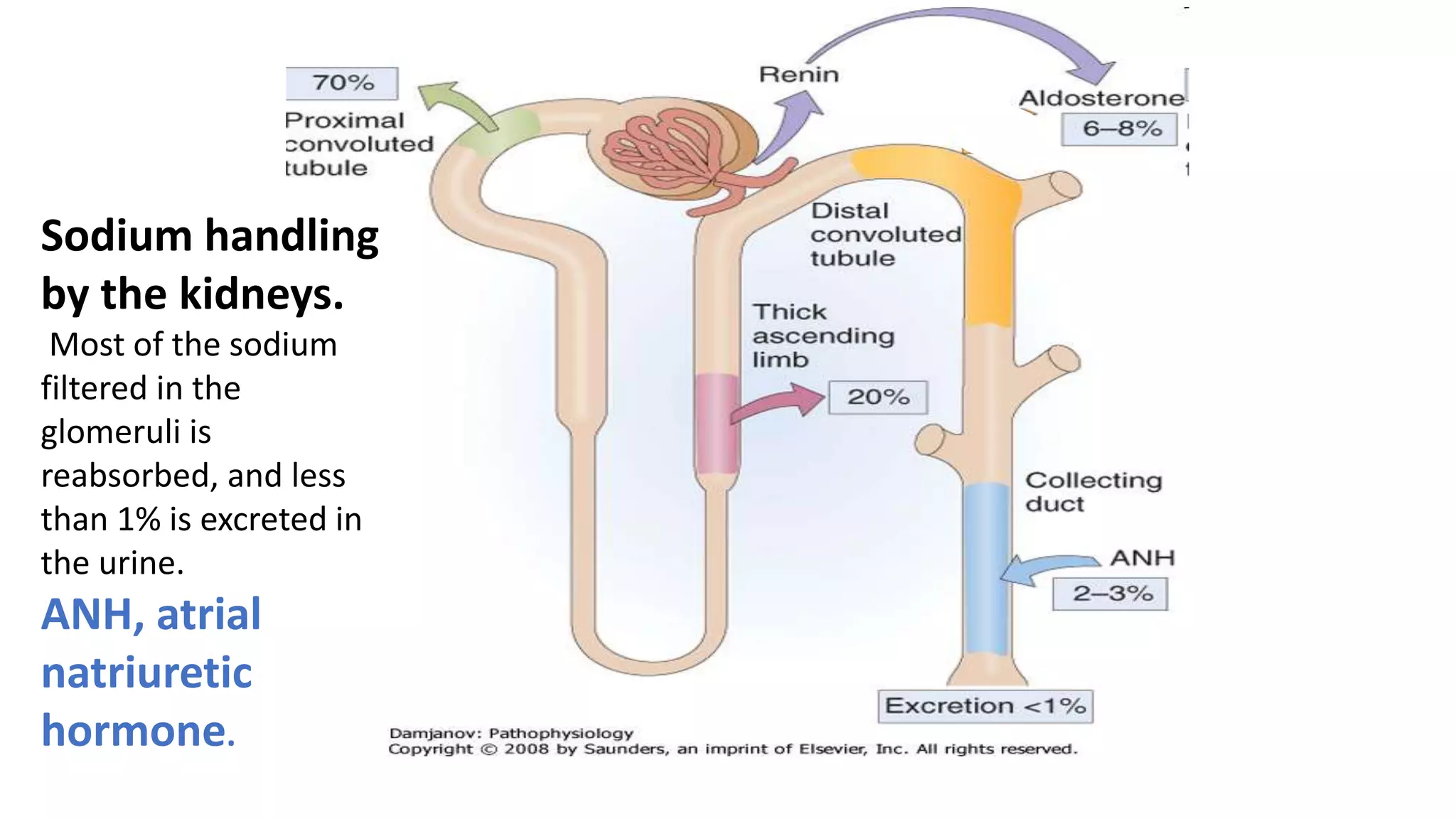
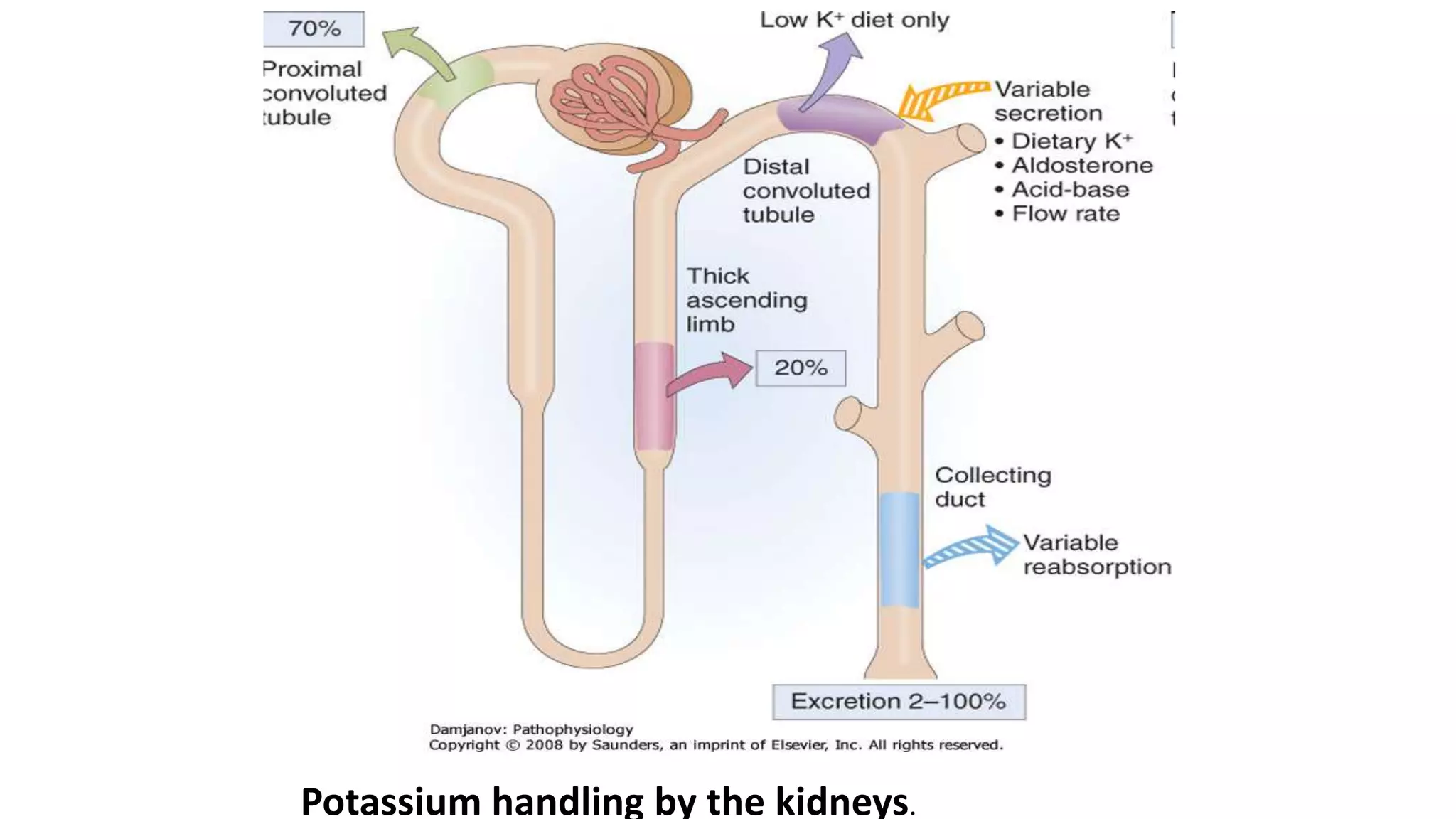
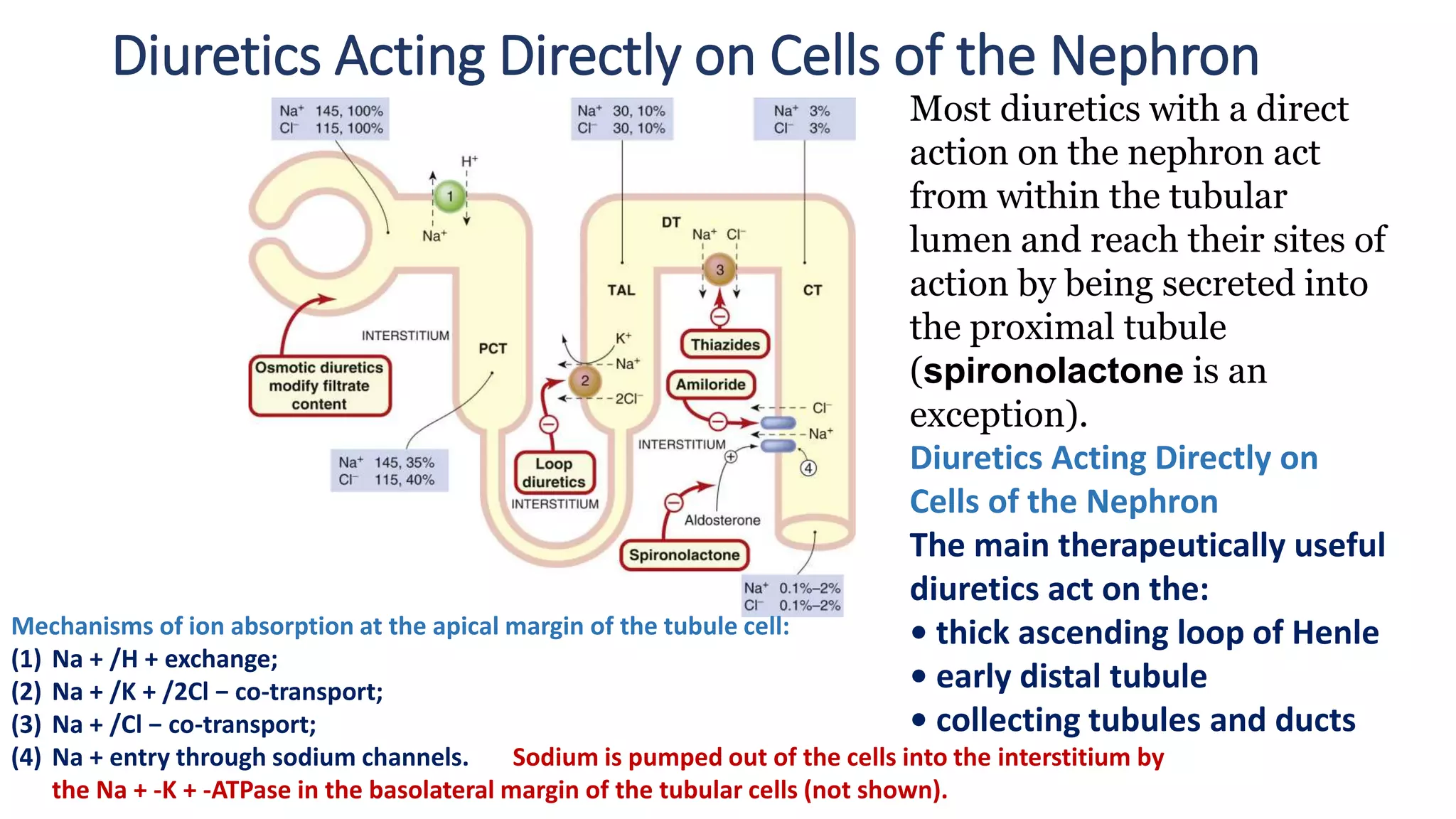
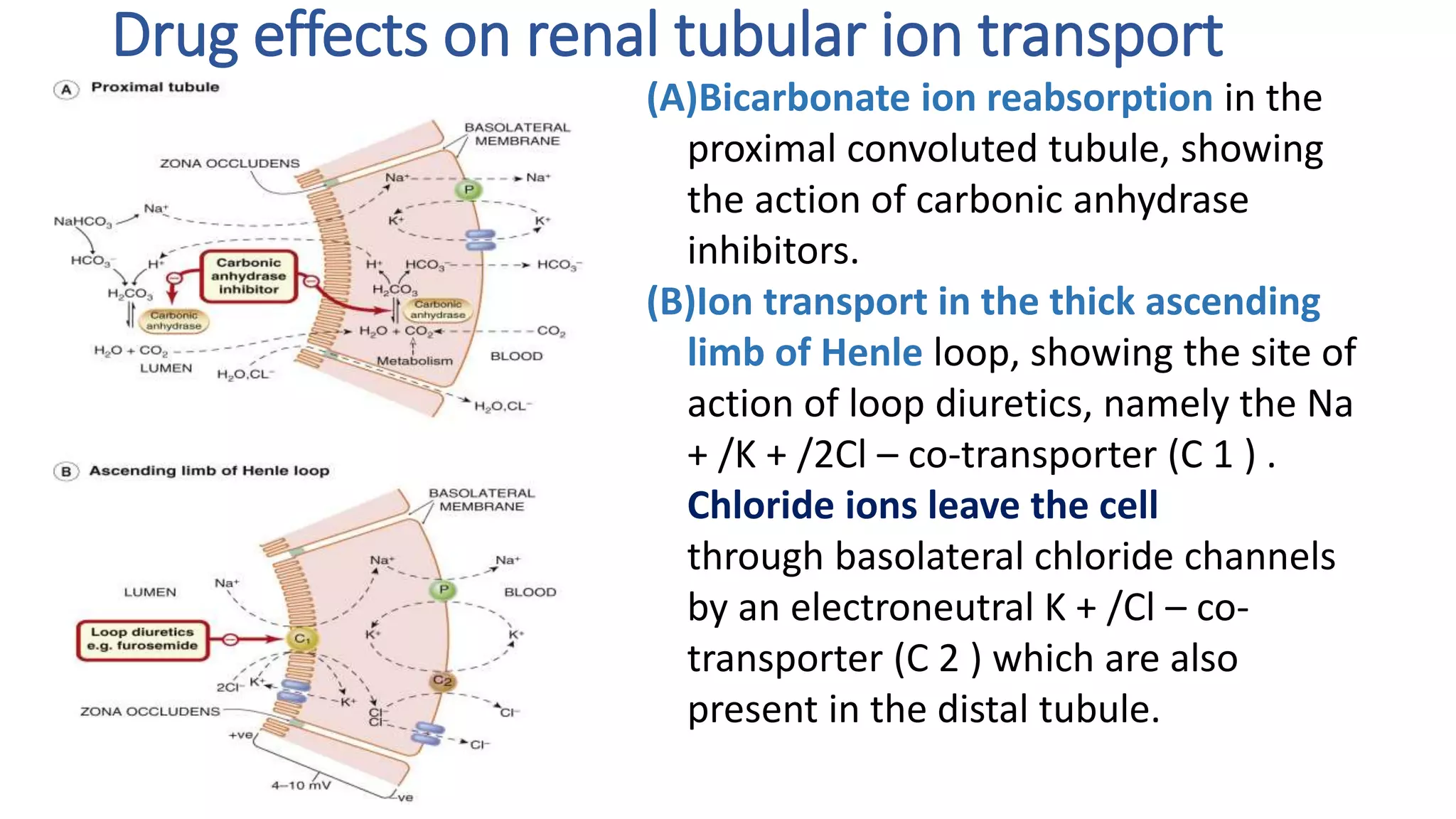
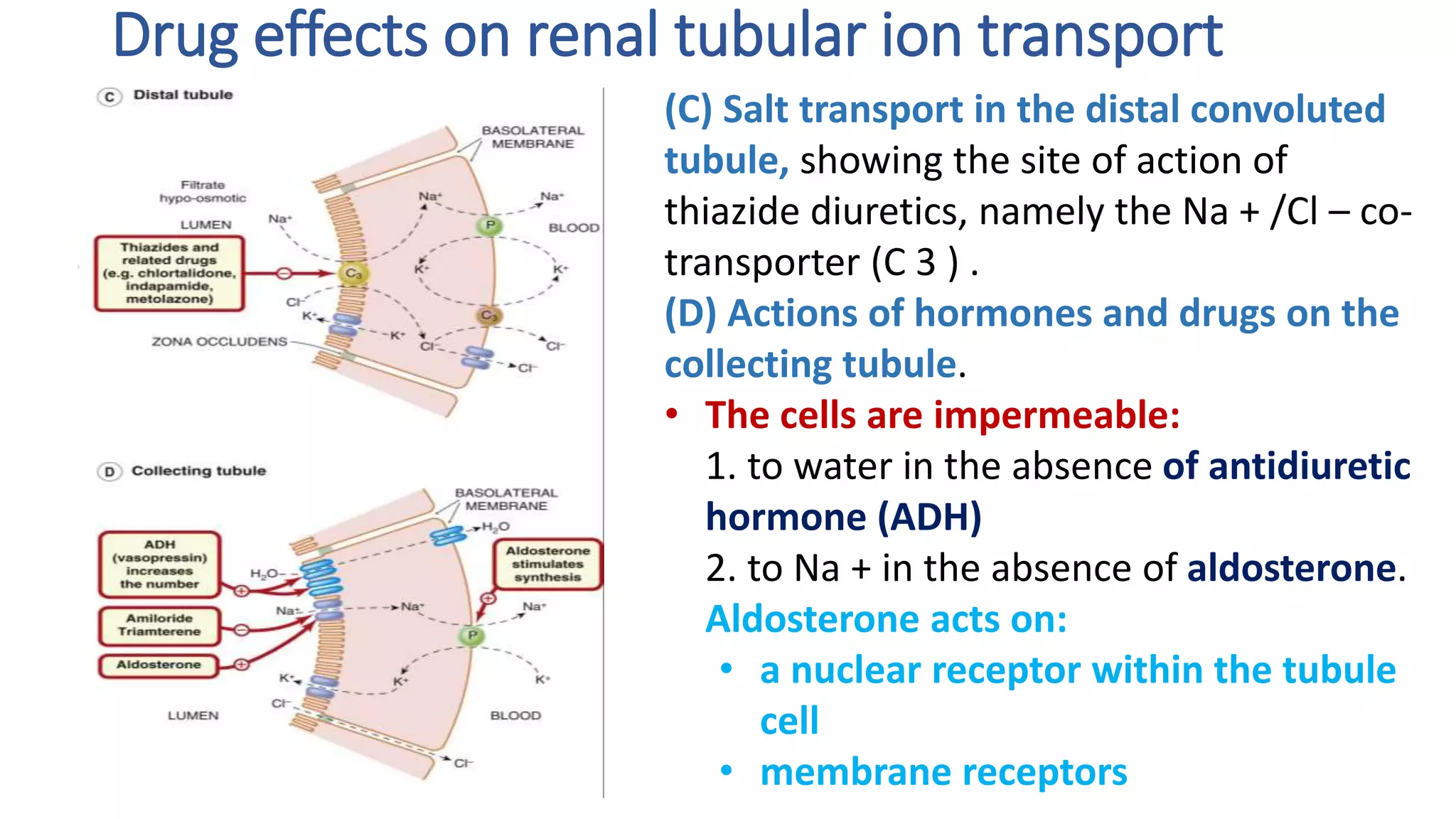
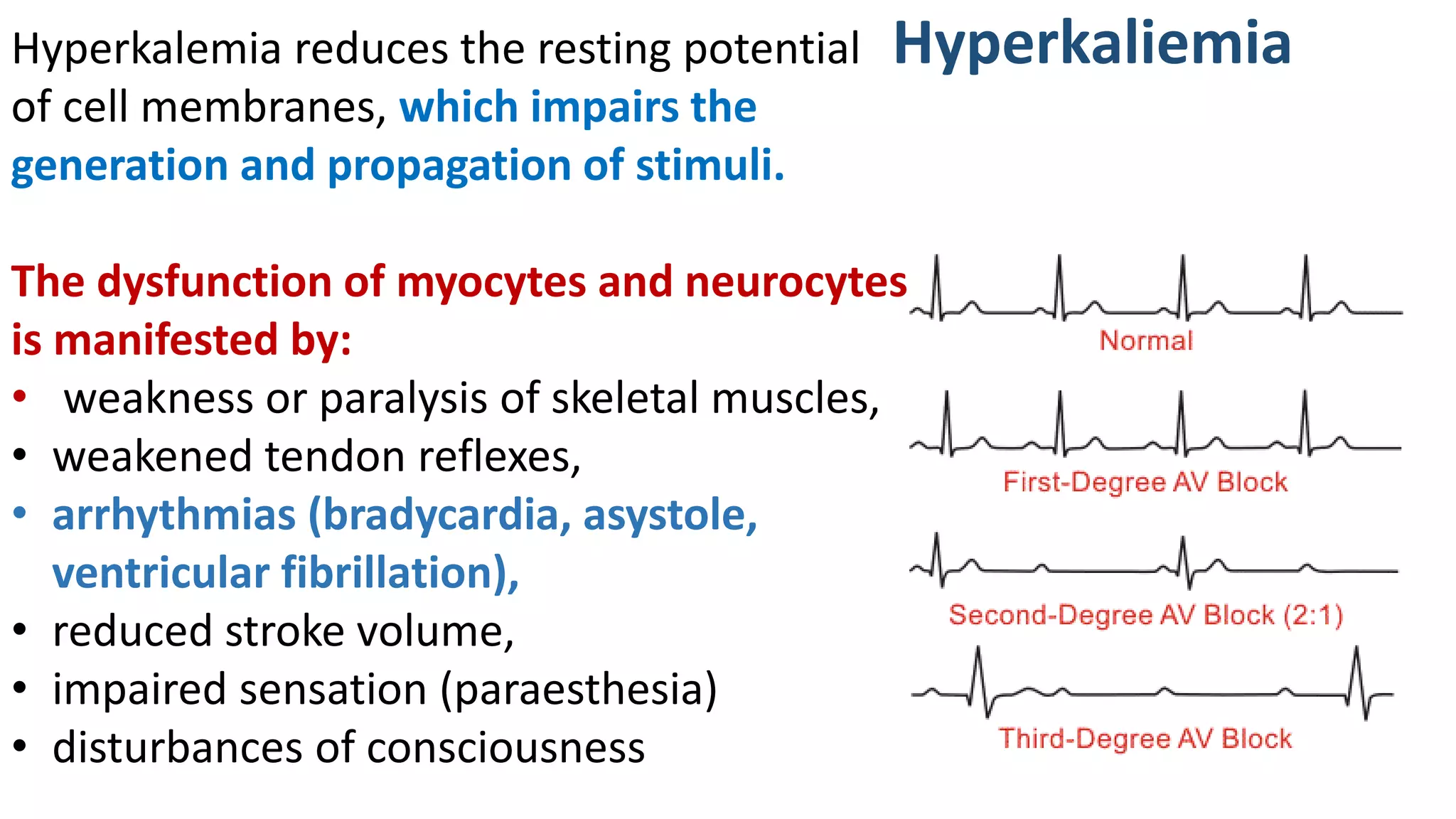
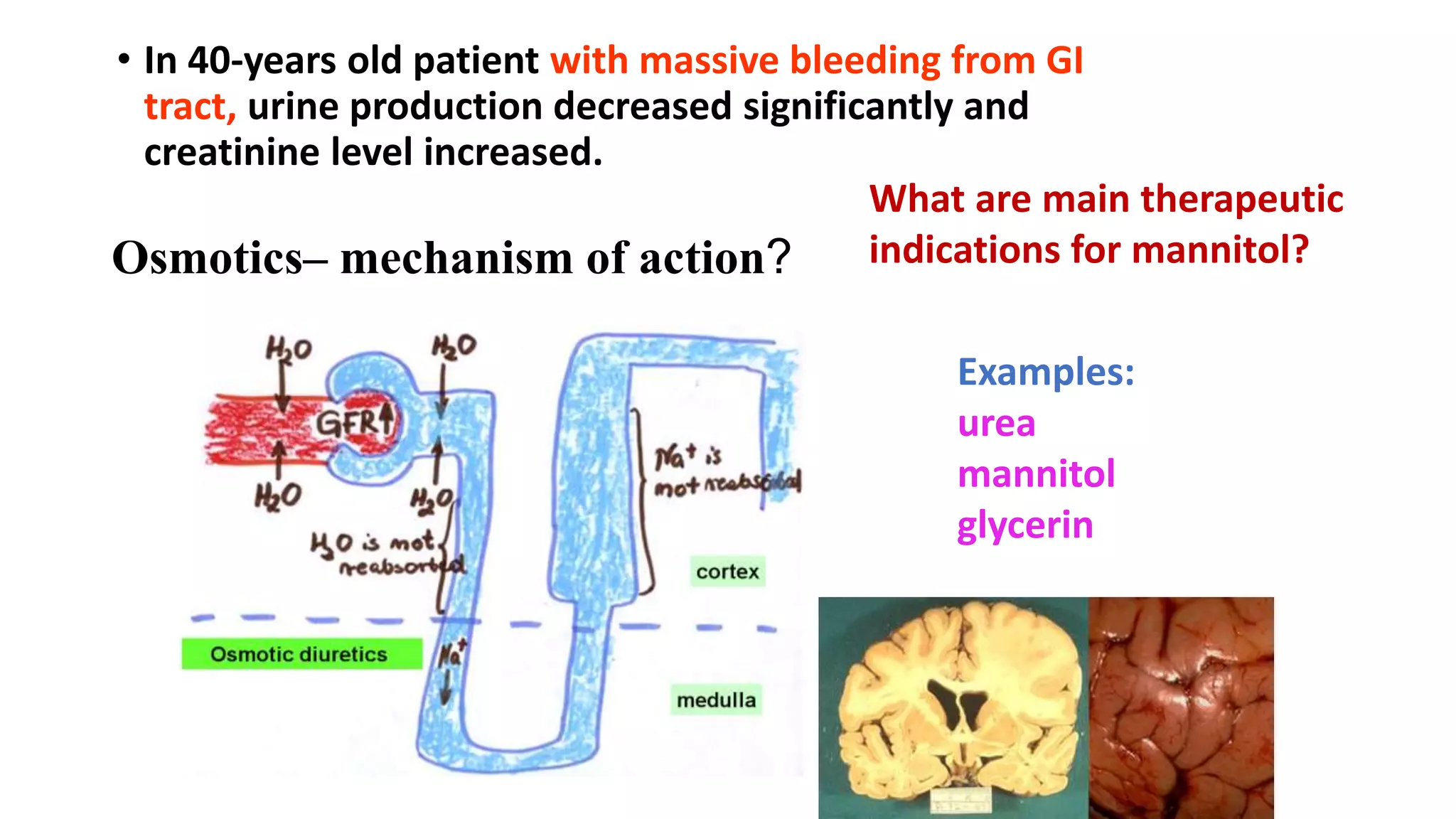
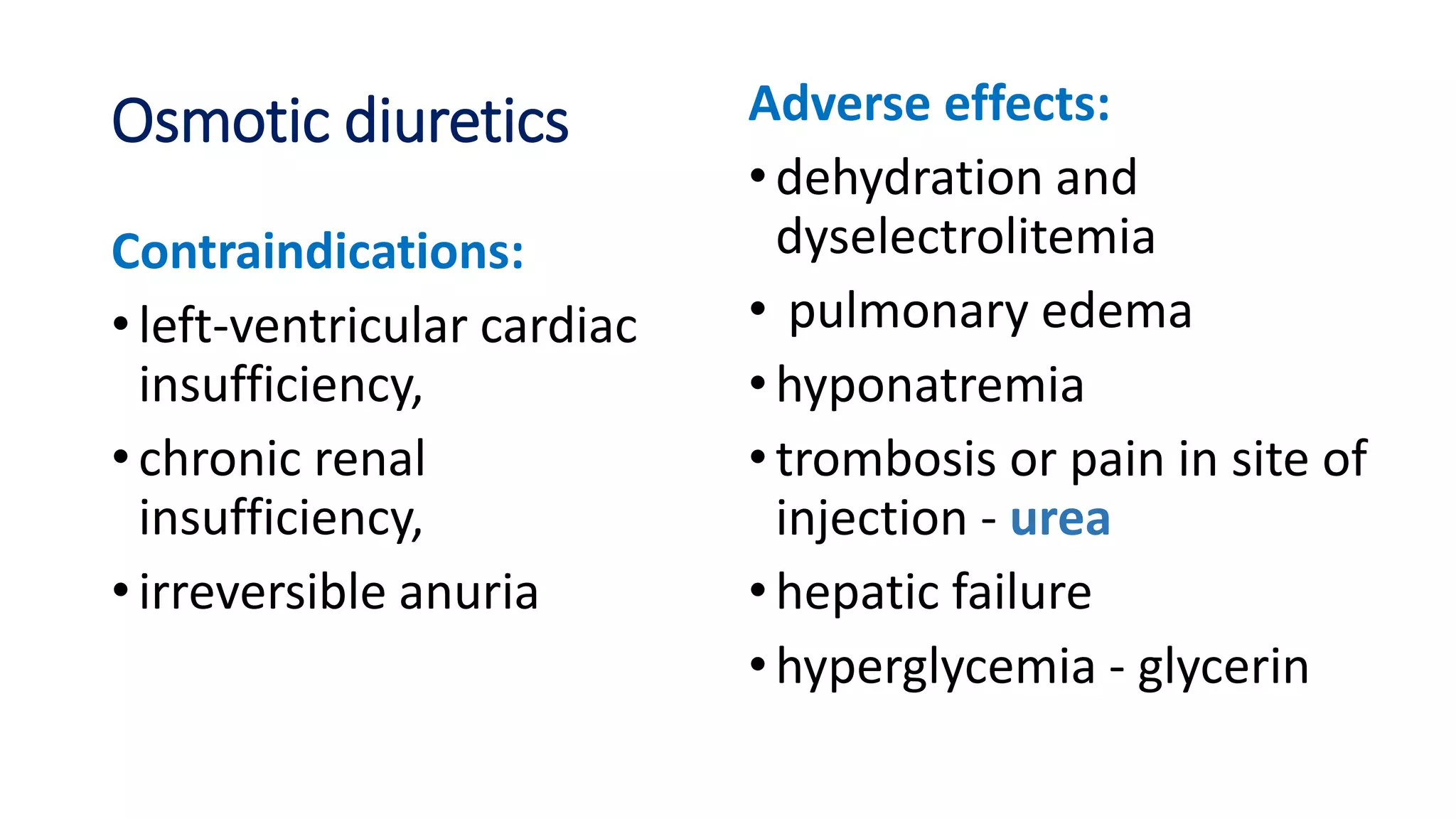
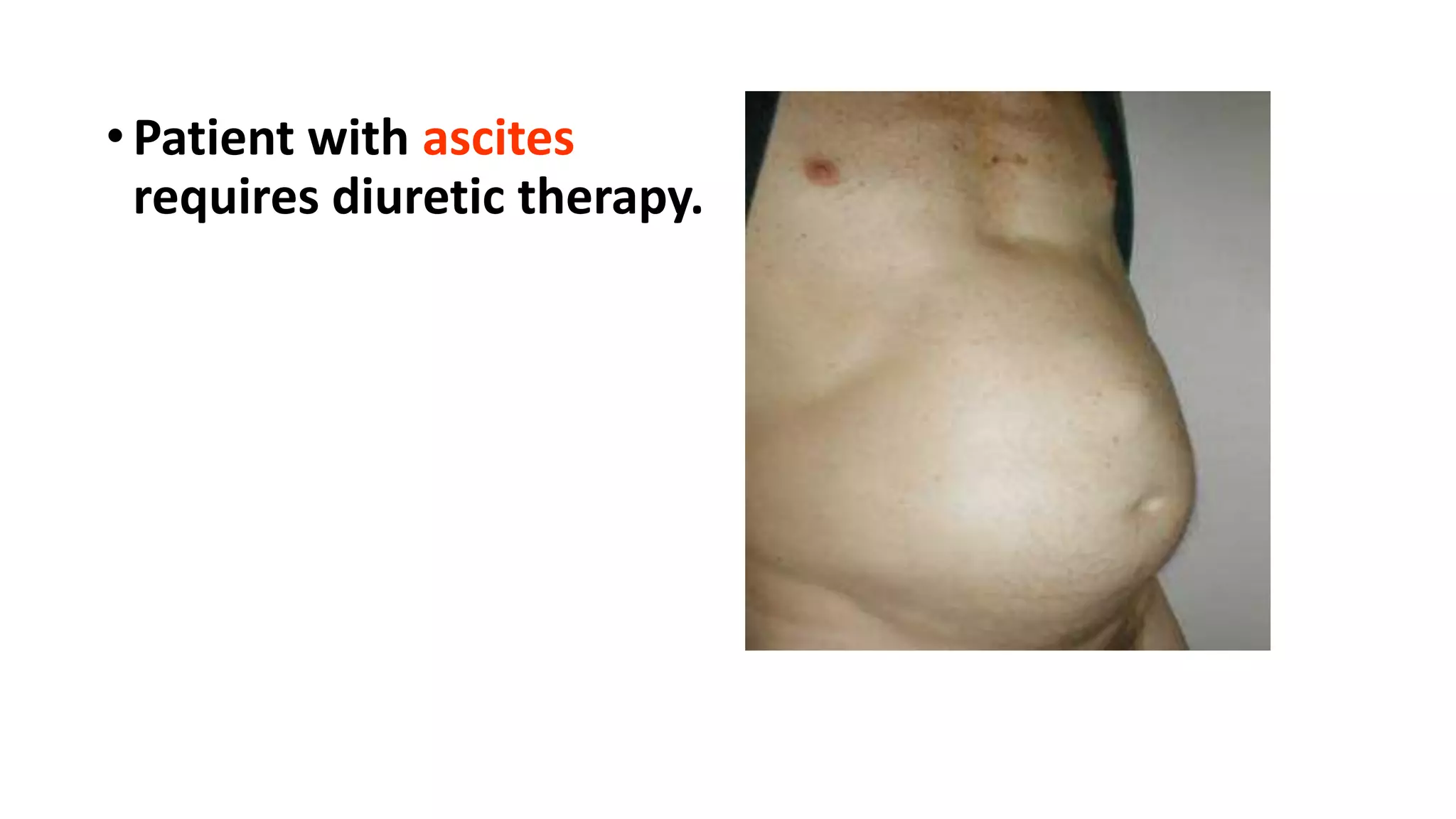
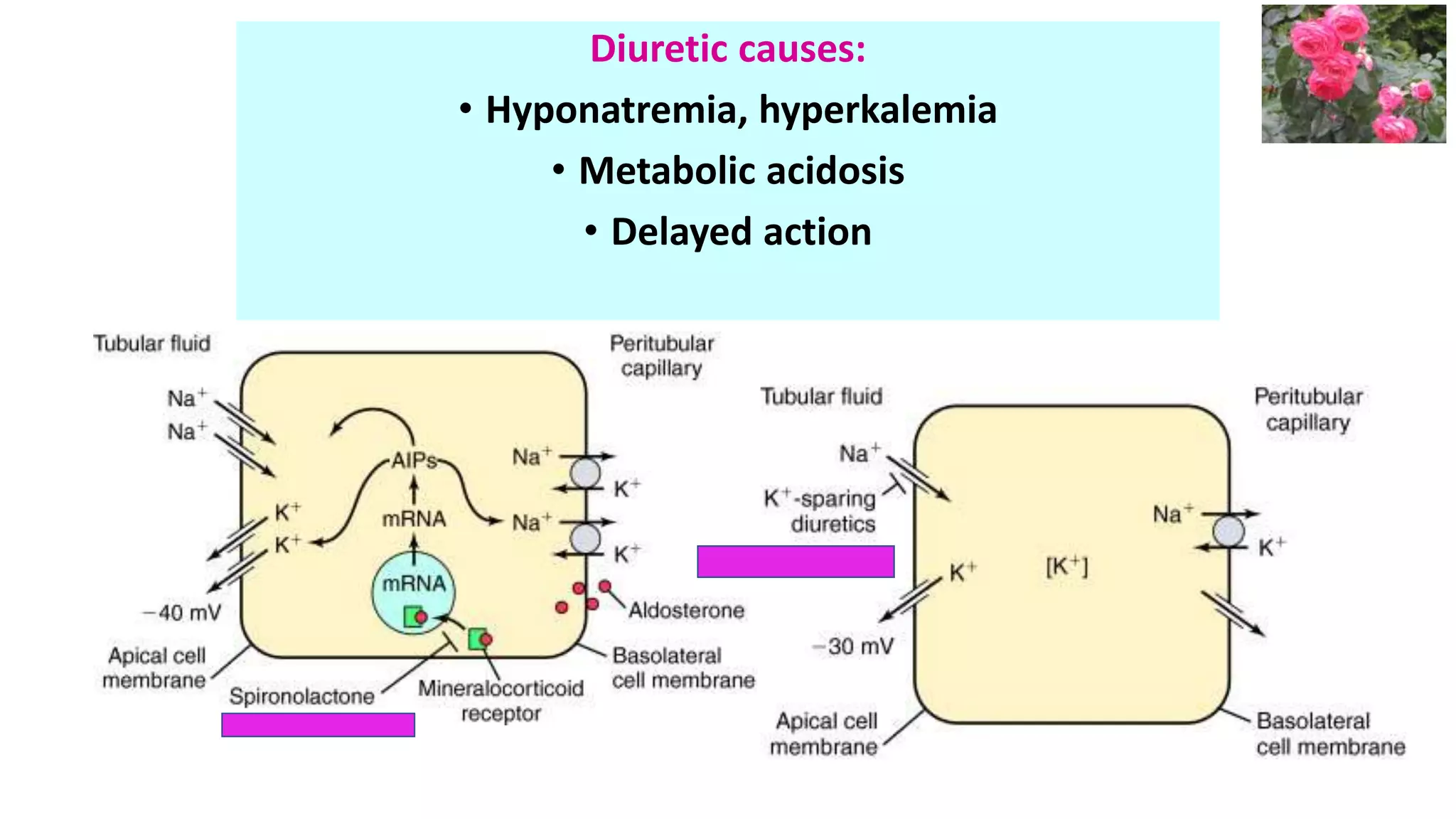
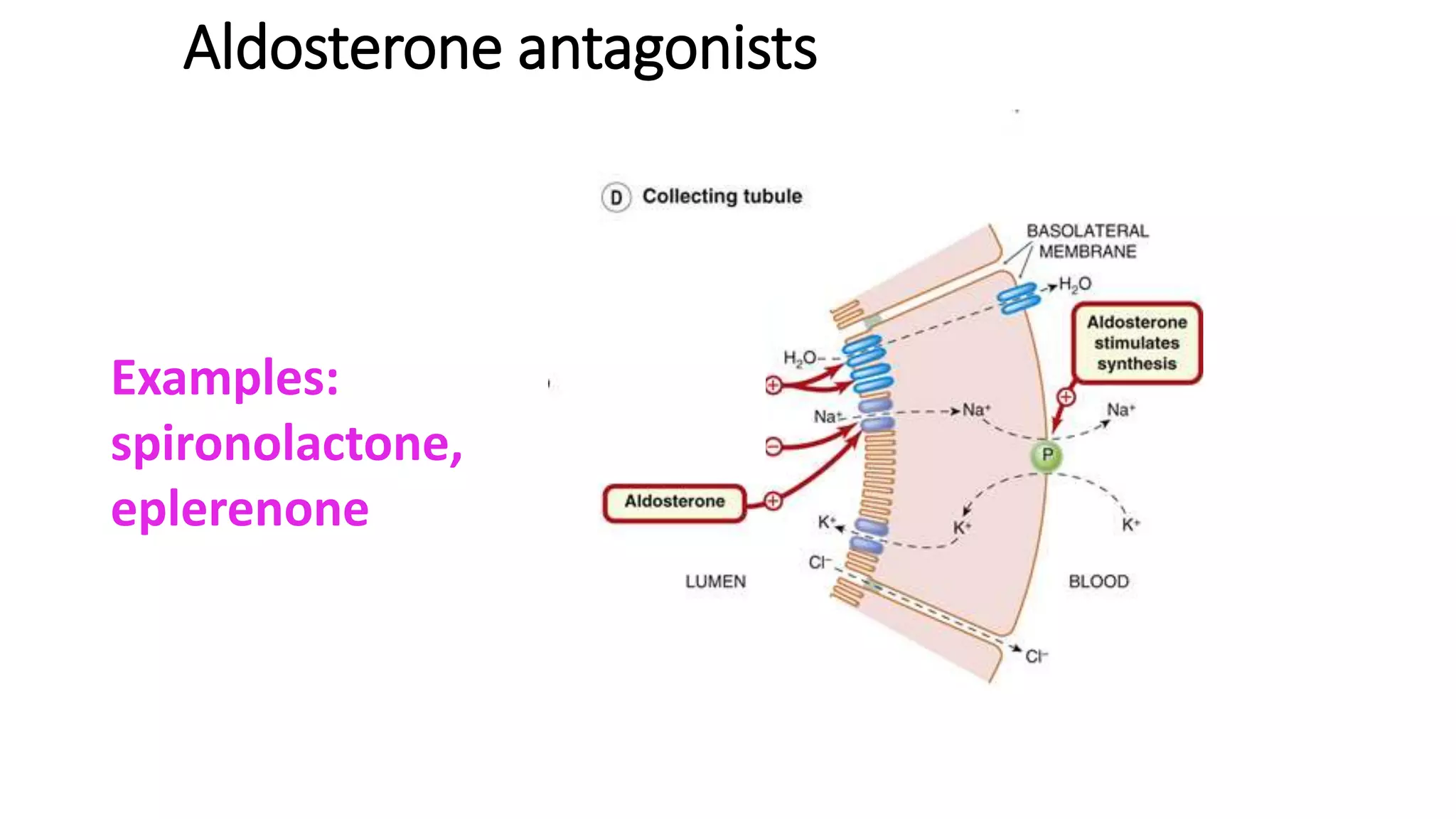
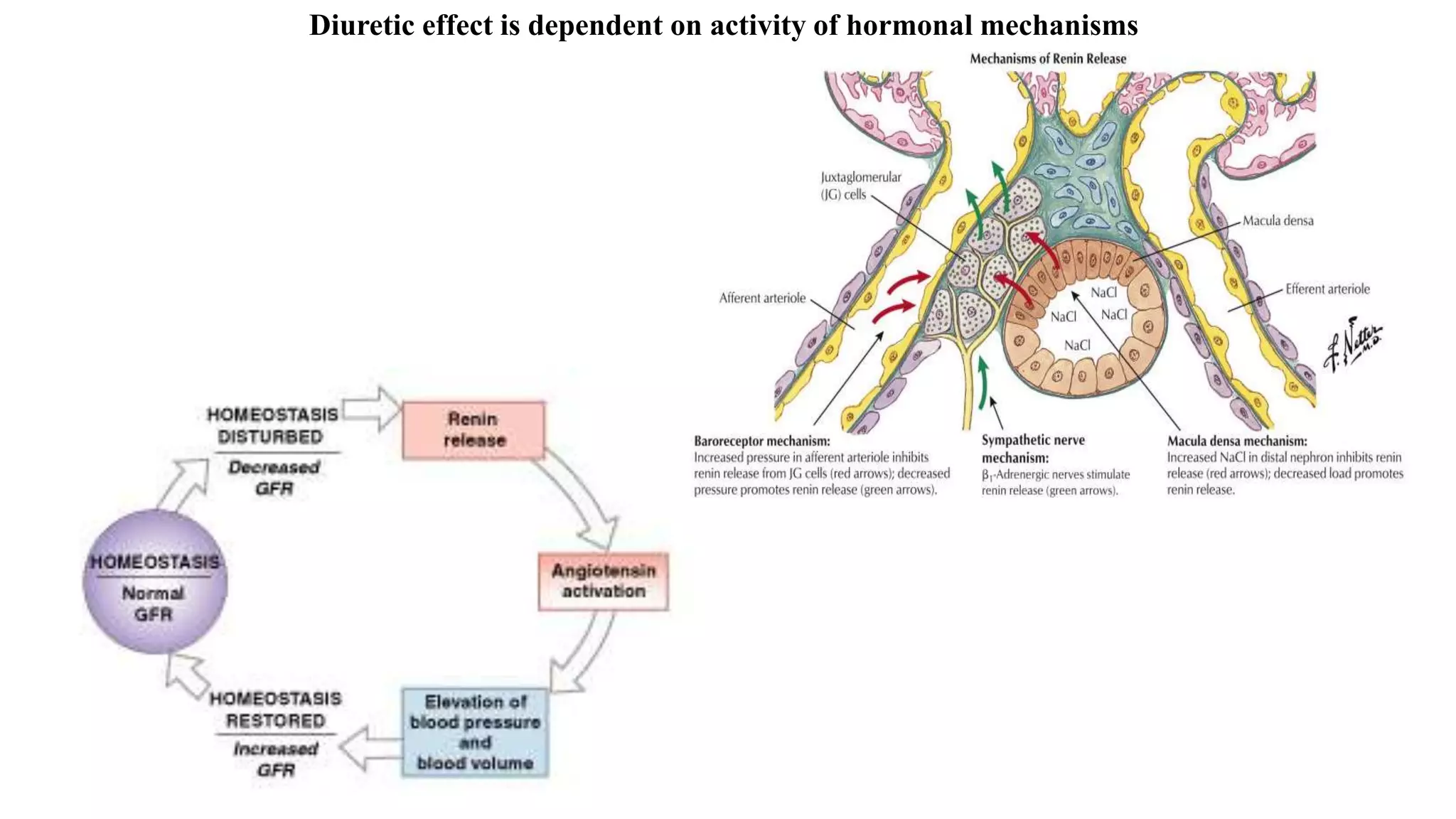
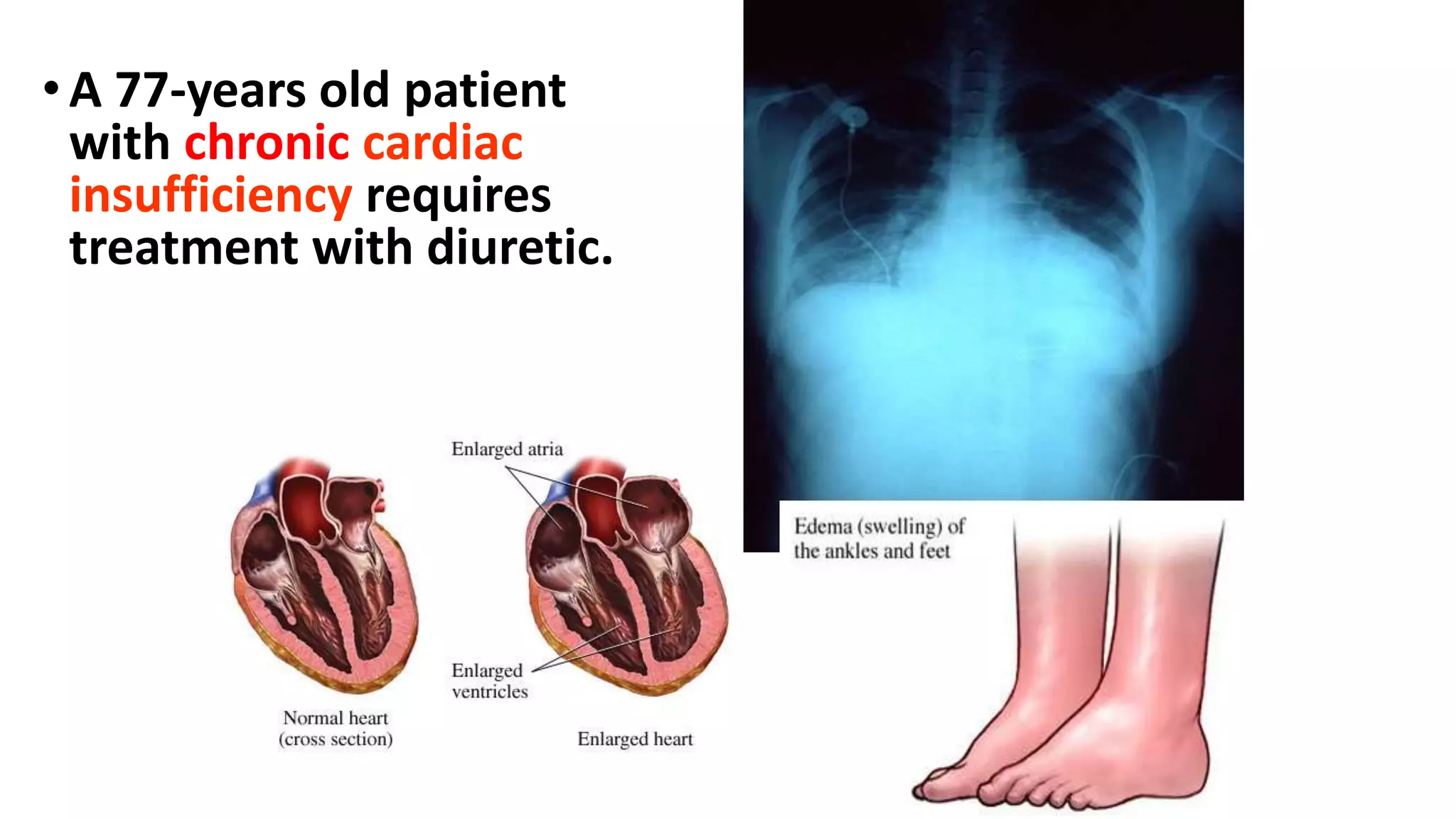
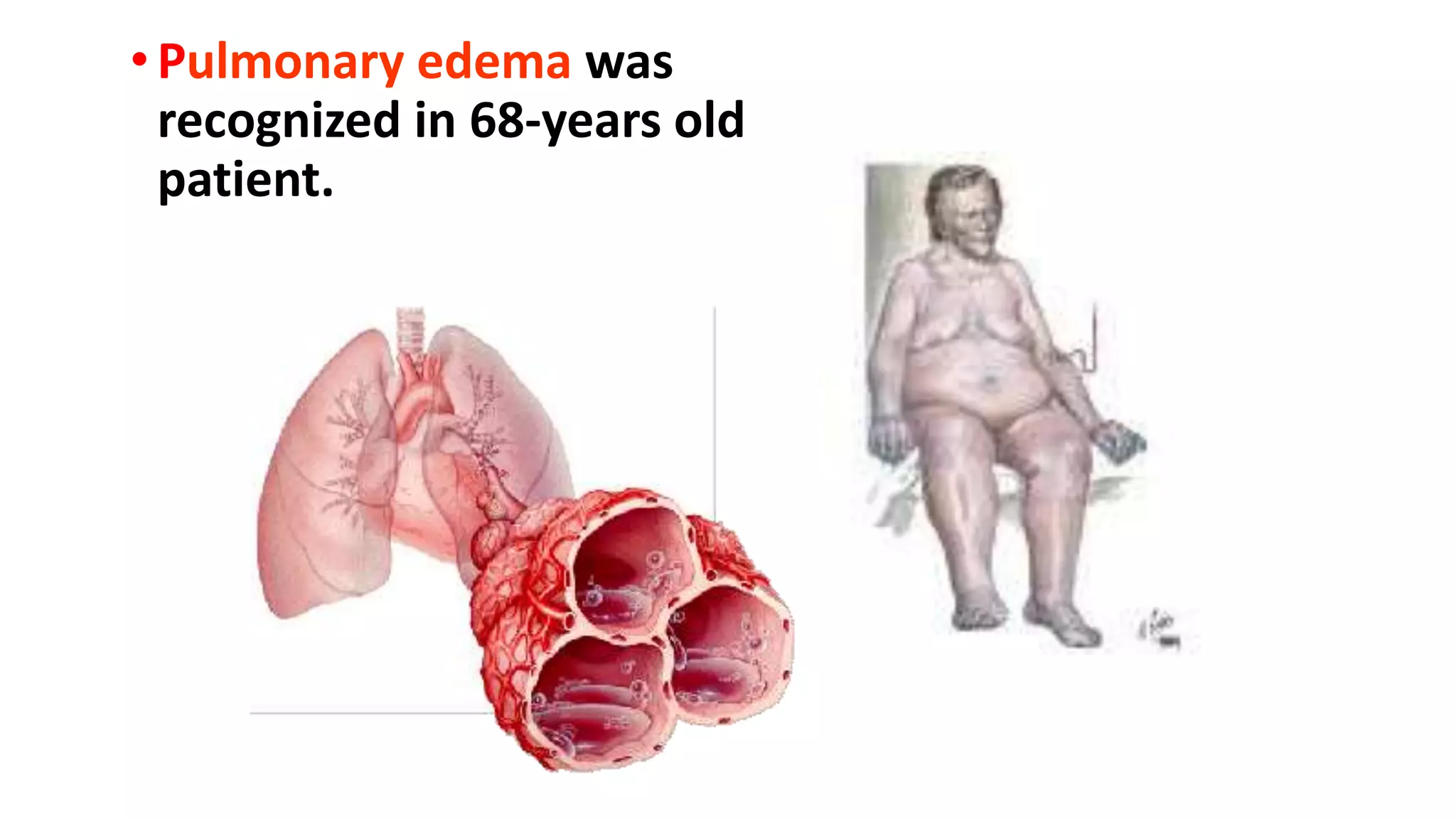
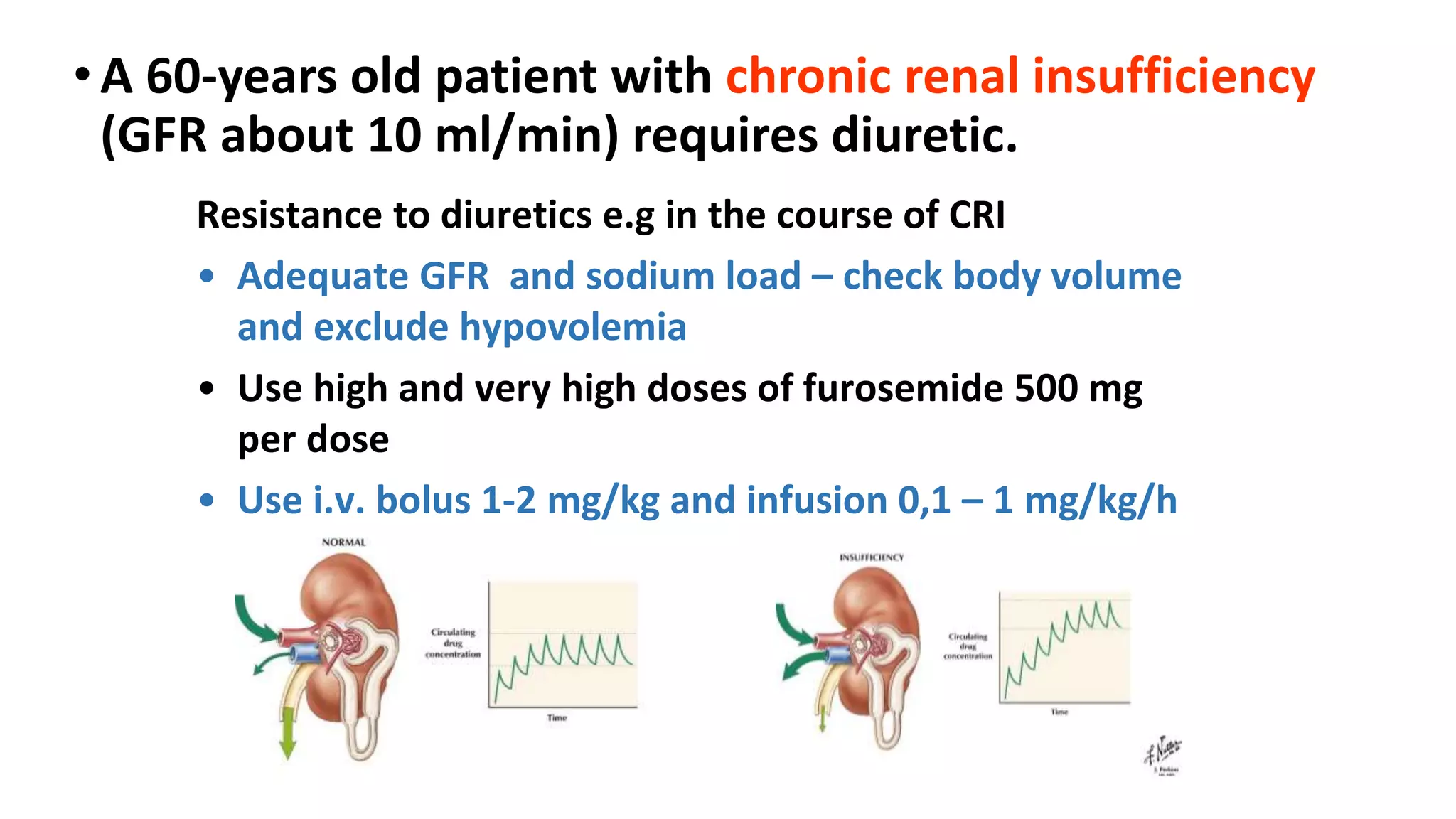
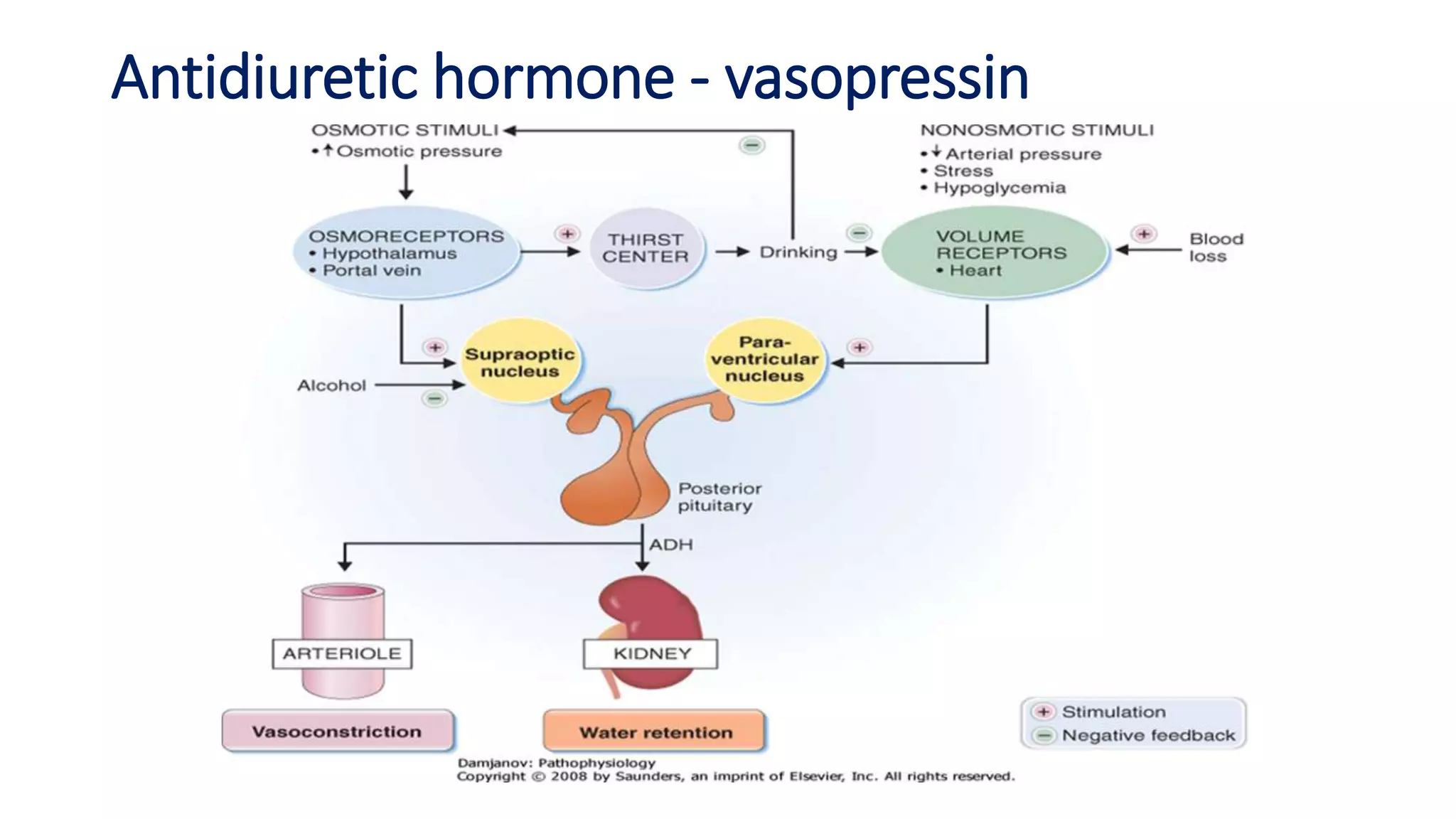
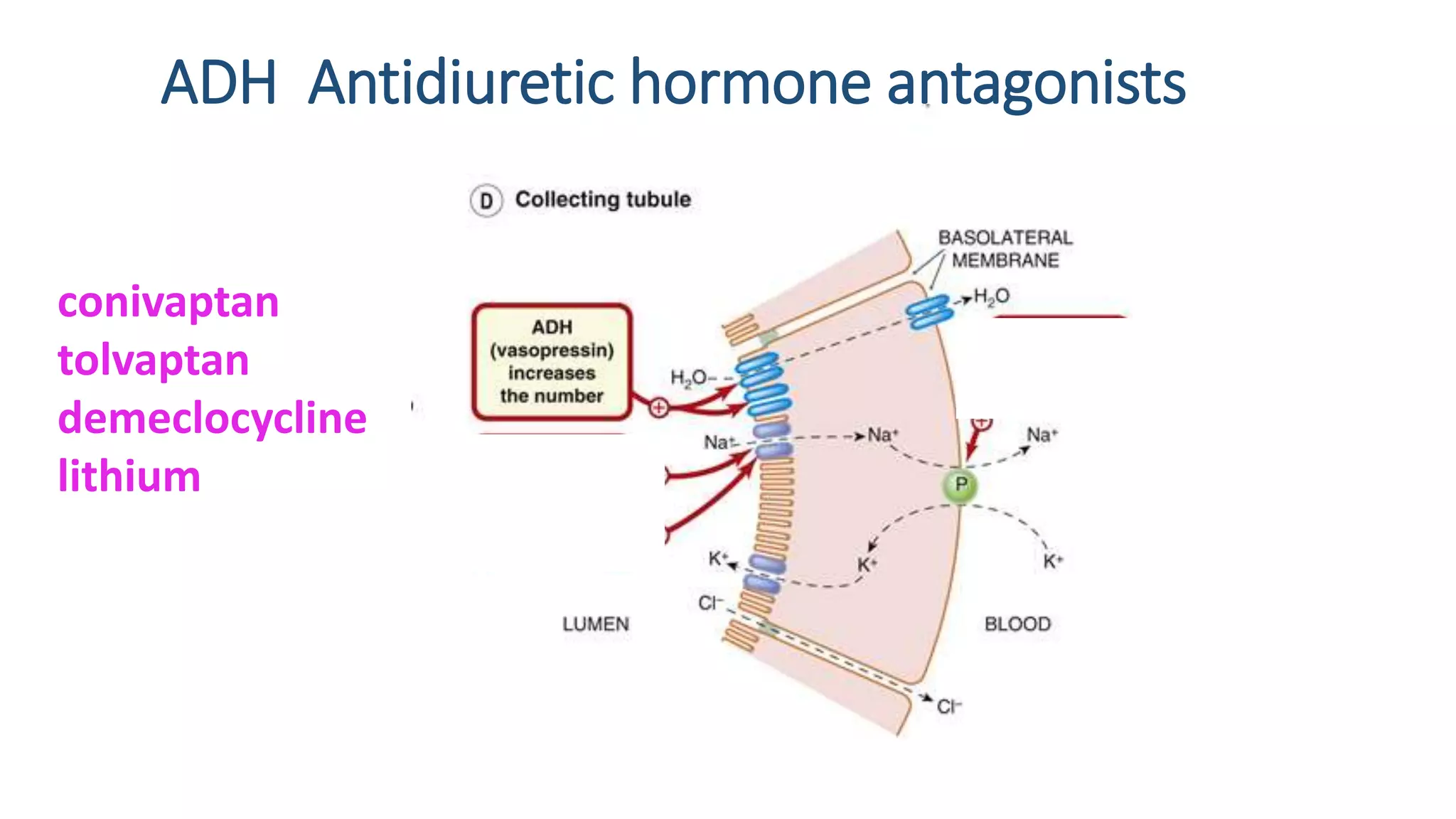
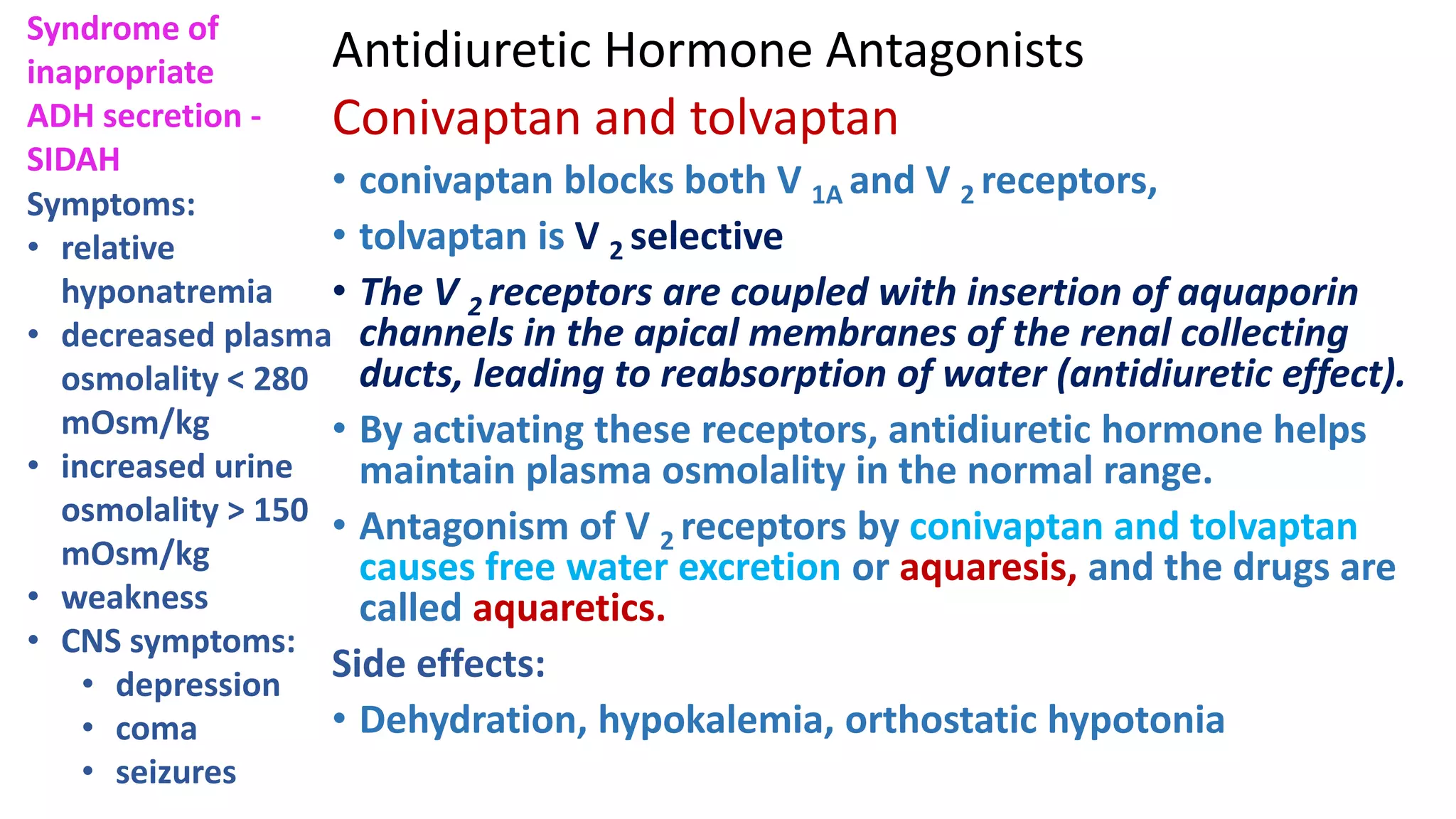
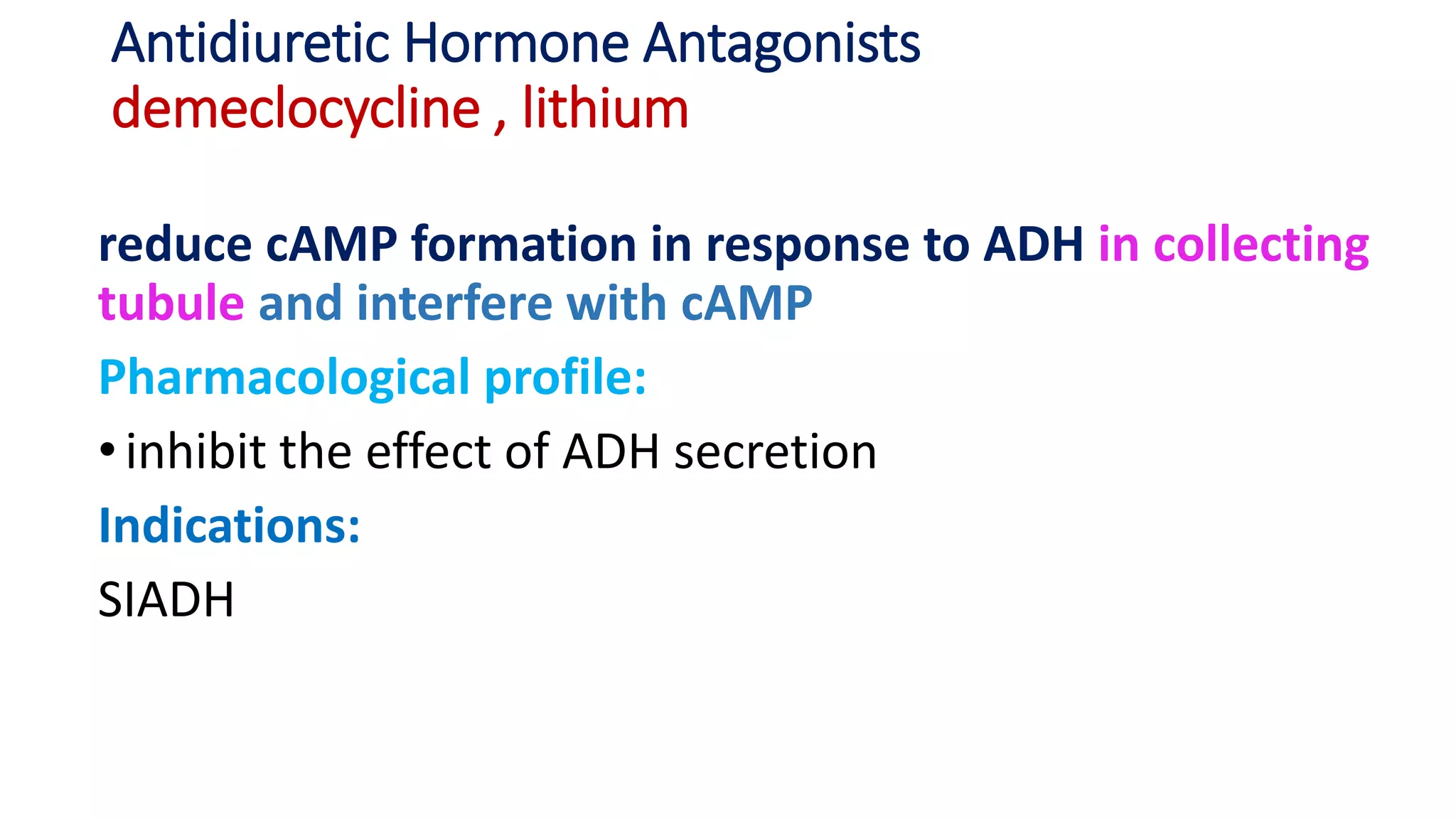
This document discusses different classes of diuretic medications, their mechanisms of action, indications, and side effects. It describes:
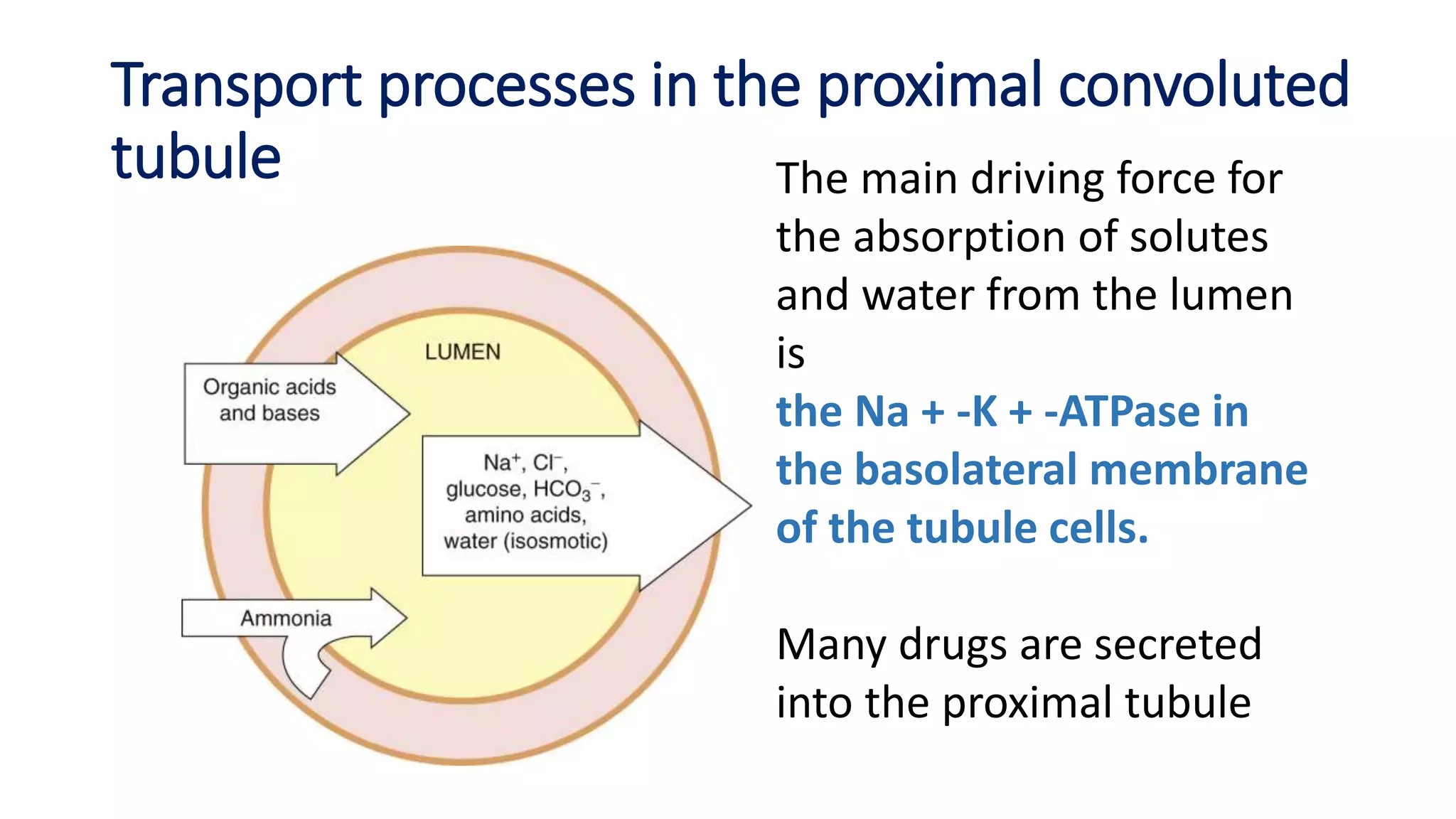
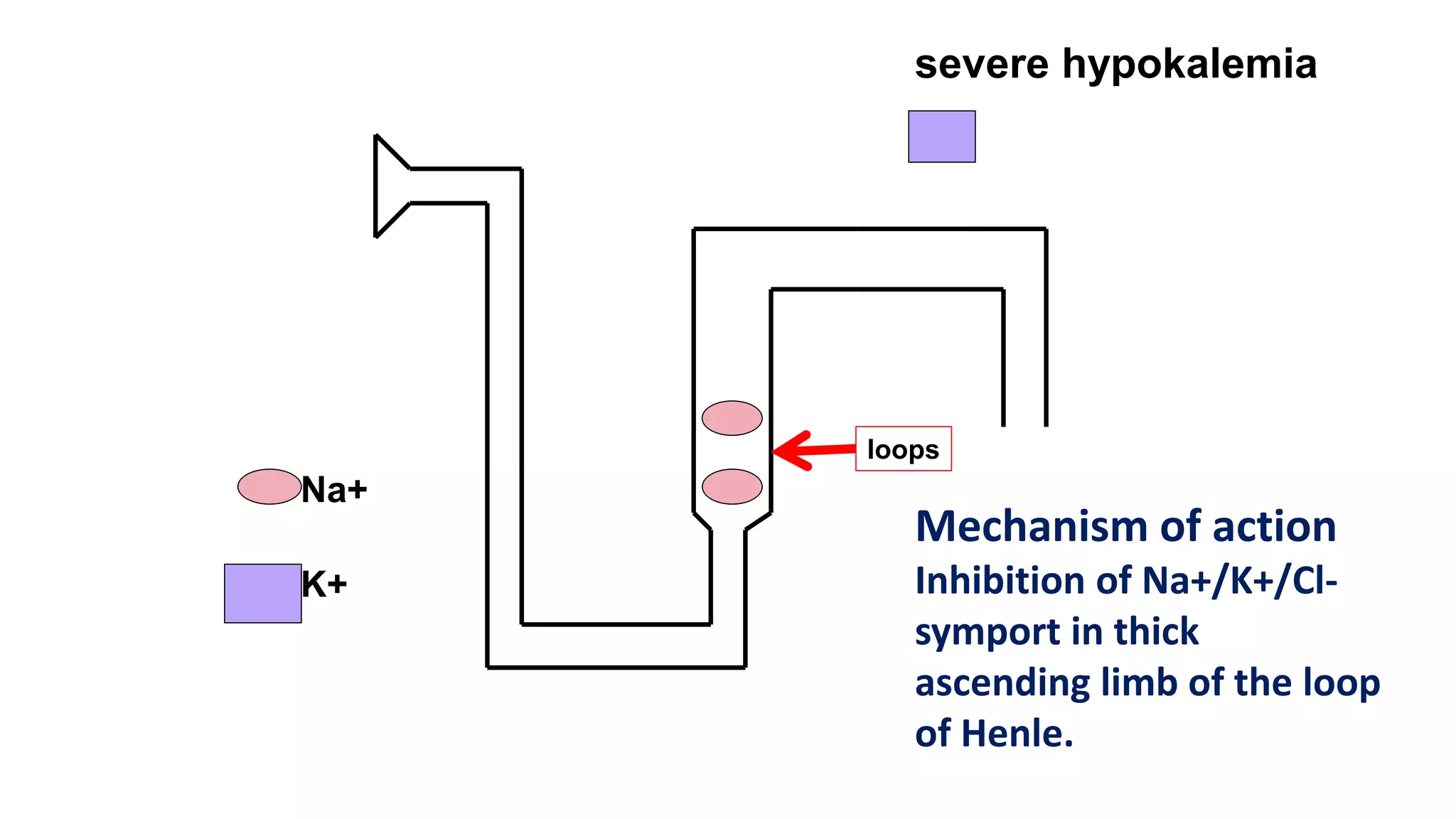
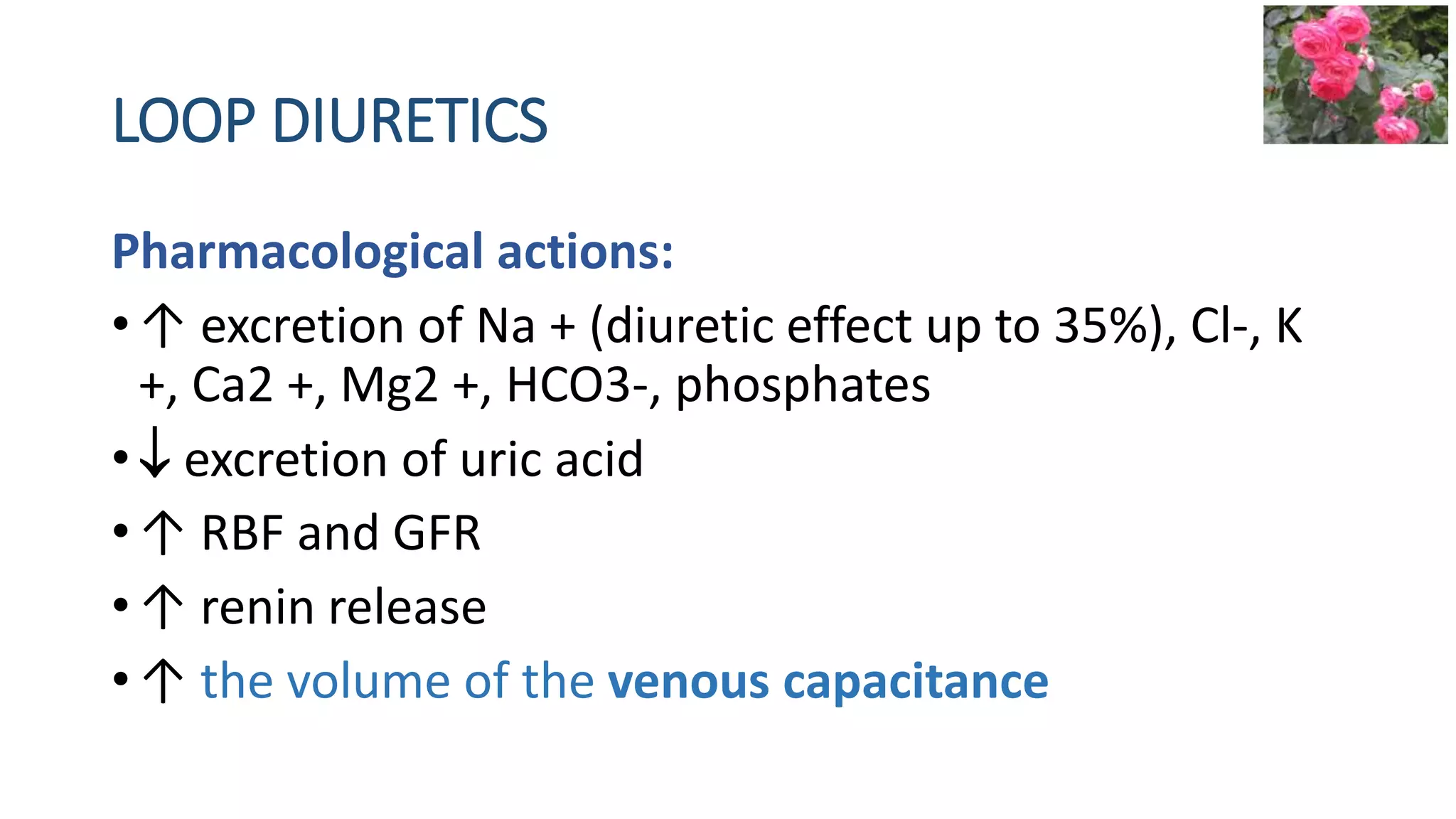
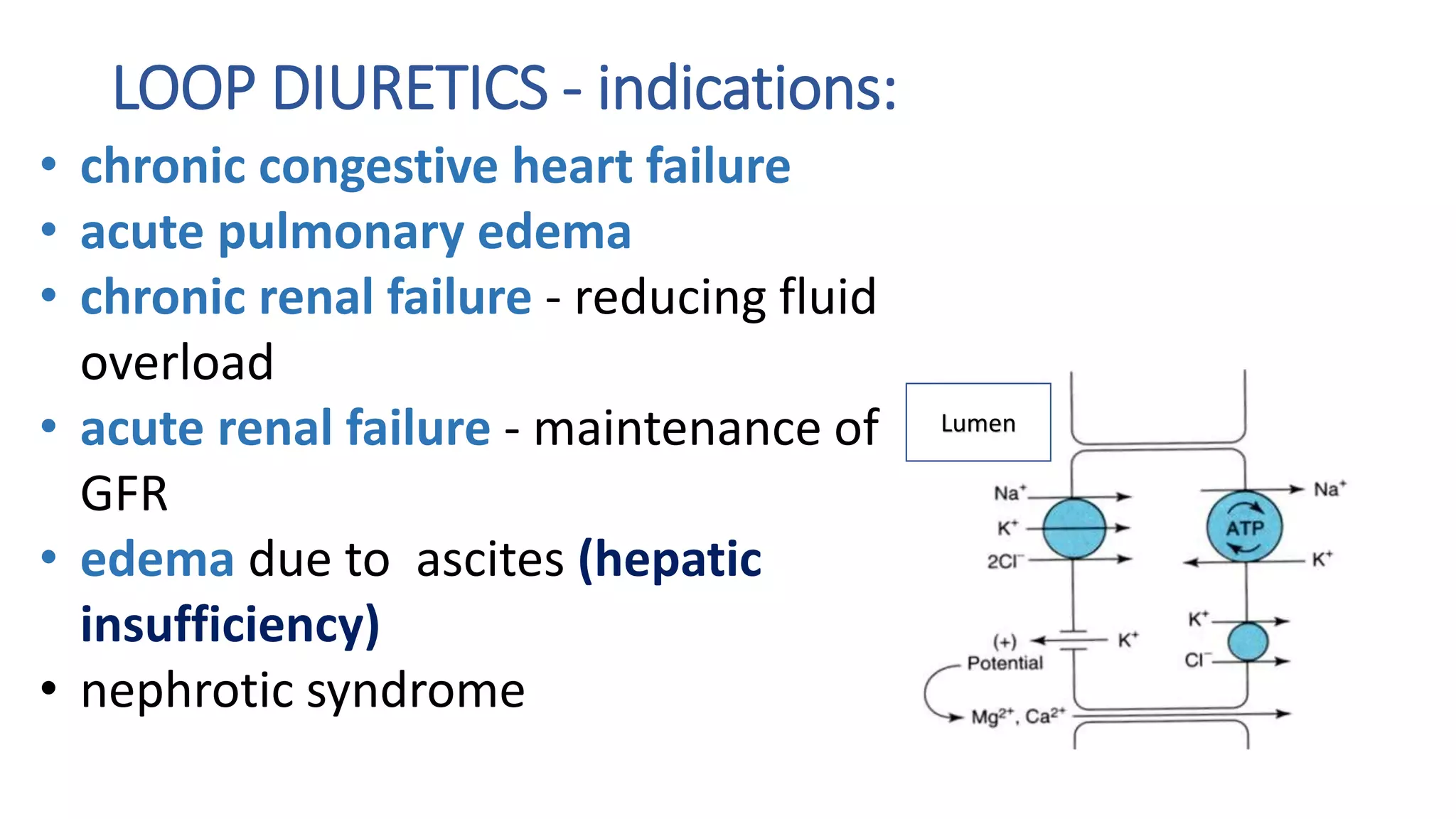
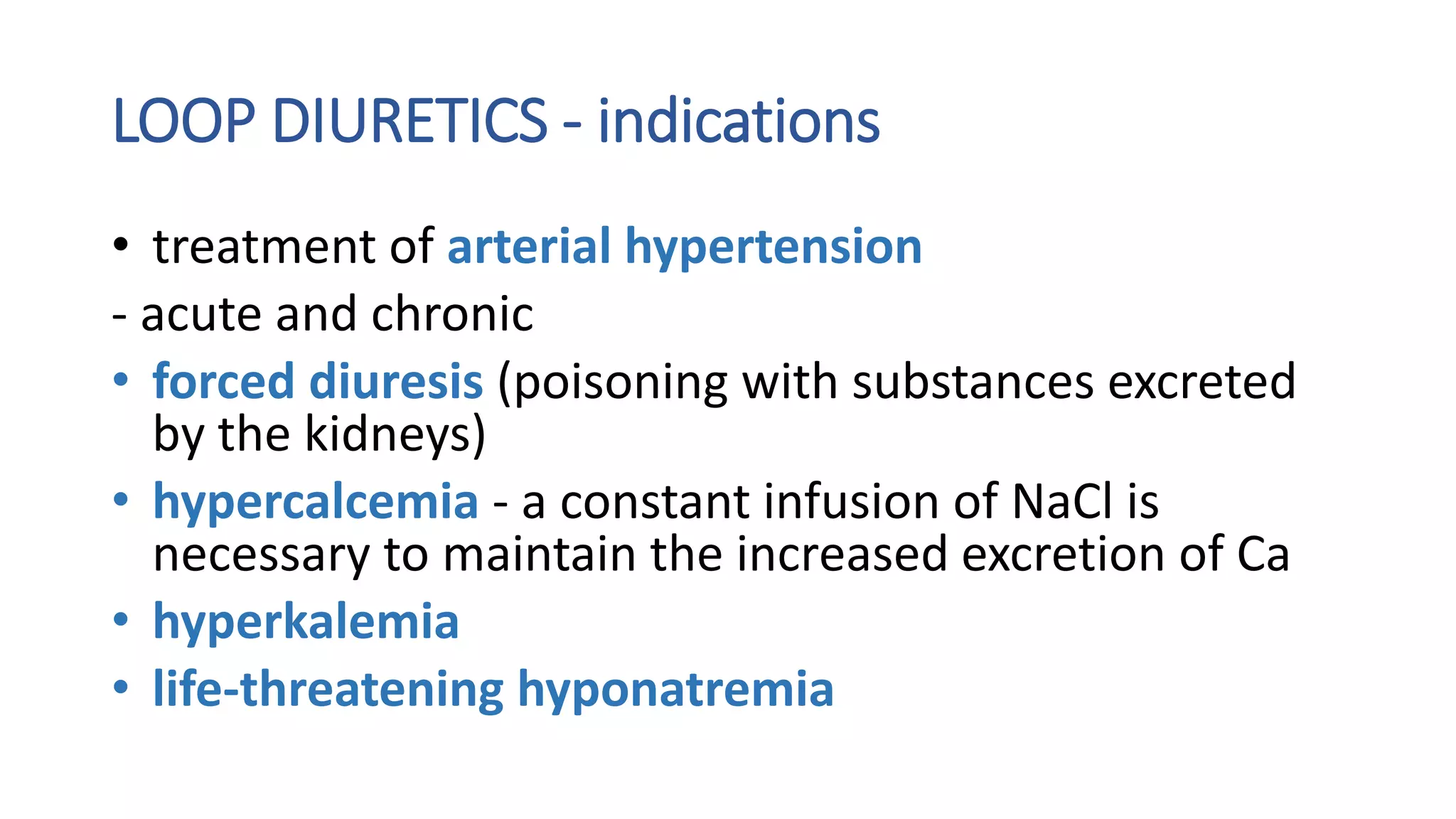
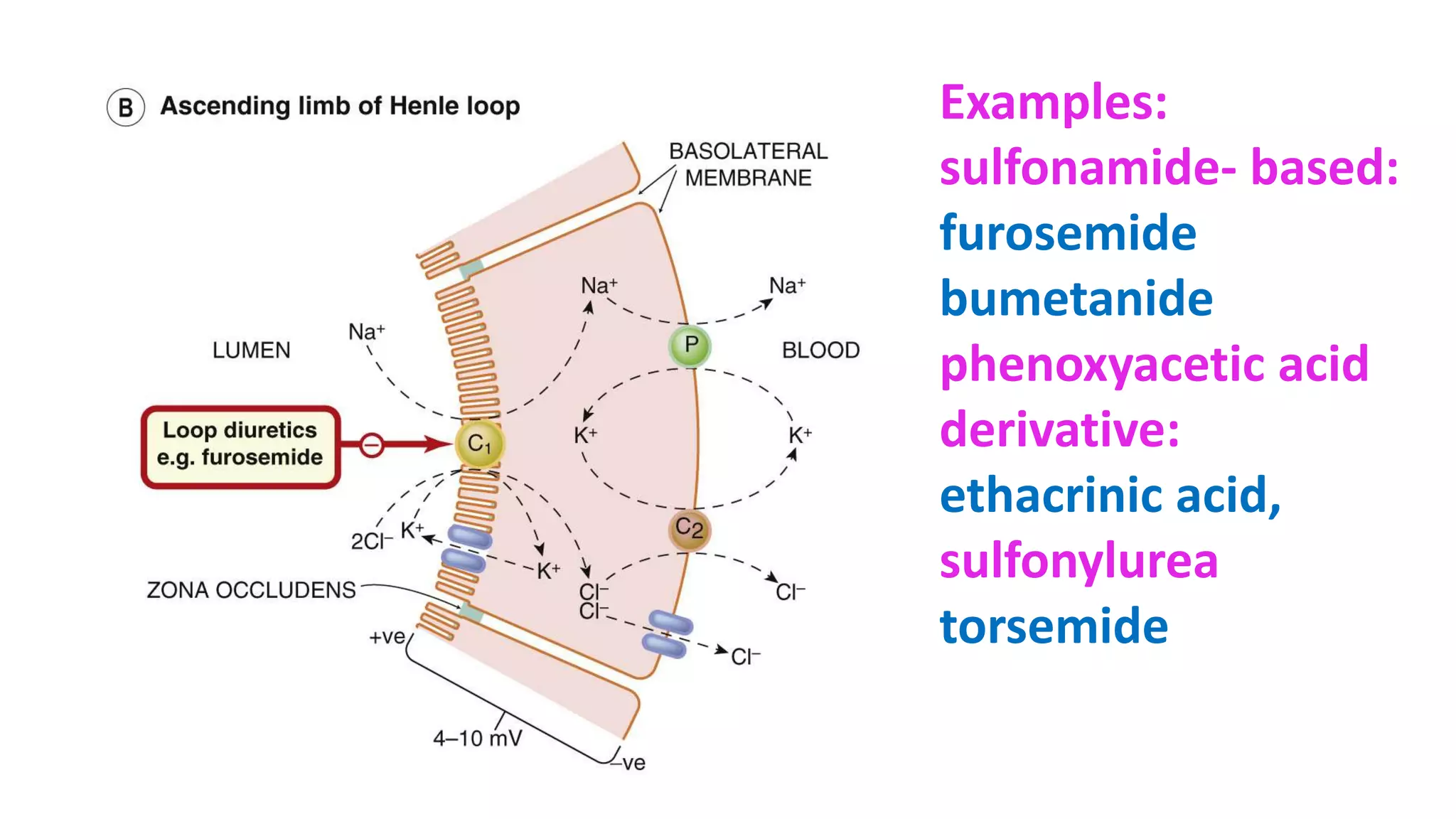
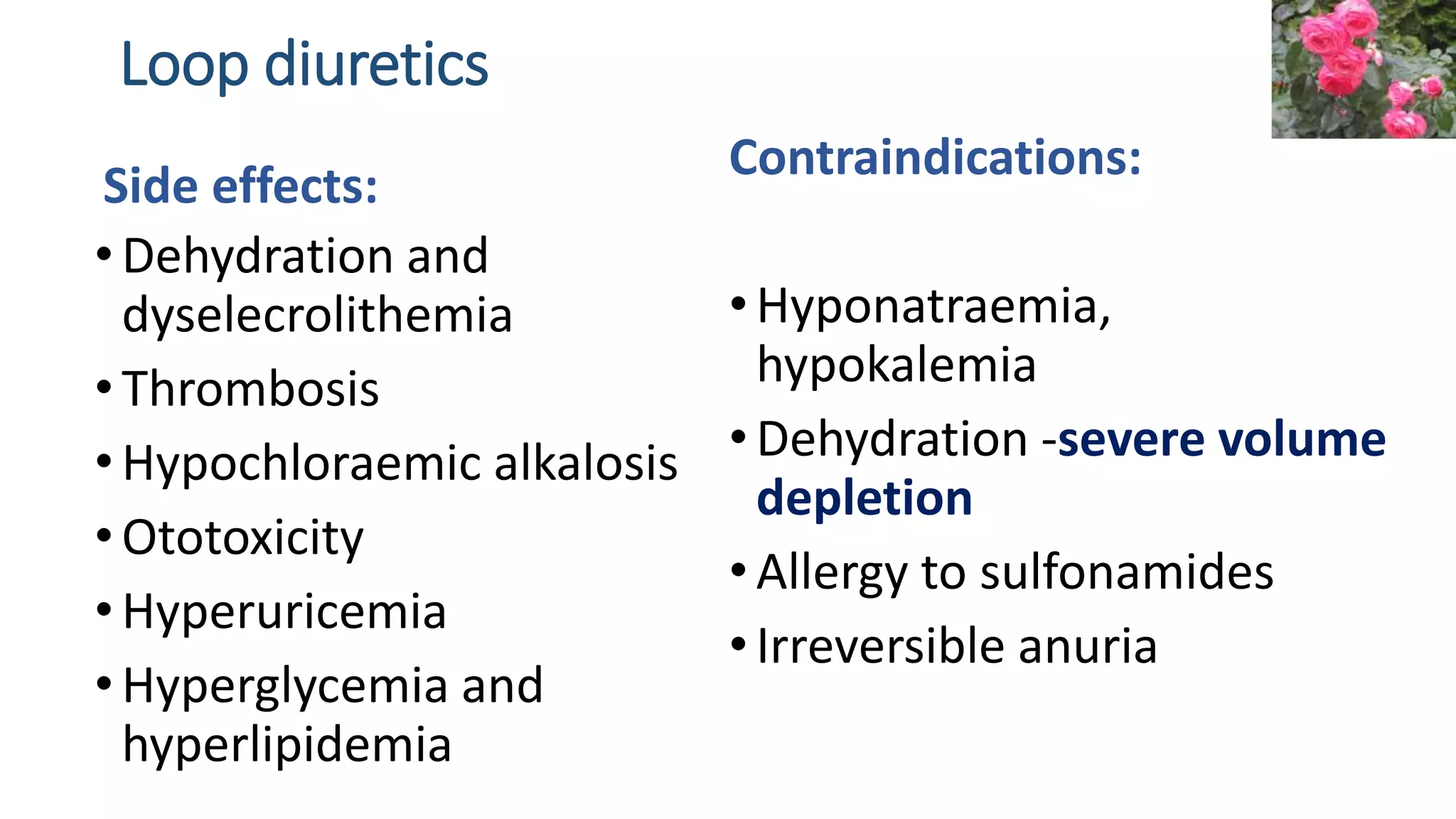
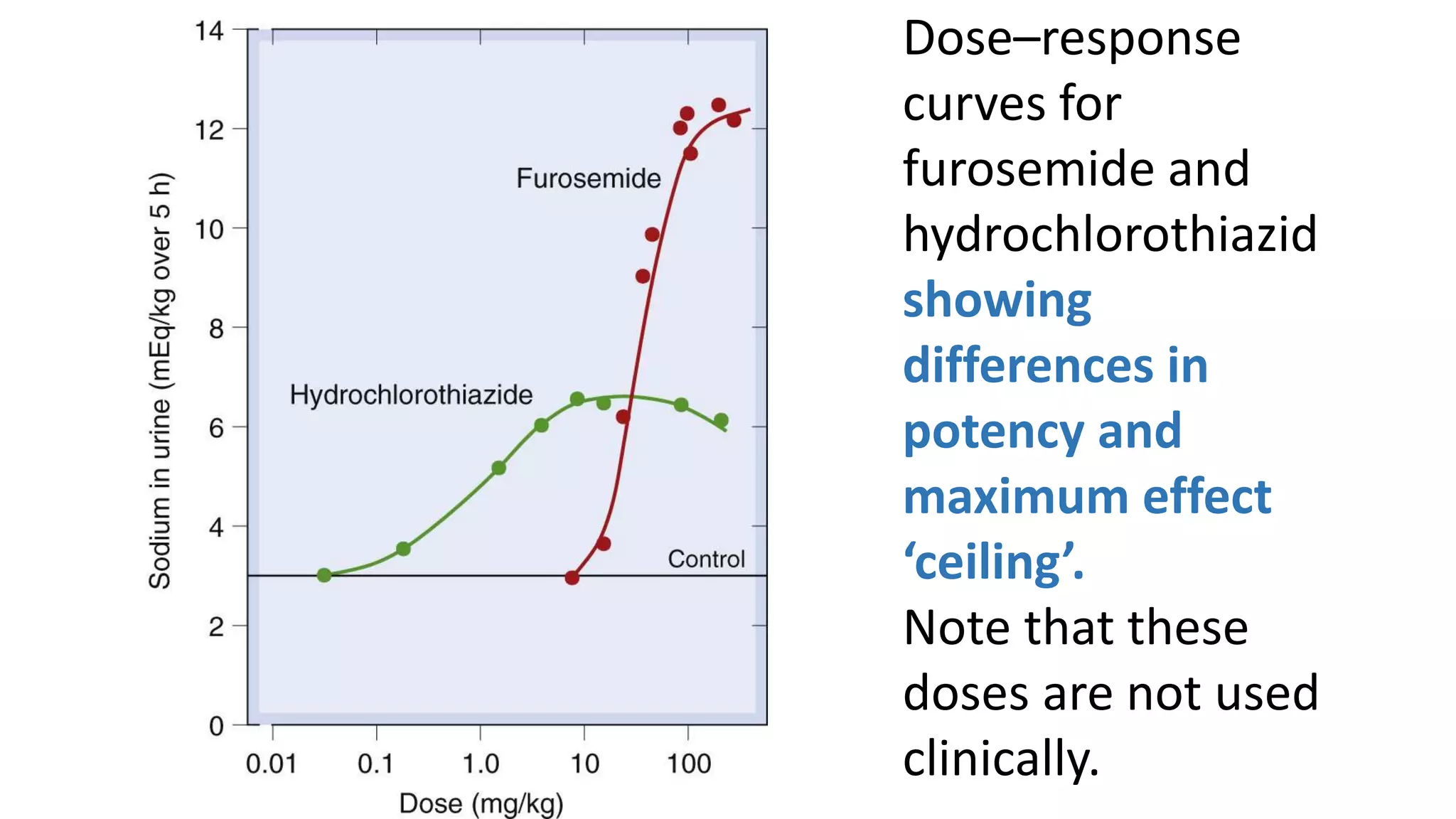
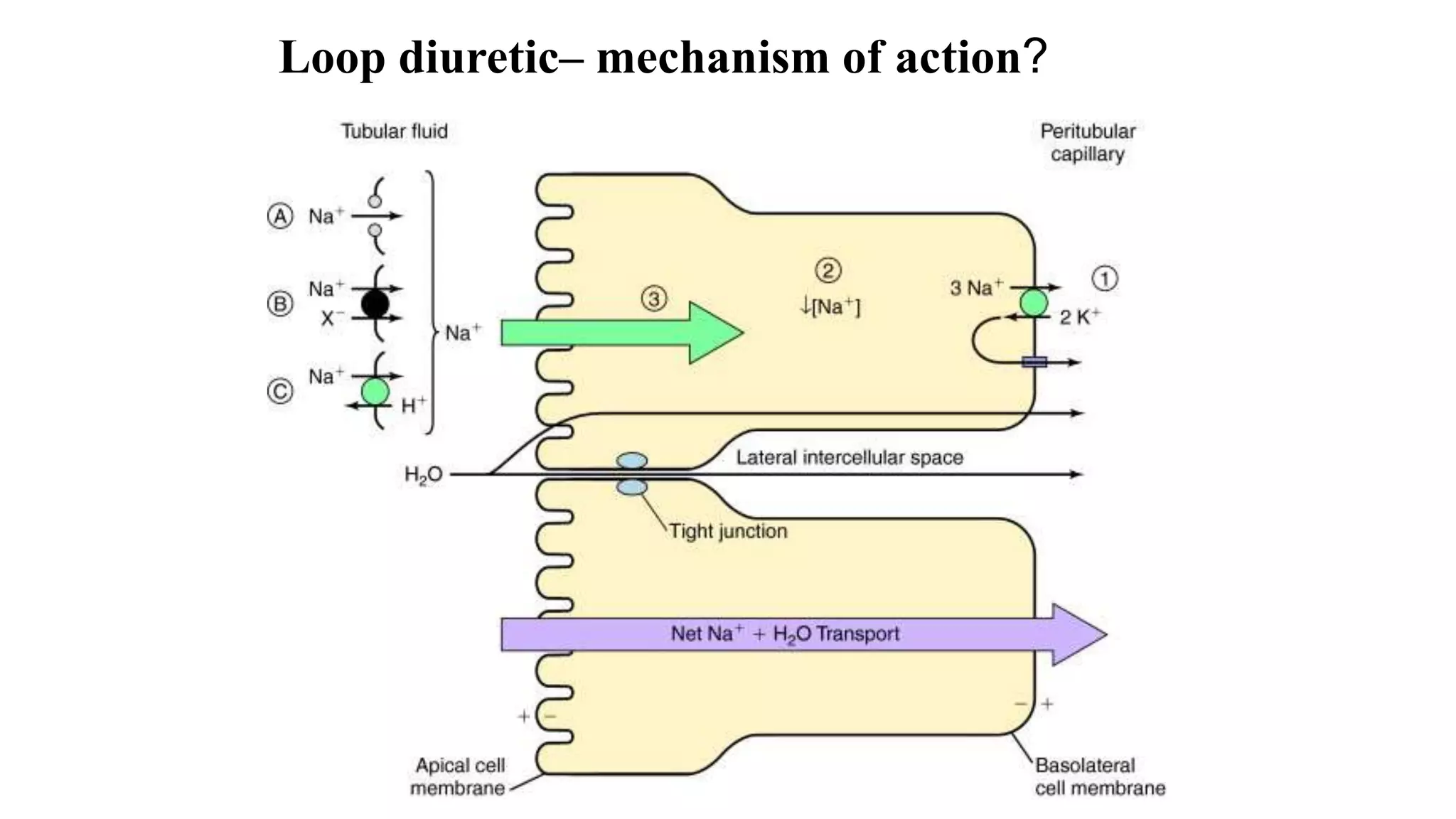
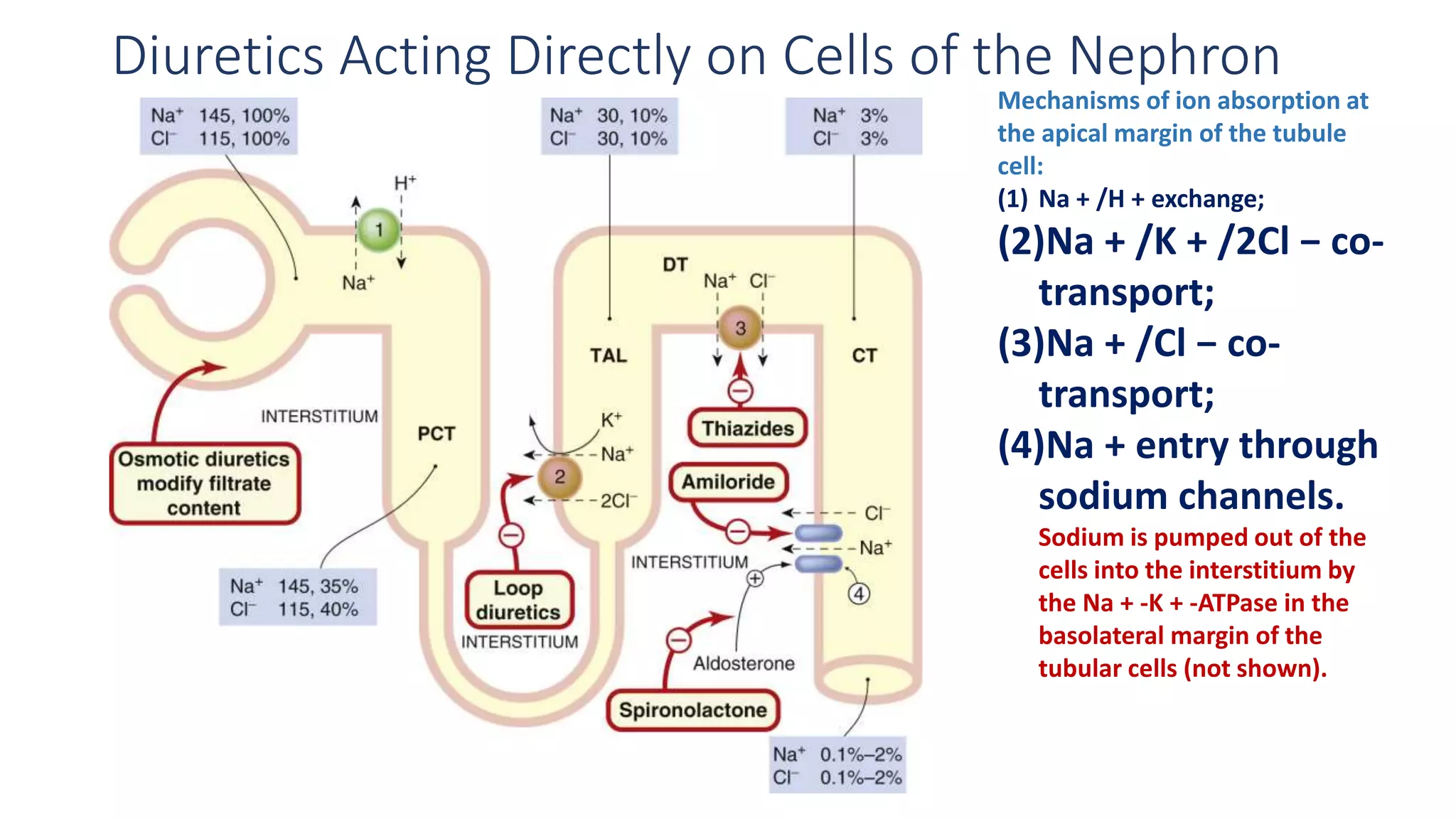
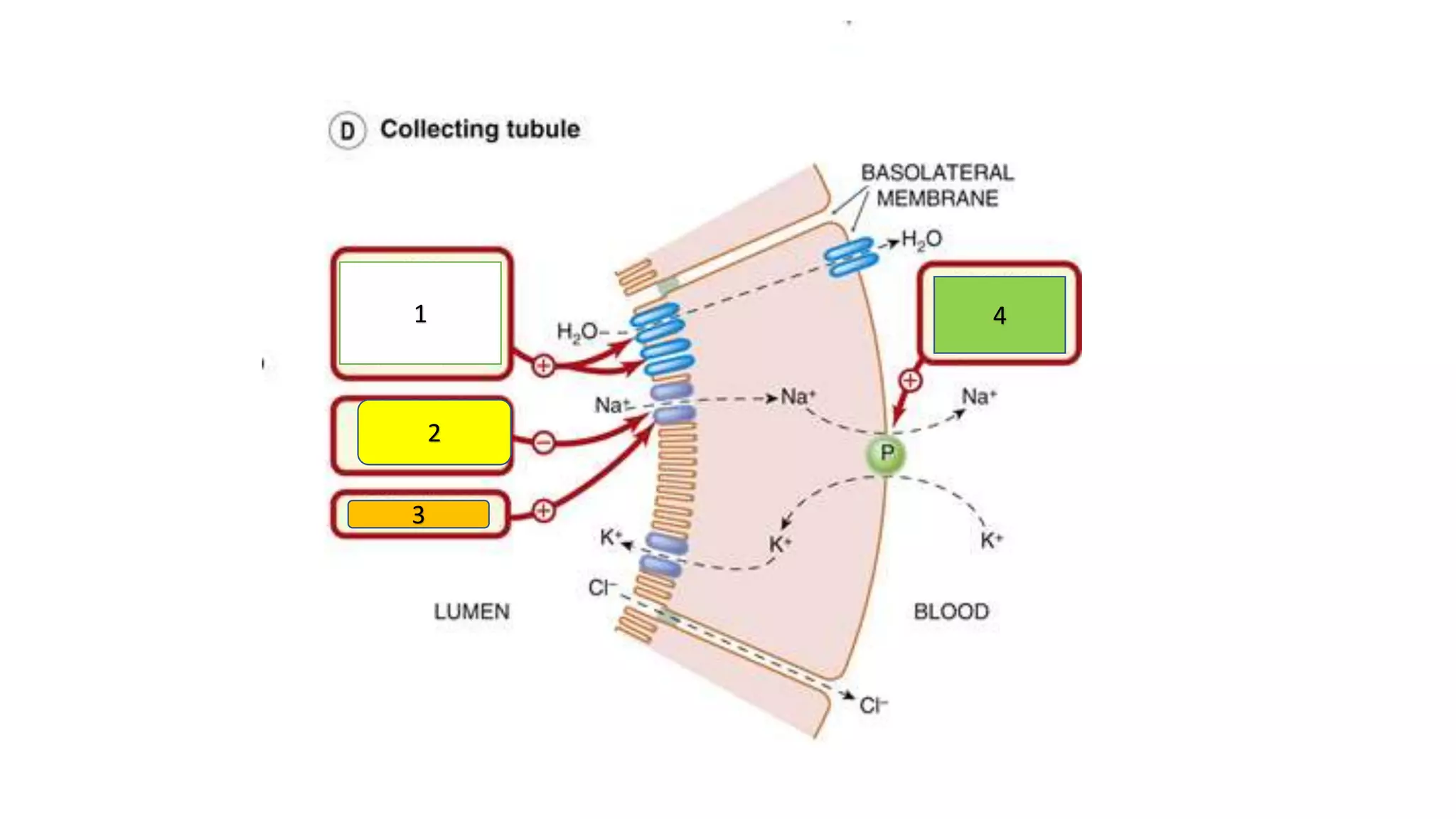
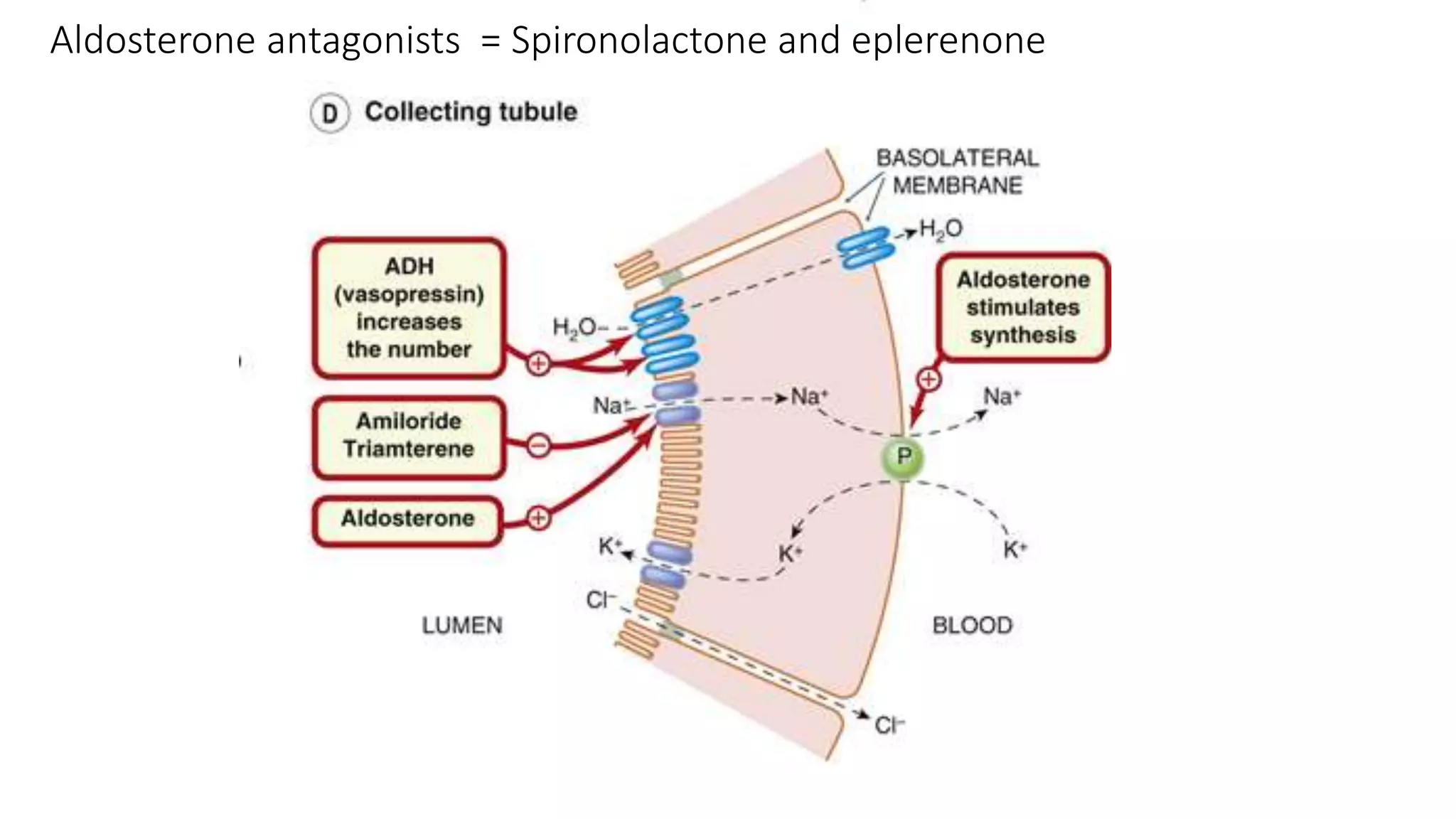
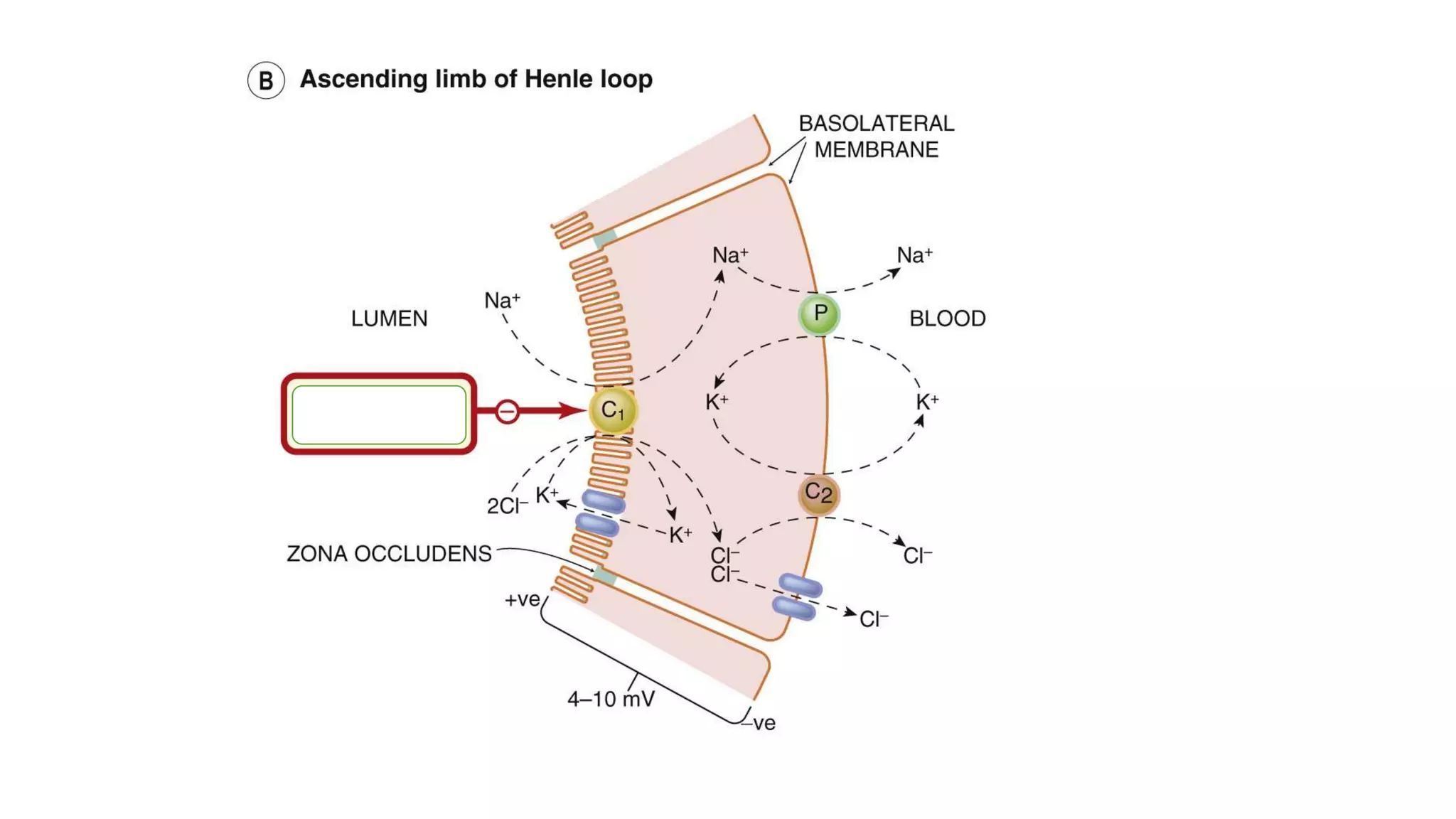
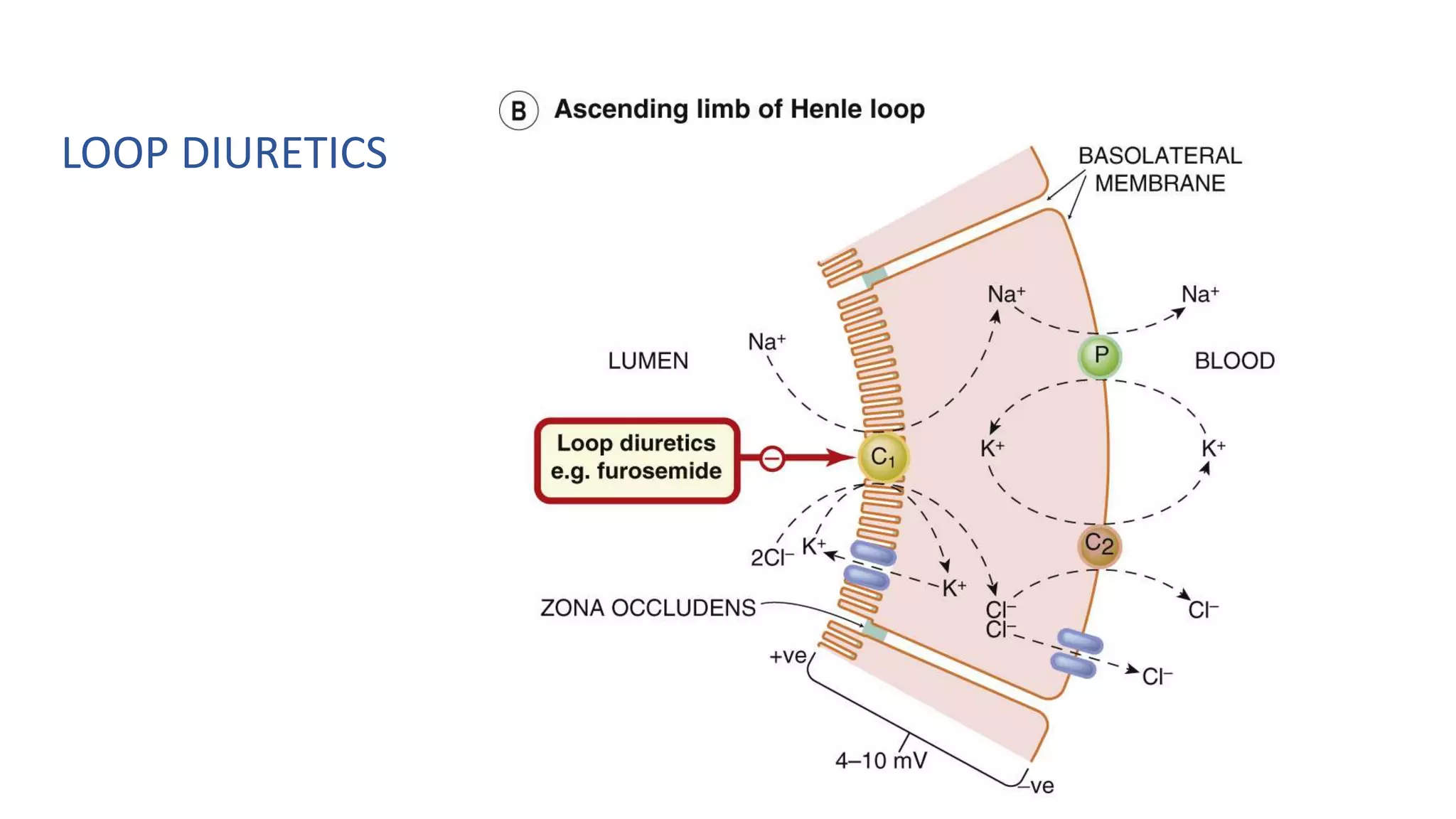
1) Loop diuretics which inhibit sodium reabsorption in the loop of Henle, causing increased excretion of sodium, chloride, and water. Their main indications include heart failure and edema.
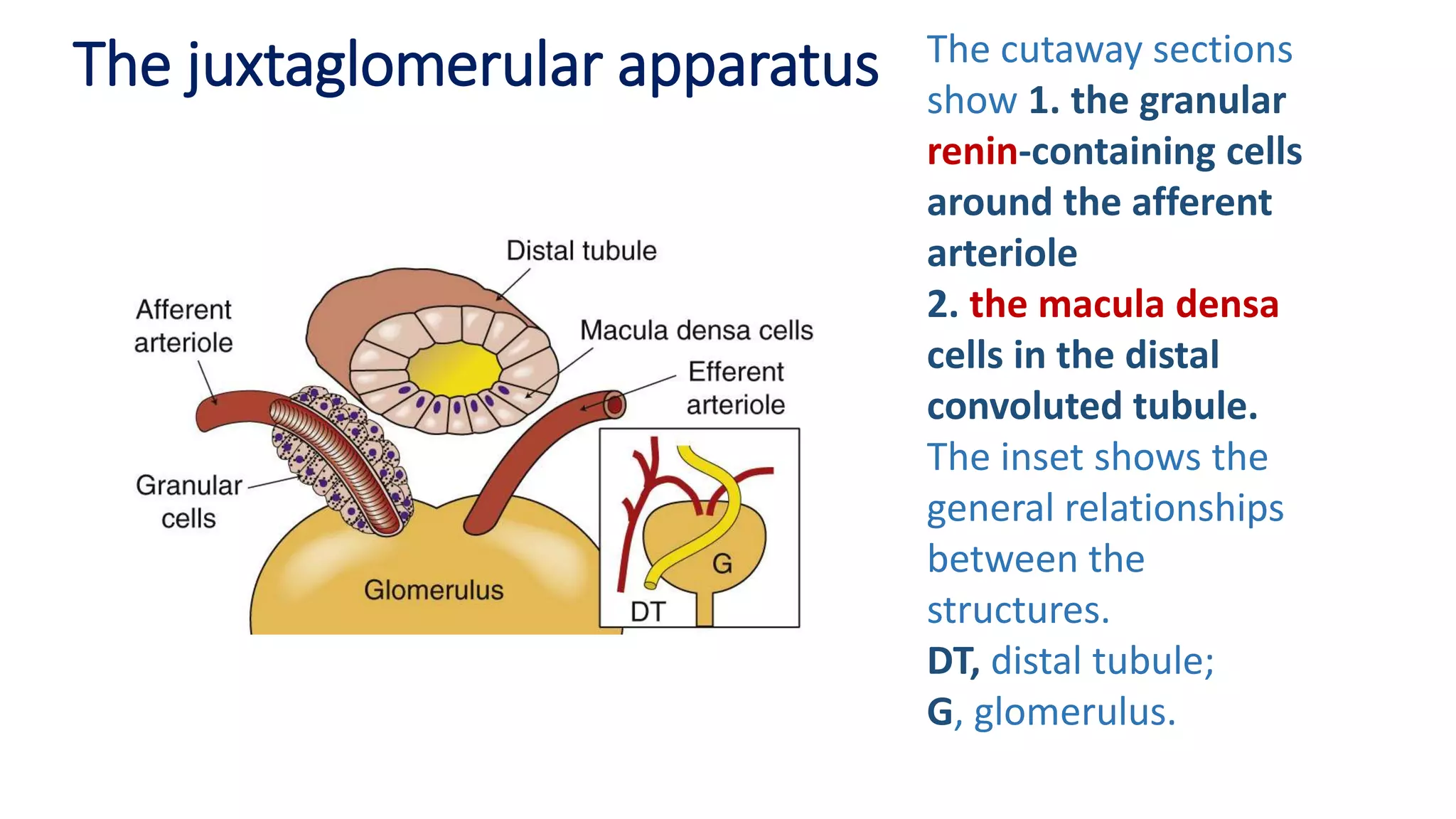
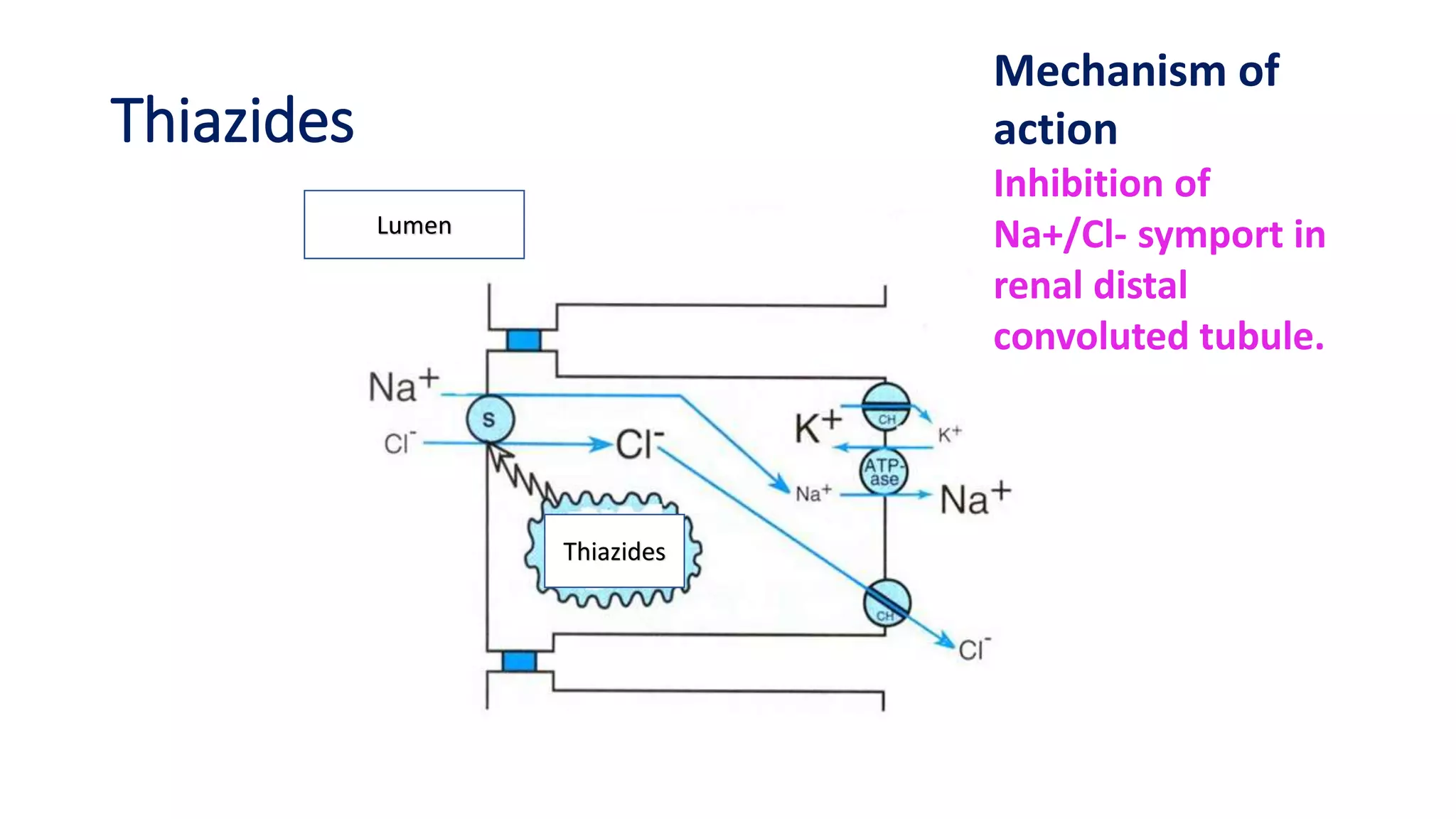
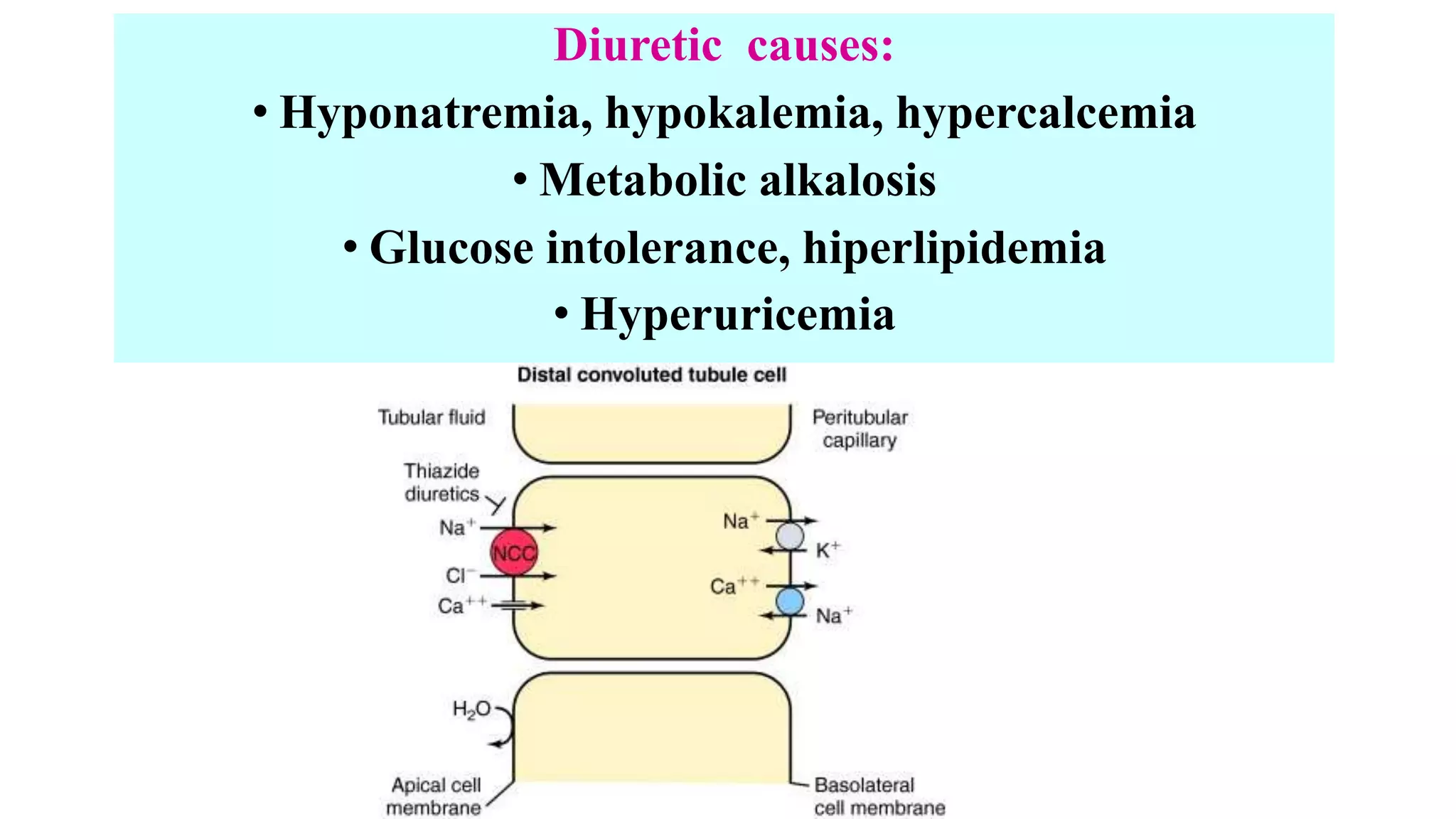
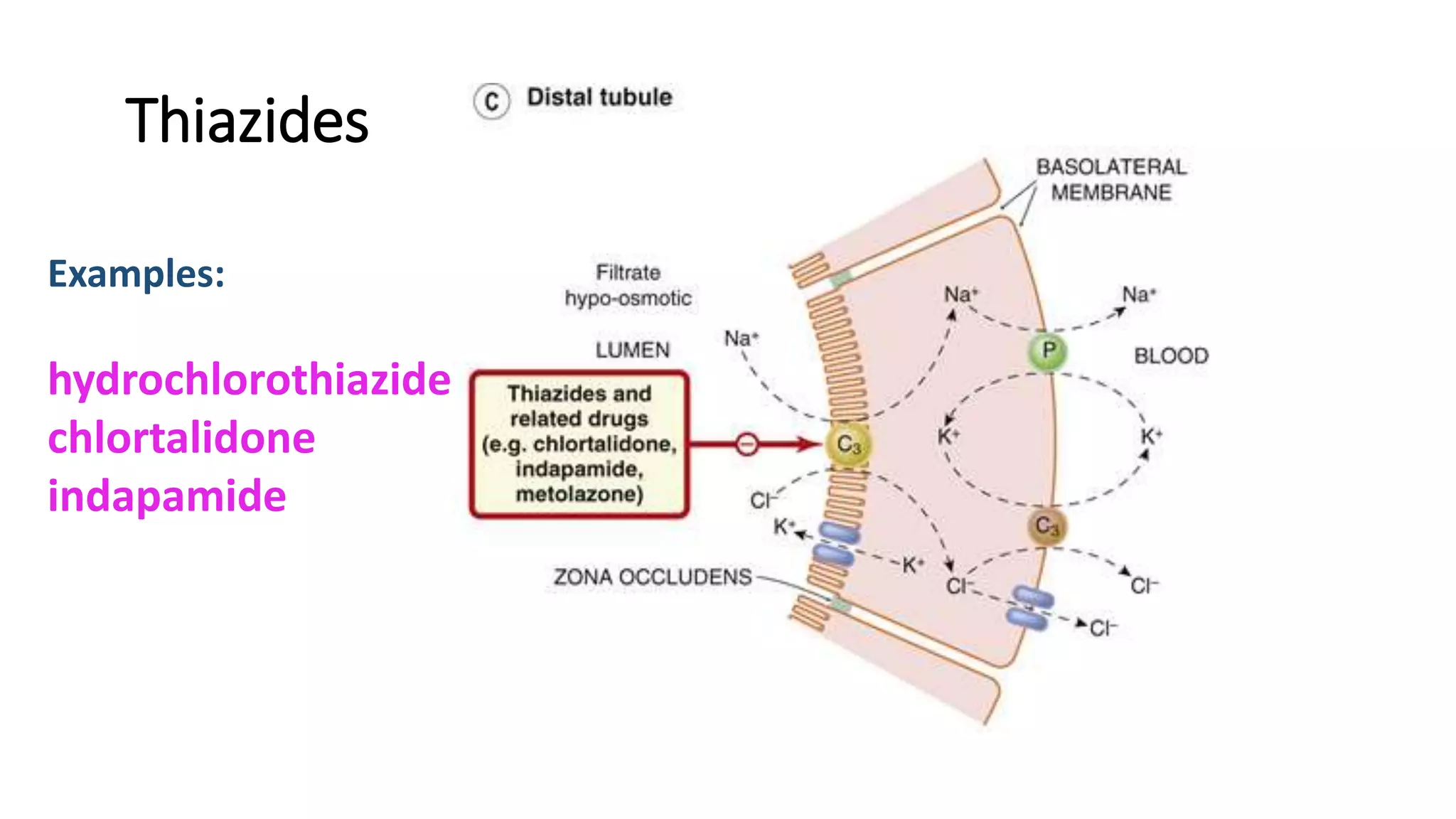
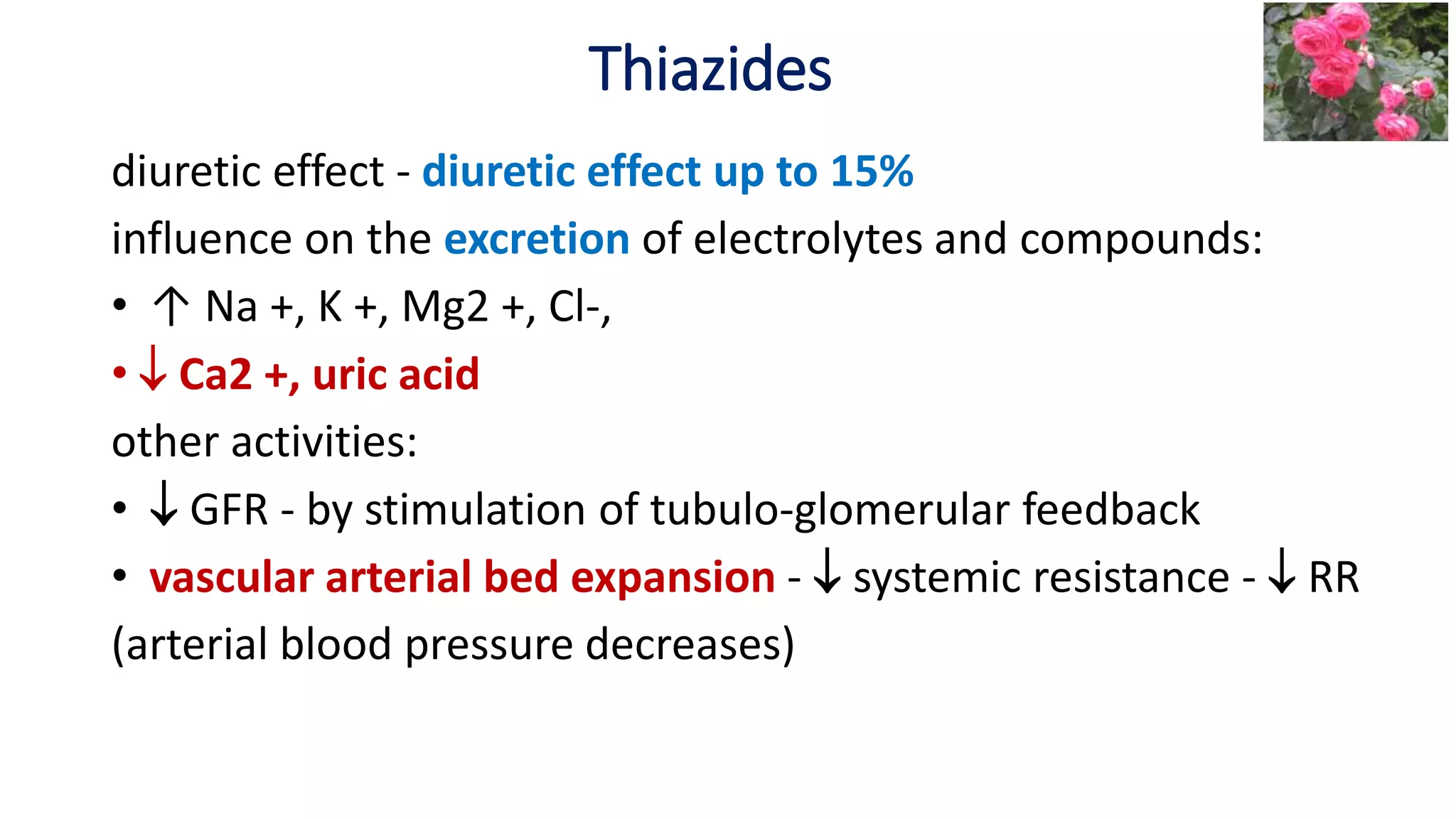
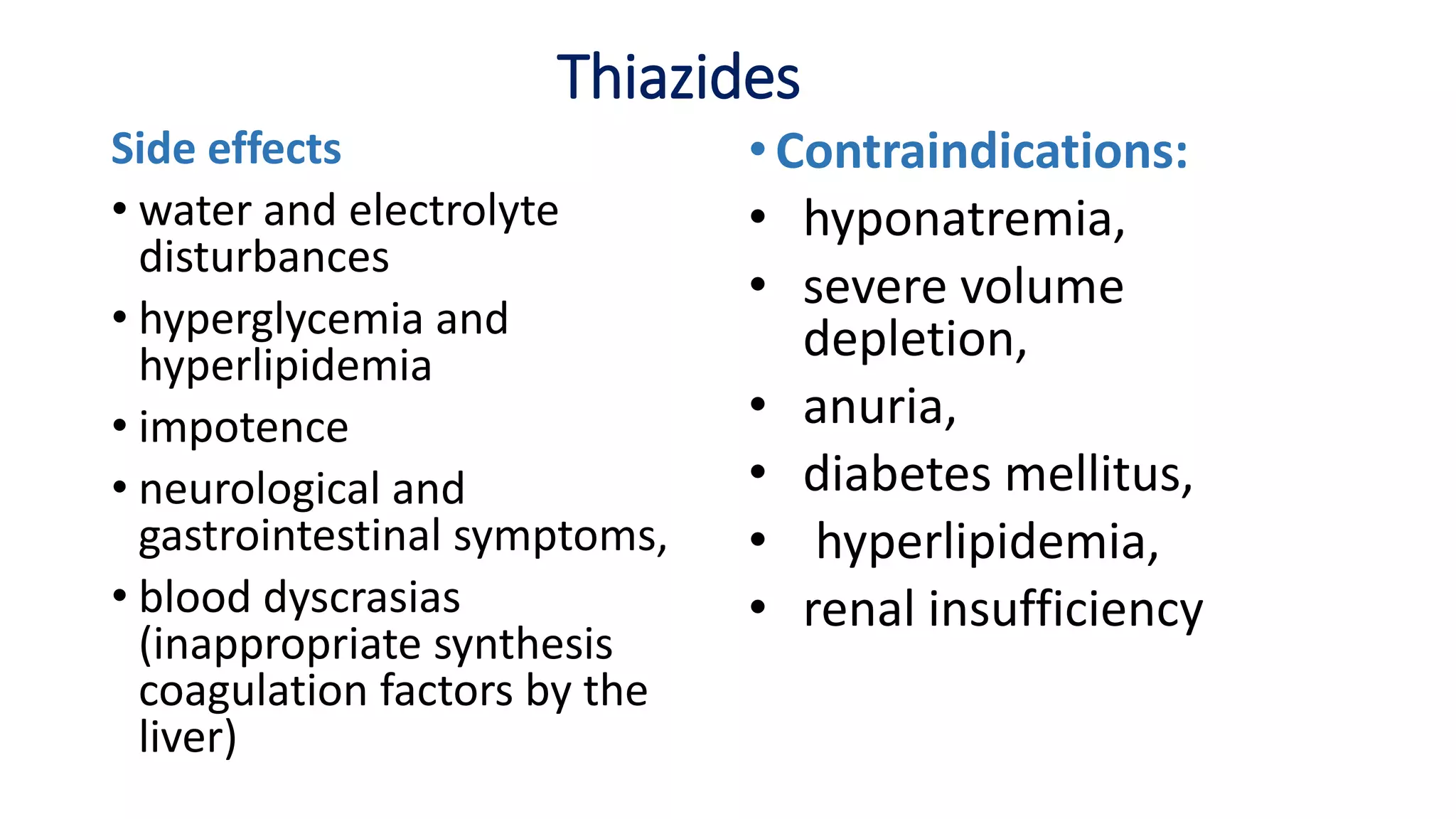
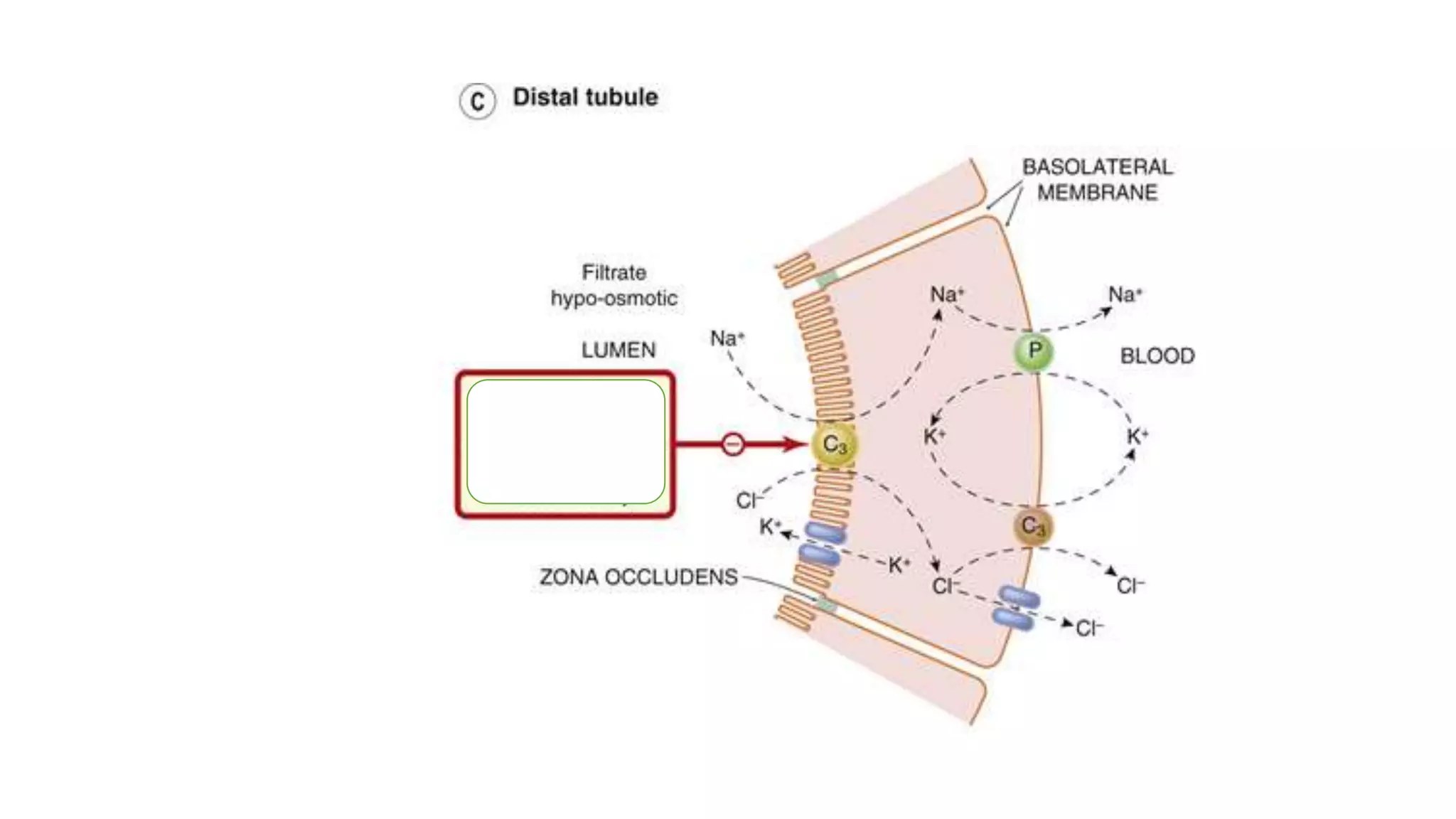
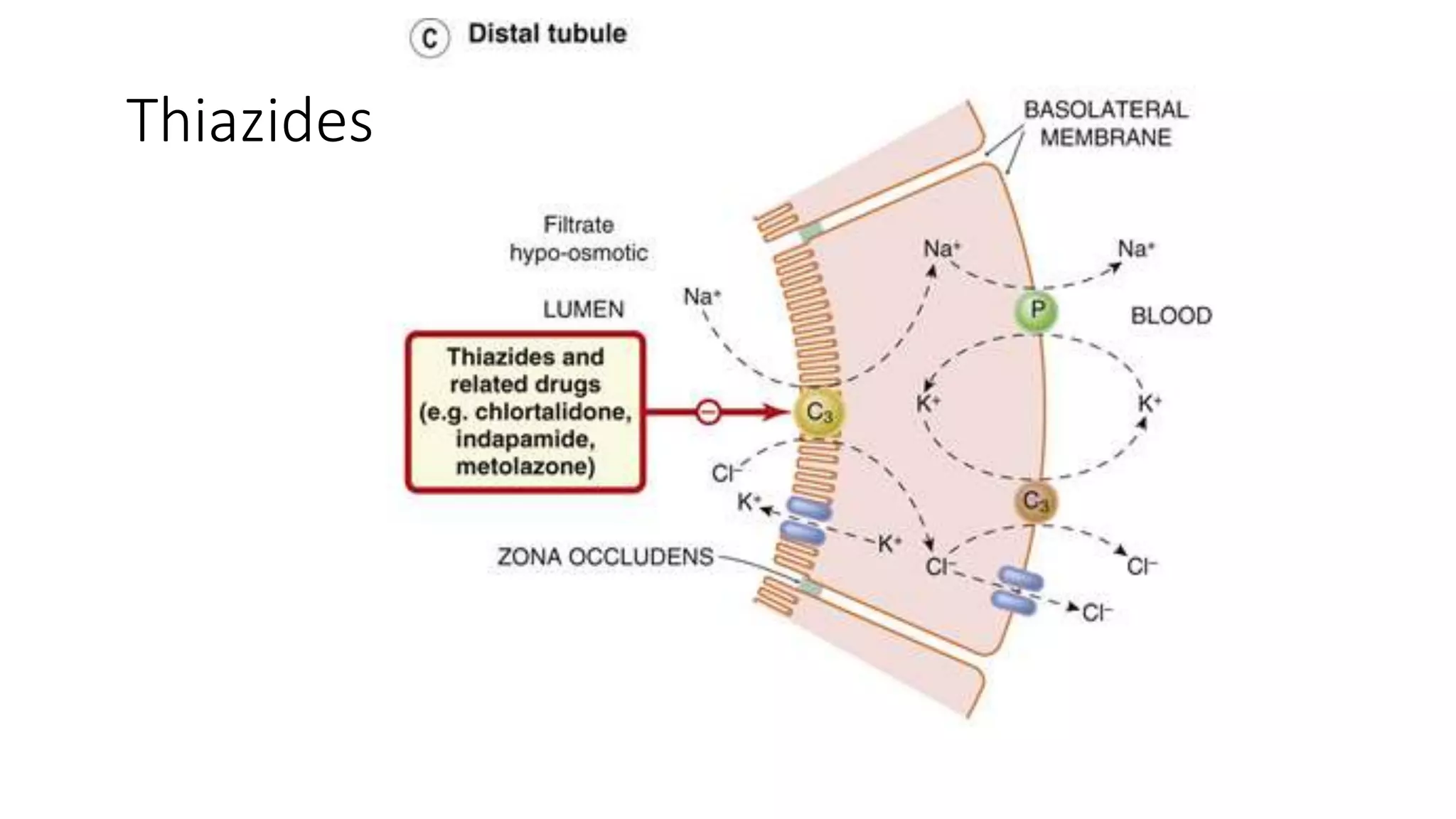
2) Thiazide diuretics which inhibit sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. They are used to treat hypertension and have fewer side effects than loop diuretics.
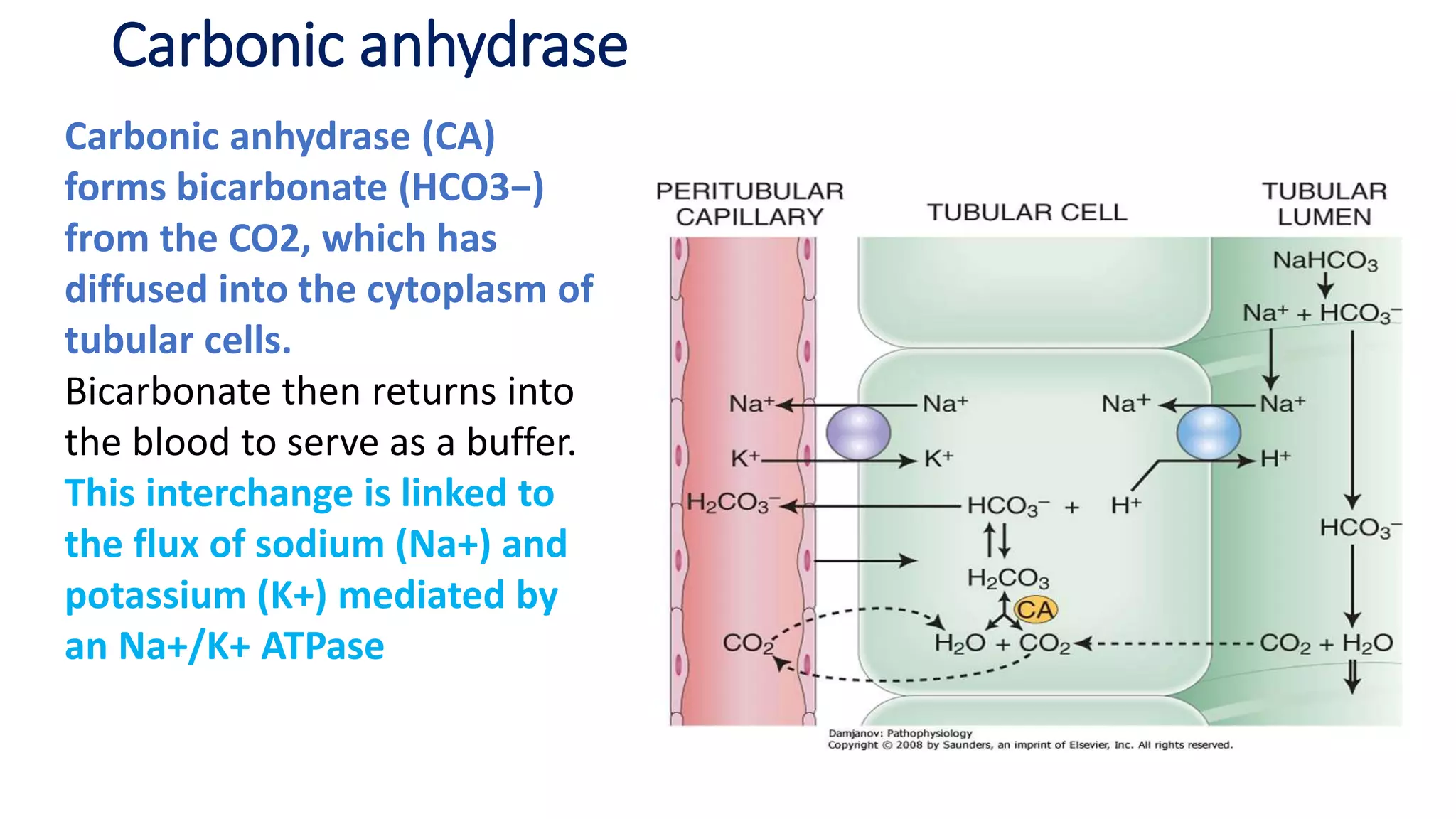
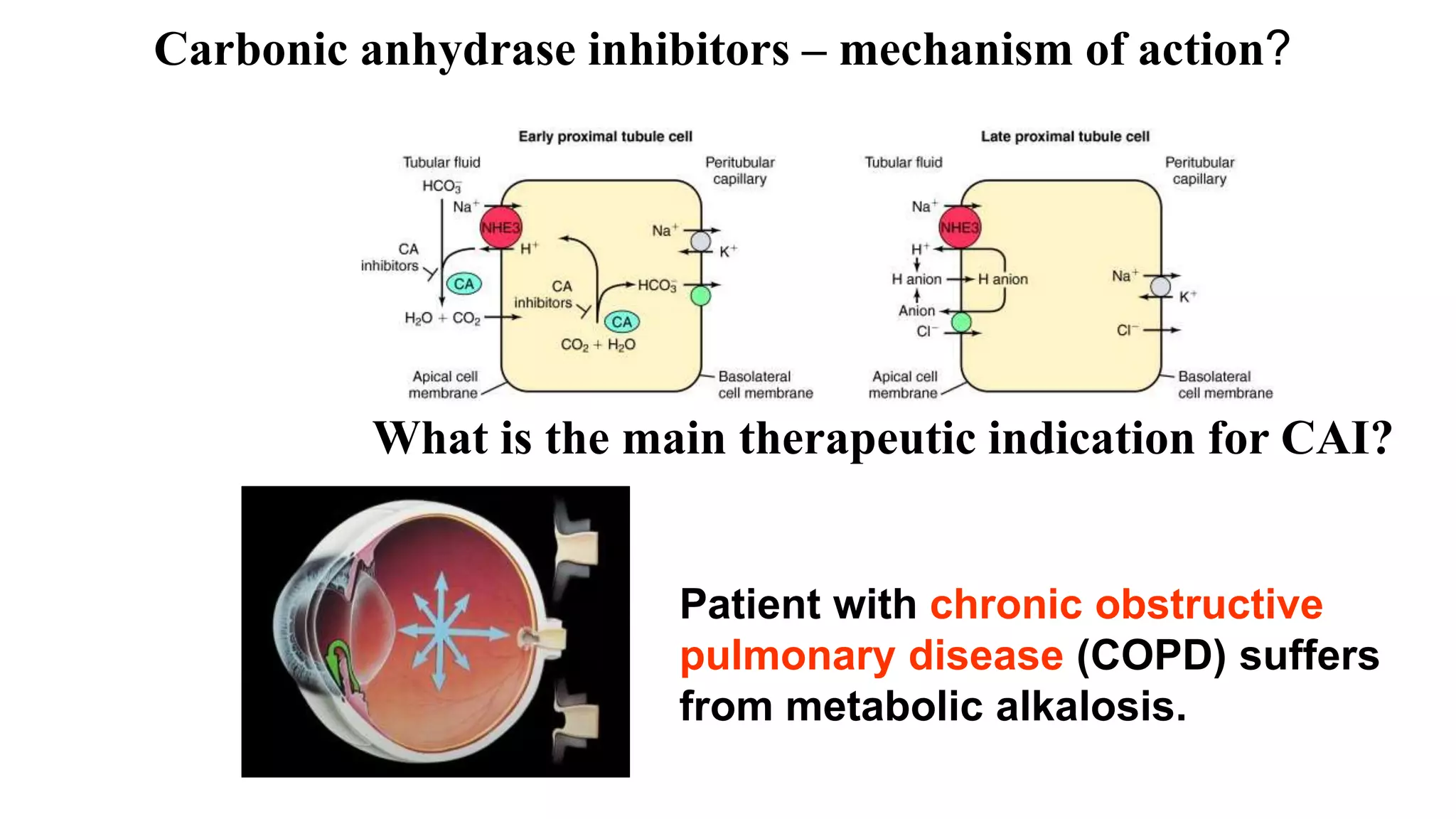
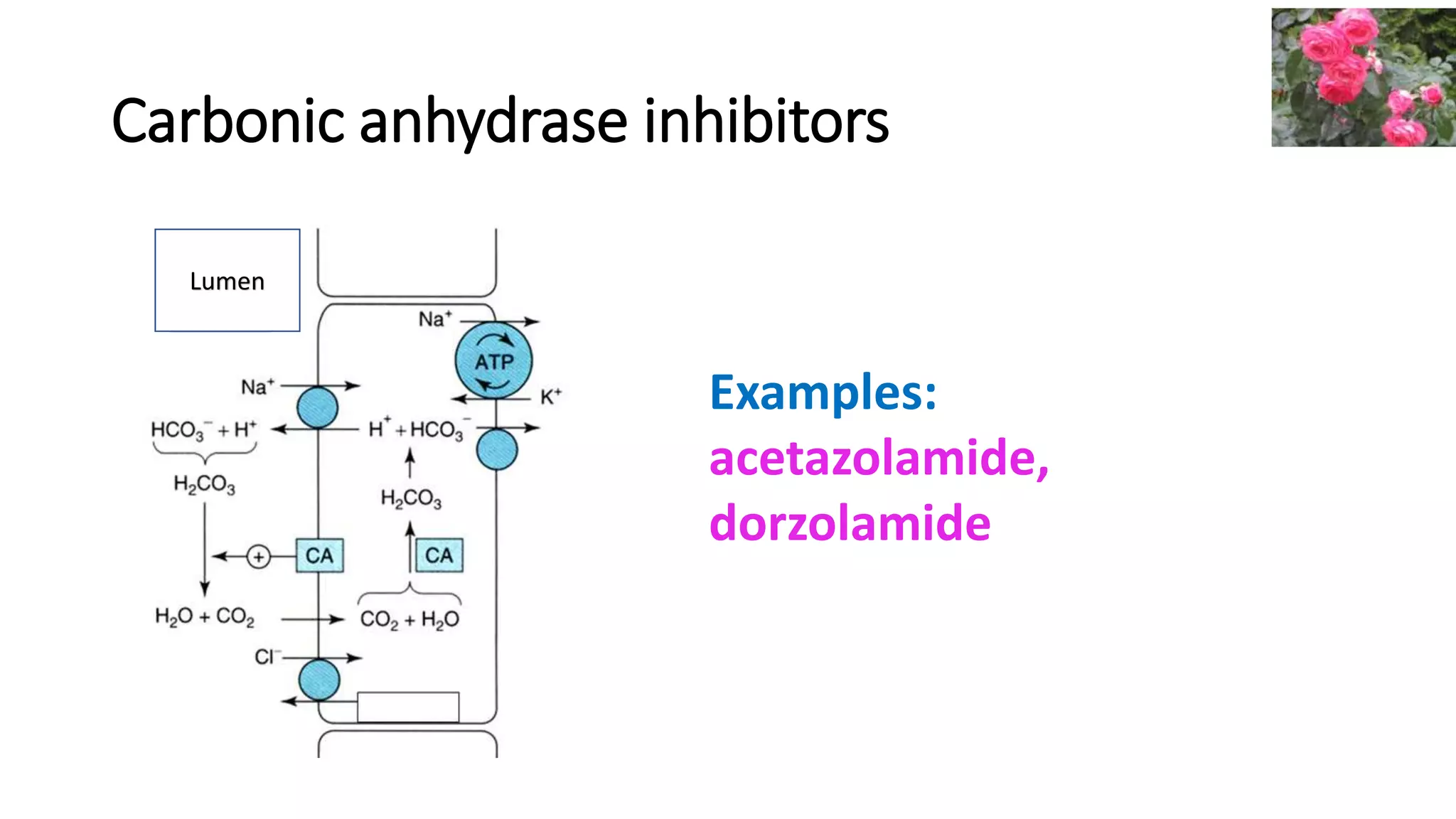
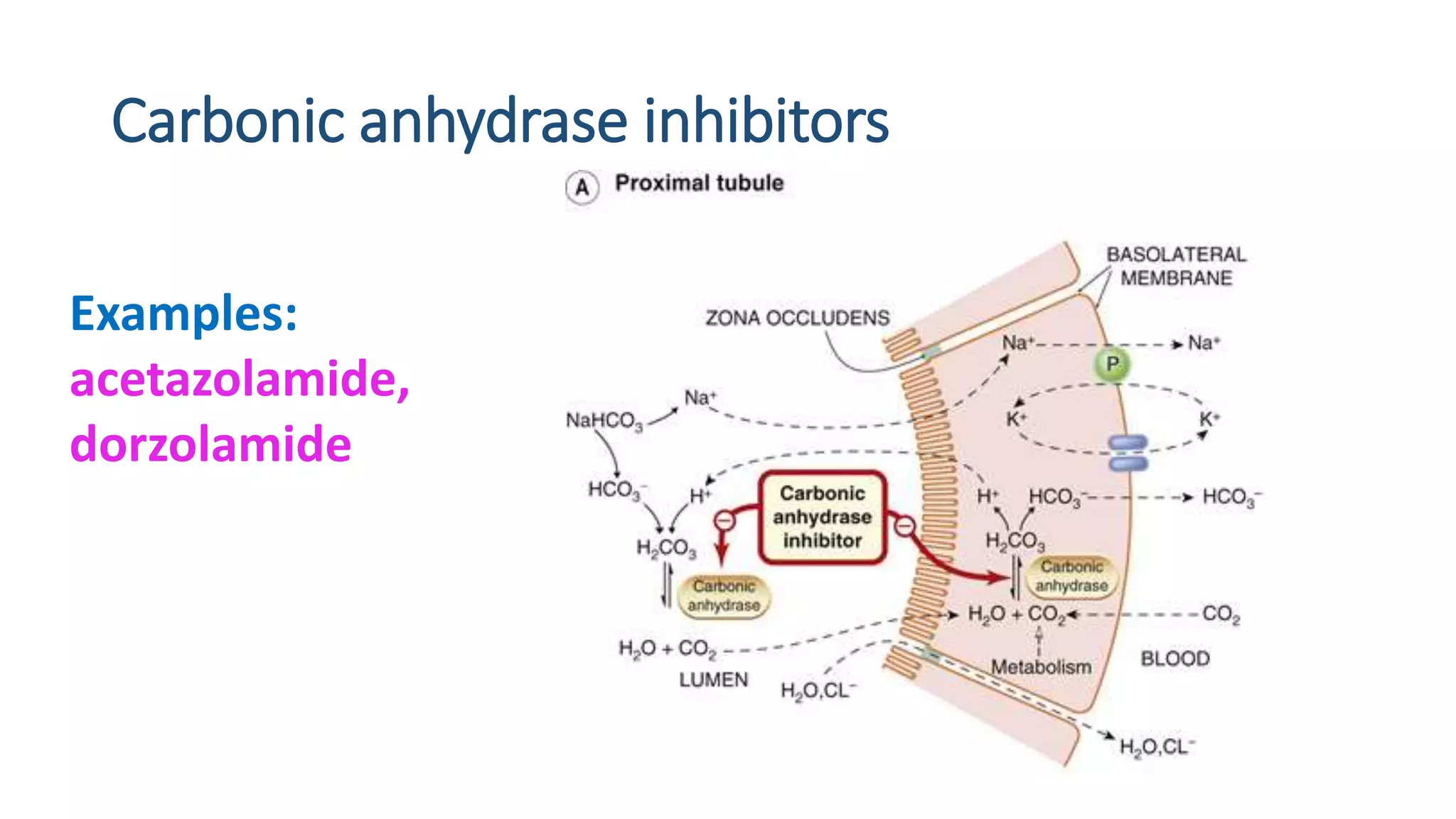
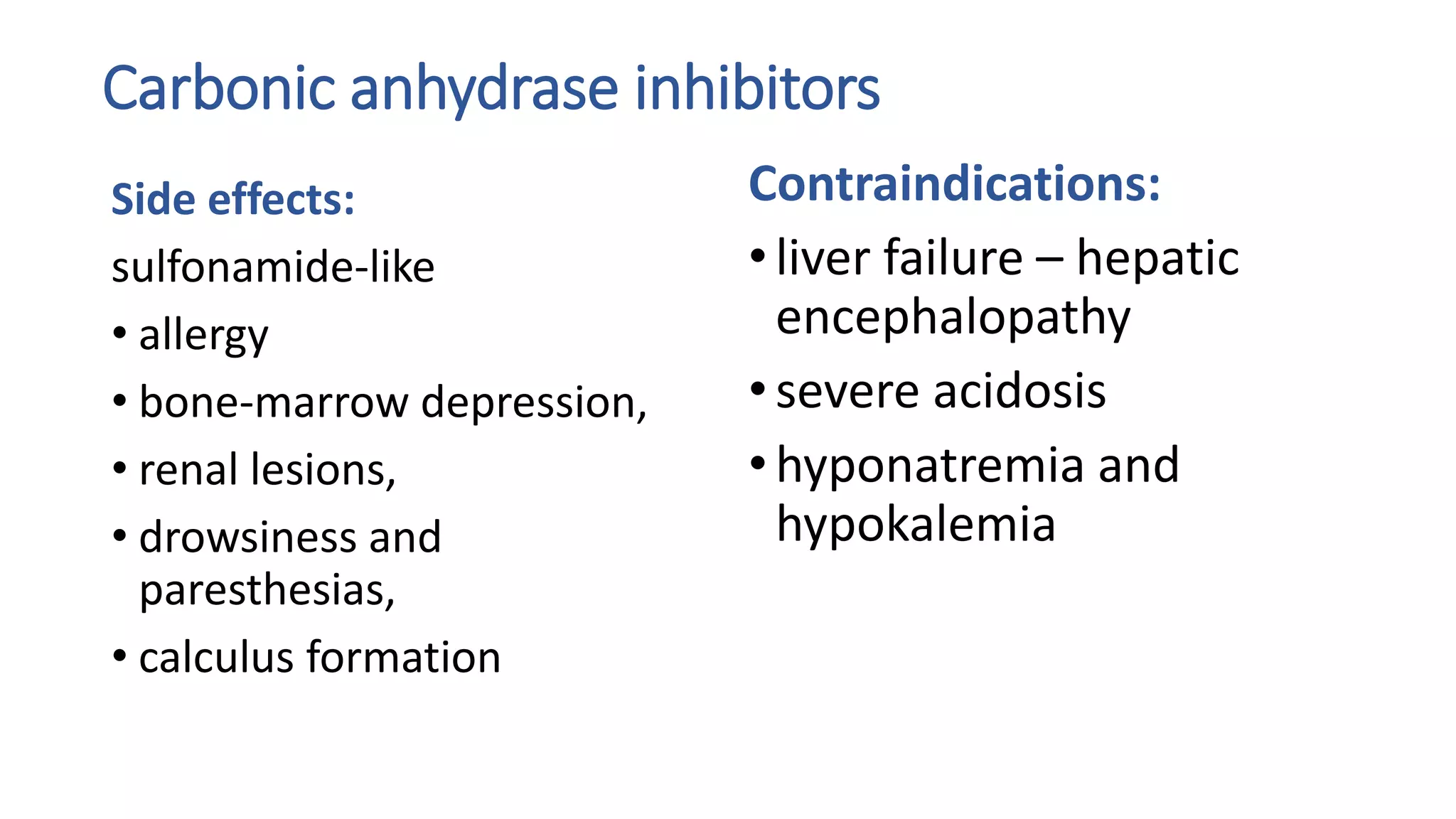
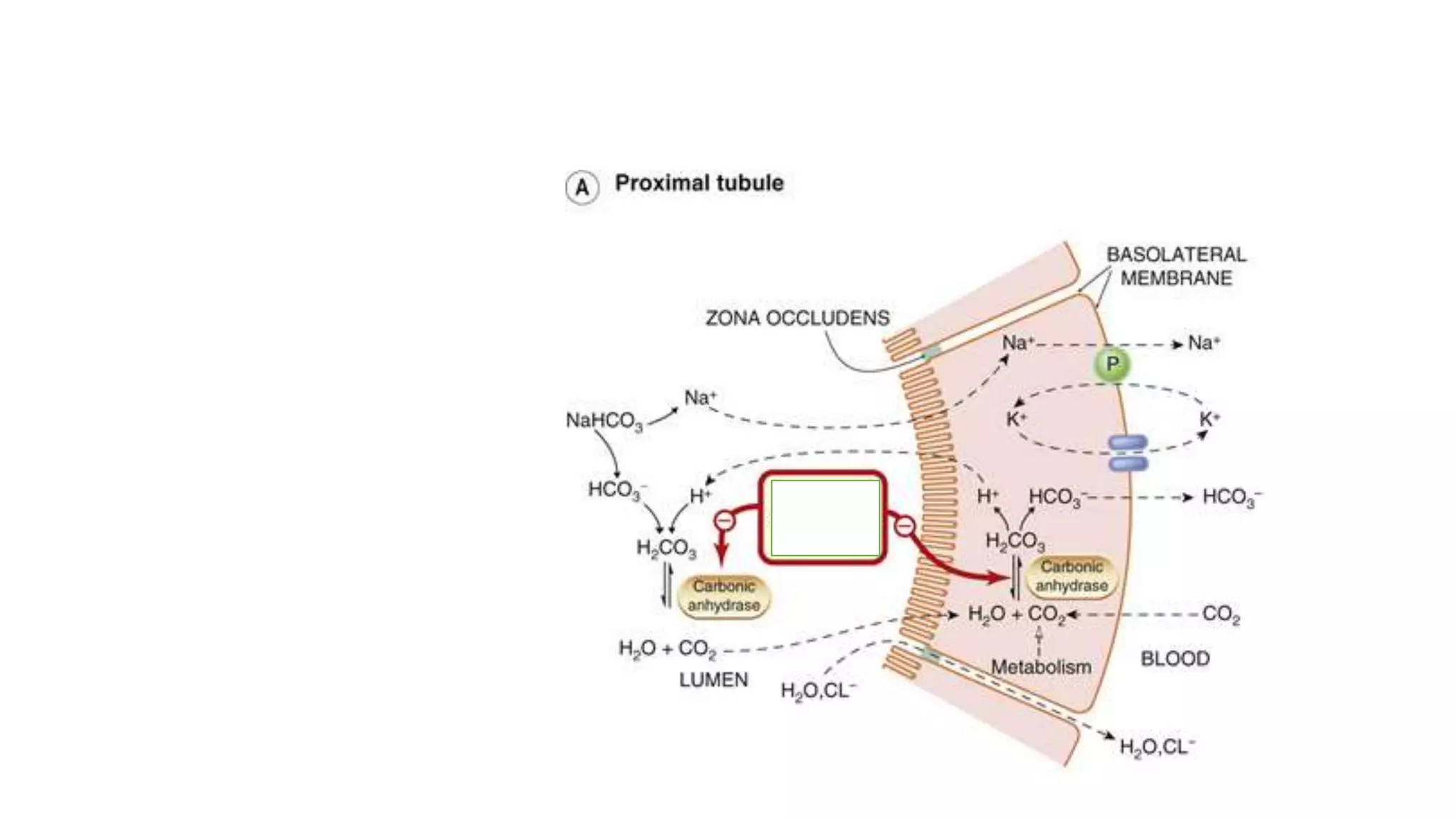
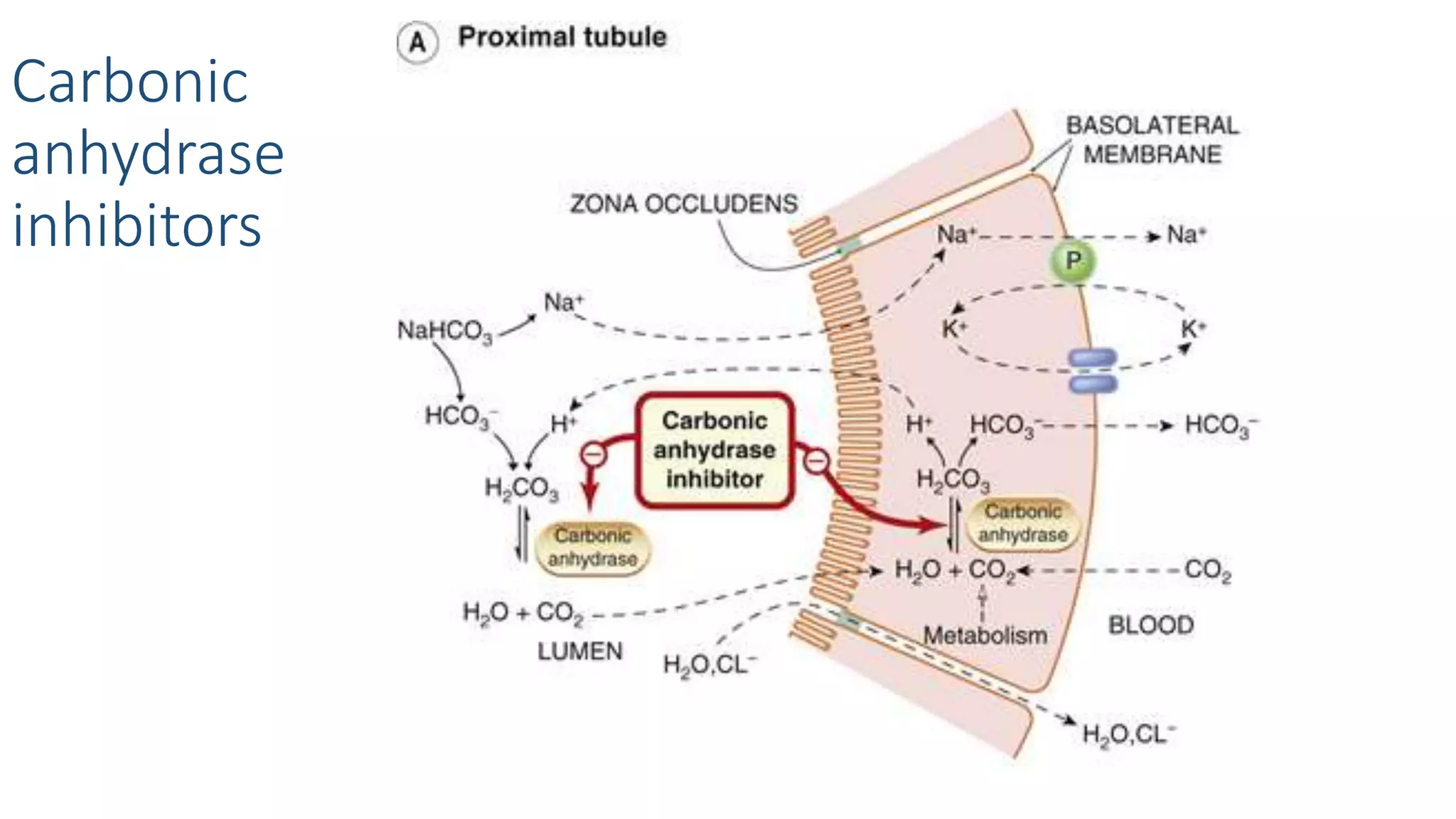
3) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors which inhibit bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal tubule, causing a metabolic acidosis. Their main use is for glaucoma.