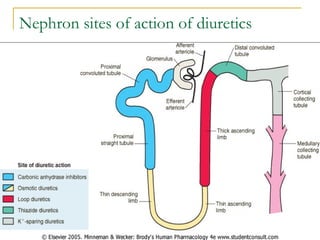
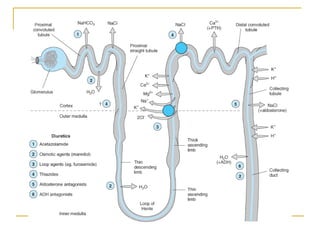
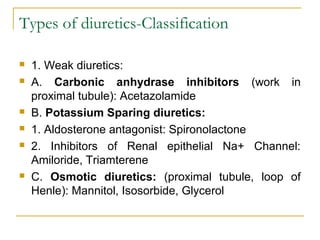
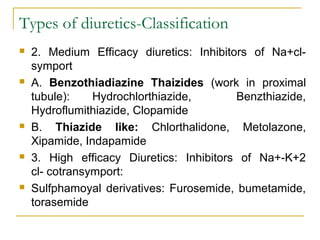
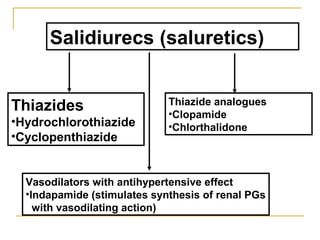
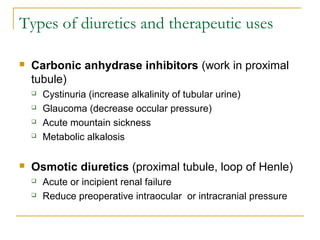
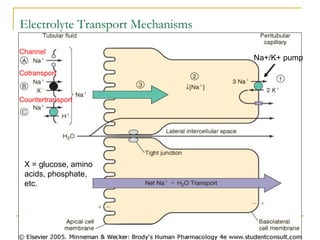
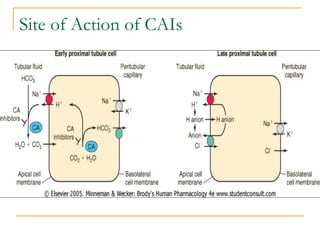
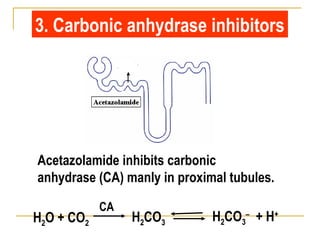
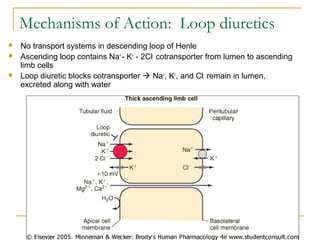
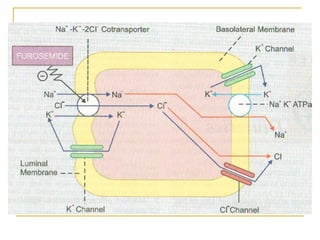
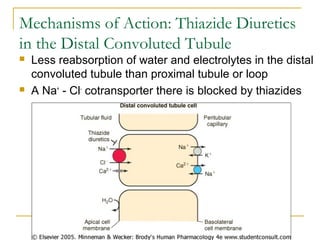
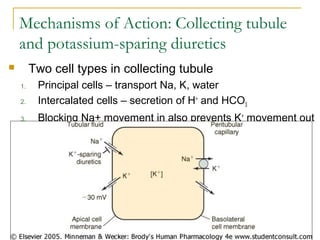
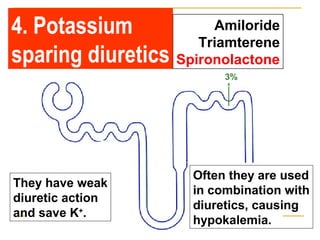
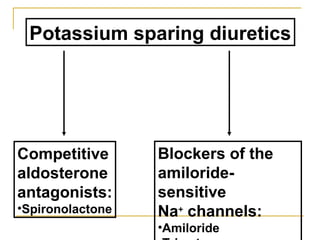
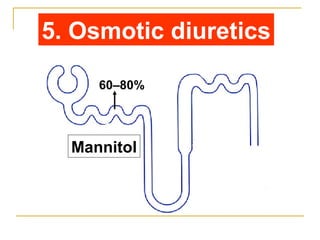
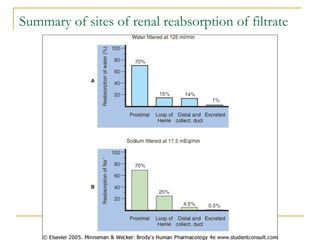
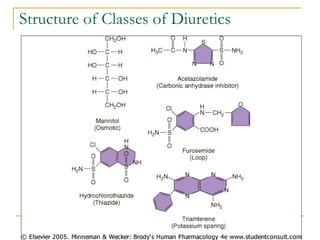
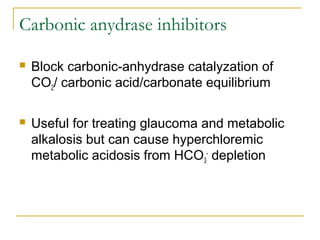
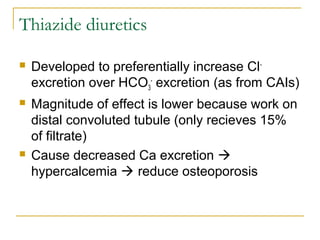
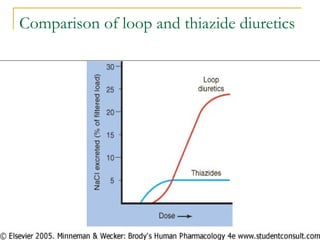
The document provides an overview of diuretics, including their mechanisms of action, classifications, and therapeutic uses. Diuretics increase the excretion of water and electrolytes, with different types affecting various renal segments and conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and renal failure. It also details the mechanisms for several classes of diuretics, including loop, thiazide, and potassium-sparing agents, as well as osmotic diuretics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.