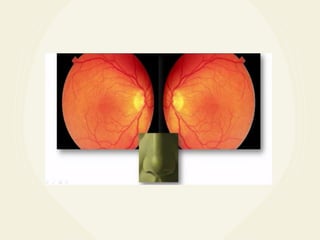
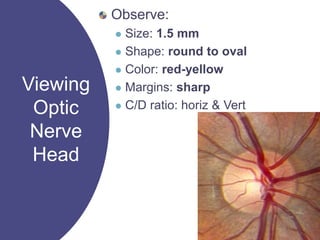
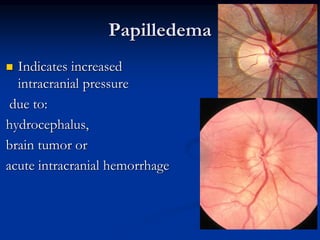
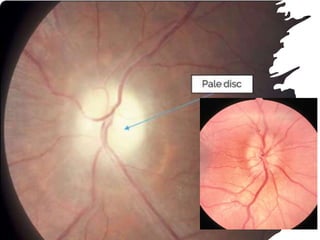
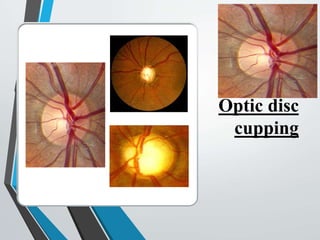
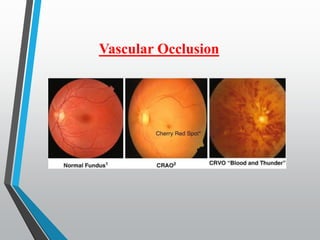
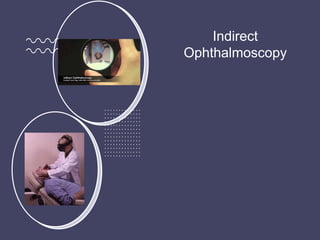
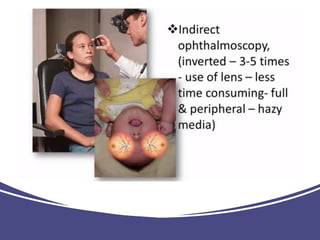
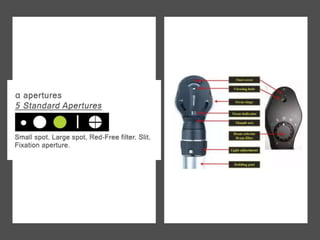
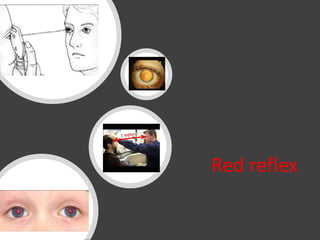
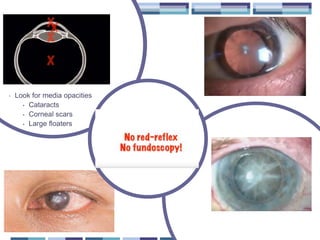
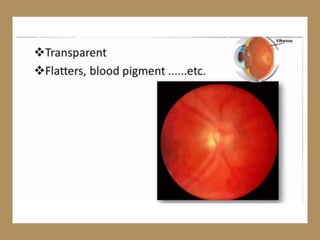
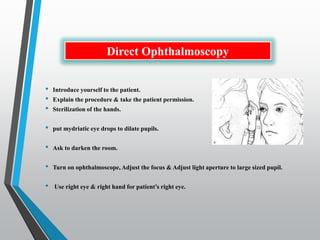
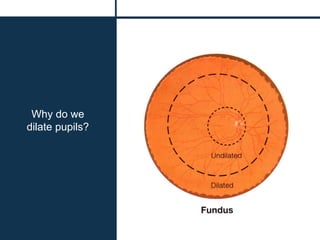
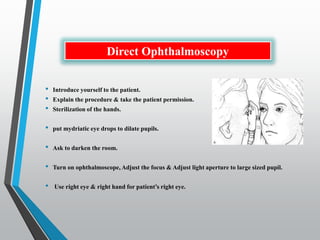
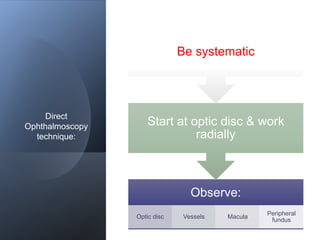
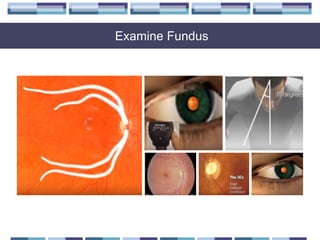
The document discusses techniques for examining the optic nerve head using direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy, highlighting the normal characteristics of the optic nerve and methods for identifying potential issues like papilledema. It also outlines preparation steps for conducting a fundus examination, including patient interaction and settings adjustments. Key techniques and contraindications for effective direct ophthalmoscopy are also mentioned.