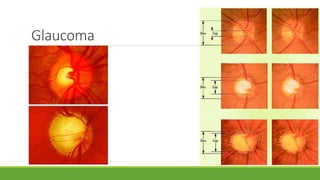
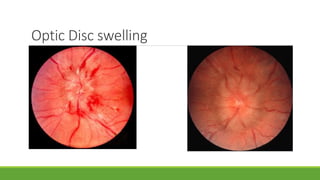
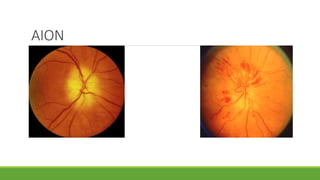
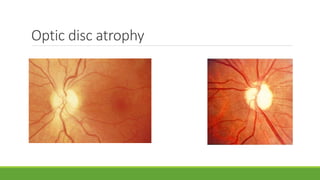
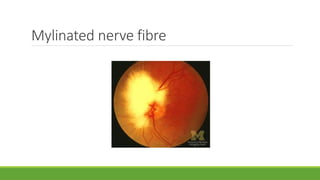
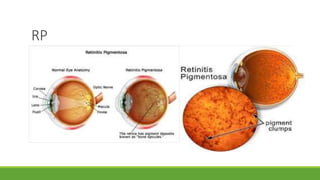
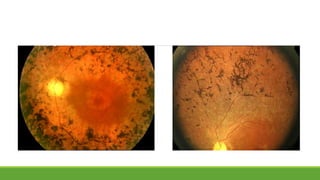
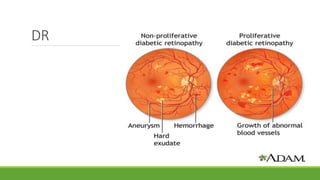
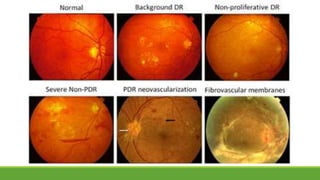
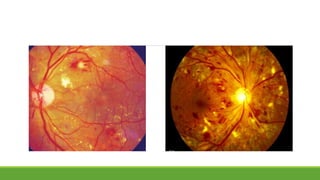
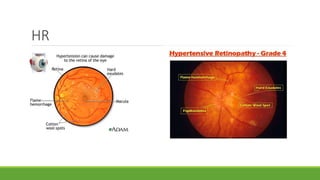
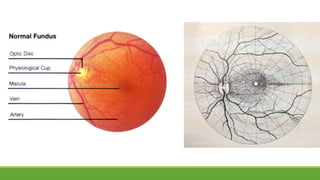
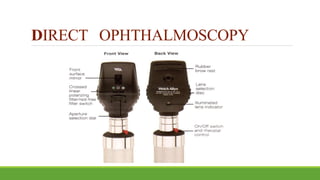
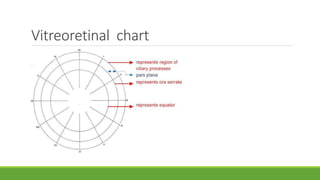
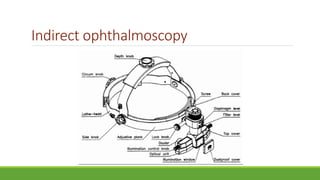
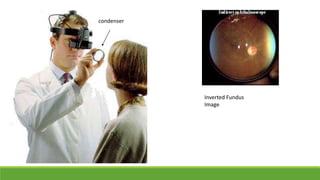
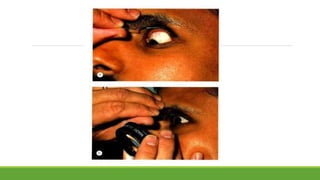
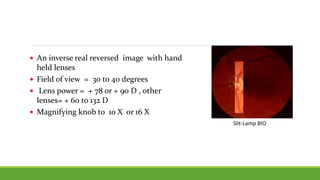
This document discusses different methods for examining the fundus of the eye, including direct ophthalmoscopy, indirect ophthalmoscopy, and indirect slit lamp biomicroscopy. It provides details on how each method works, including magnification, field of view, advantages, and disadvantages. Key structures that can be observed during fundus examination are also described, such as the optic disc, blood vessels, macula, and signs of common eye conditions like glaucoma, optic nerve diseases, retinal problems, and diabetes-related changes.



![PUPILLARY DILATION
Combination of phenylephrine [2.5 %] &
tropicamide [1 %]
then eyes closed
Dilation attained = 15-30 min
Normal reactivity = 4 - 8 hrs
Conditions which to avoid : iris supported lens
shallow AC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundusexamination-170813095622/85/Fundus-examination-5-320.jpg)








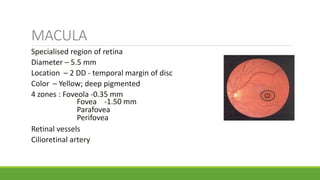
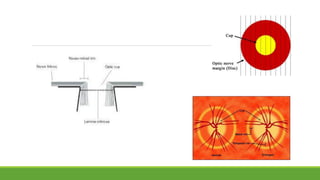
![Optic disc
DISC:
DIAMETER – 1.5mm [1 disc diameter]
COLOR – Pale pink
SHAPE – Circular
EDGES – Regular
TERMINATION OF ALL
LAYERS EXCEPT NFL
CUP: C/D ratio – 0.3 to 0.4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundusexamination-170813095622/85/Fundus-examination-22-320.jpg)