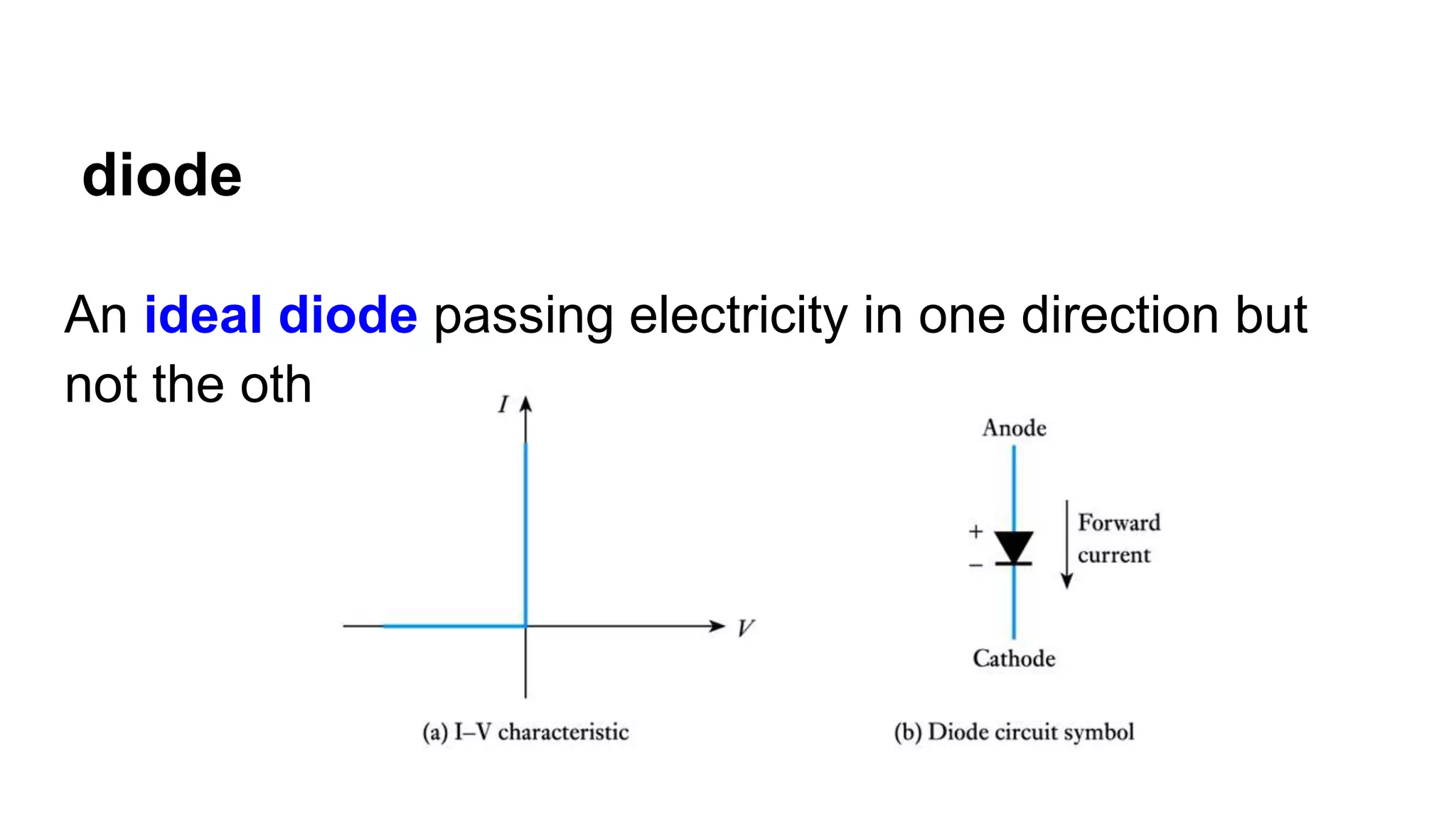
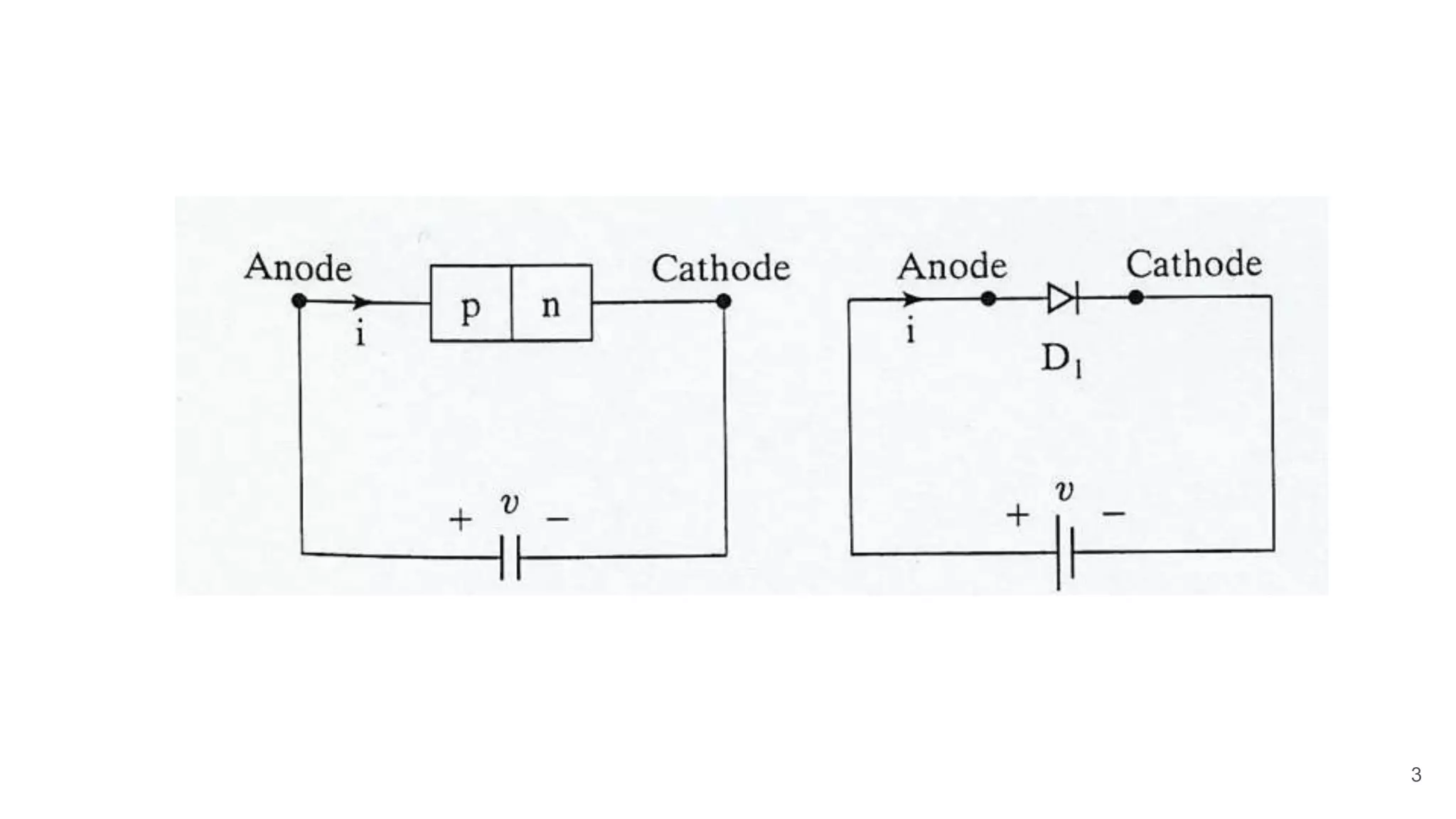
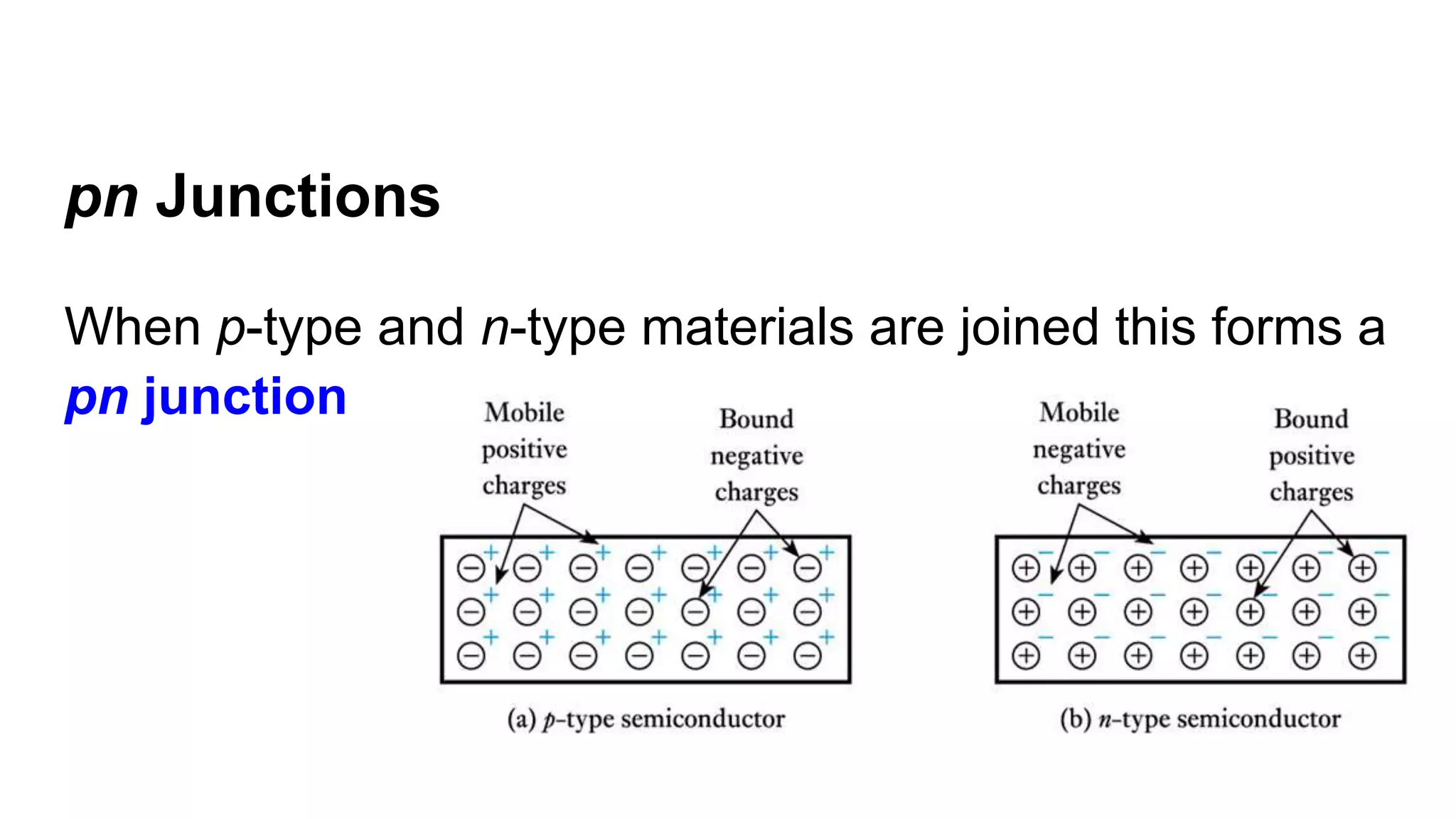
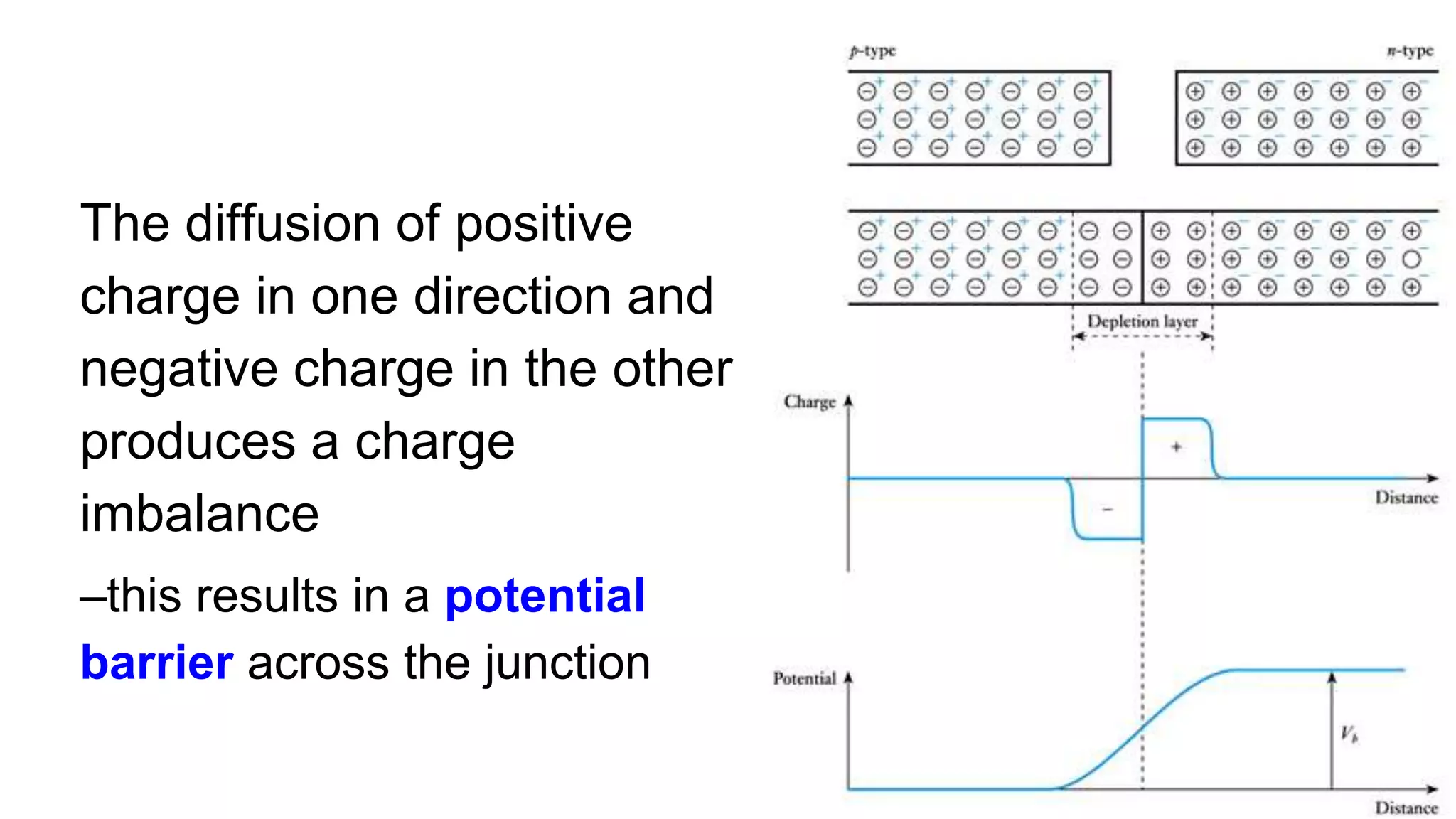
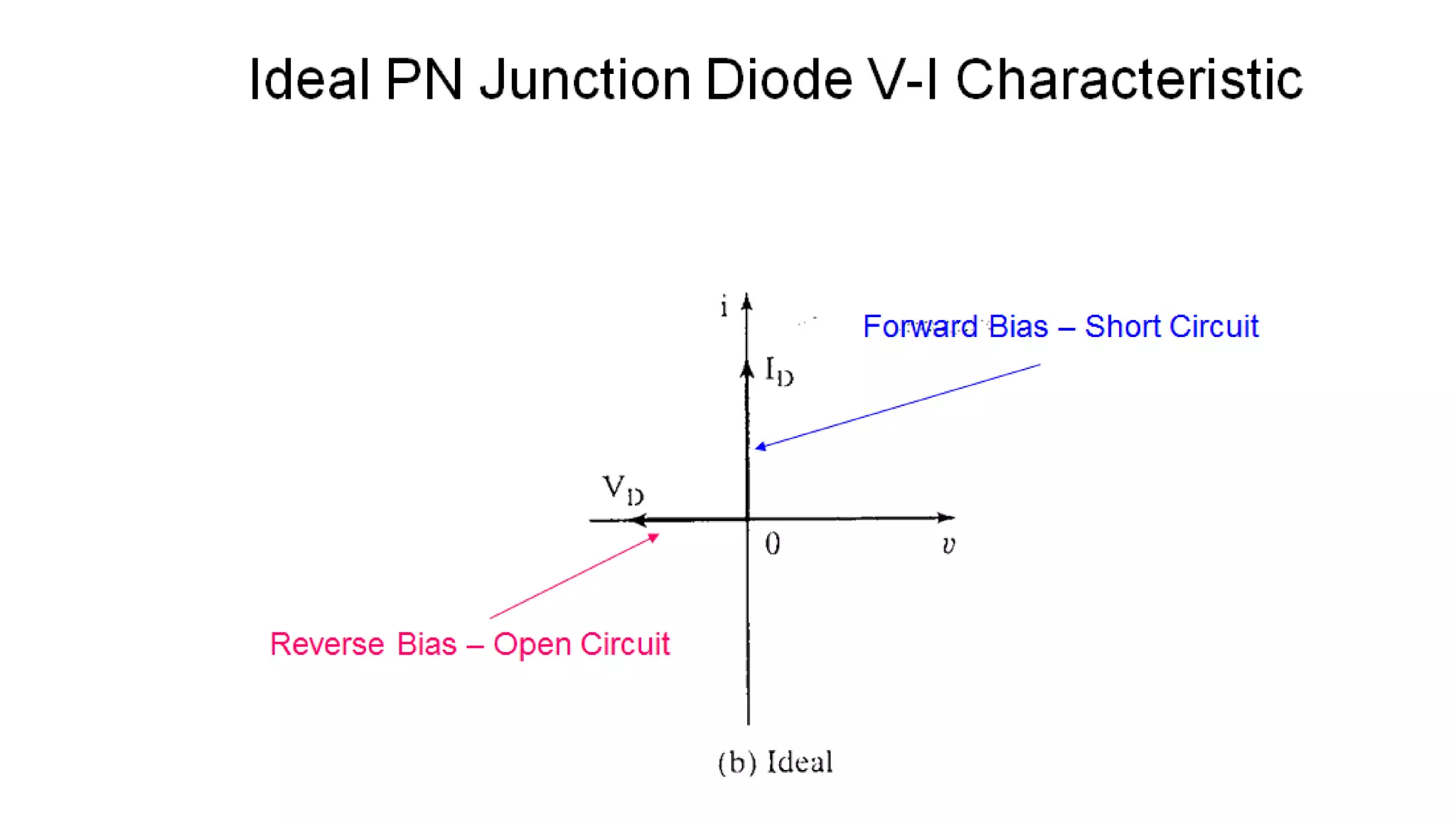
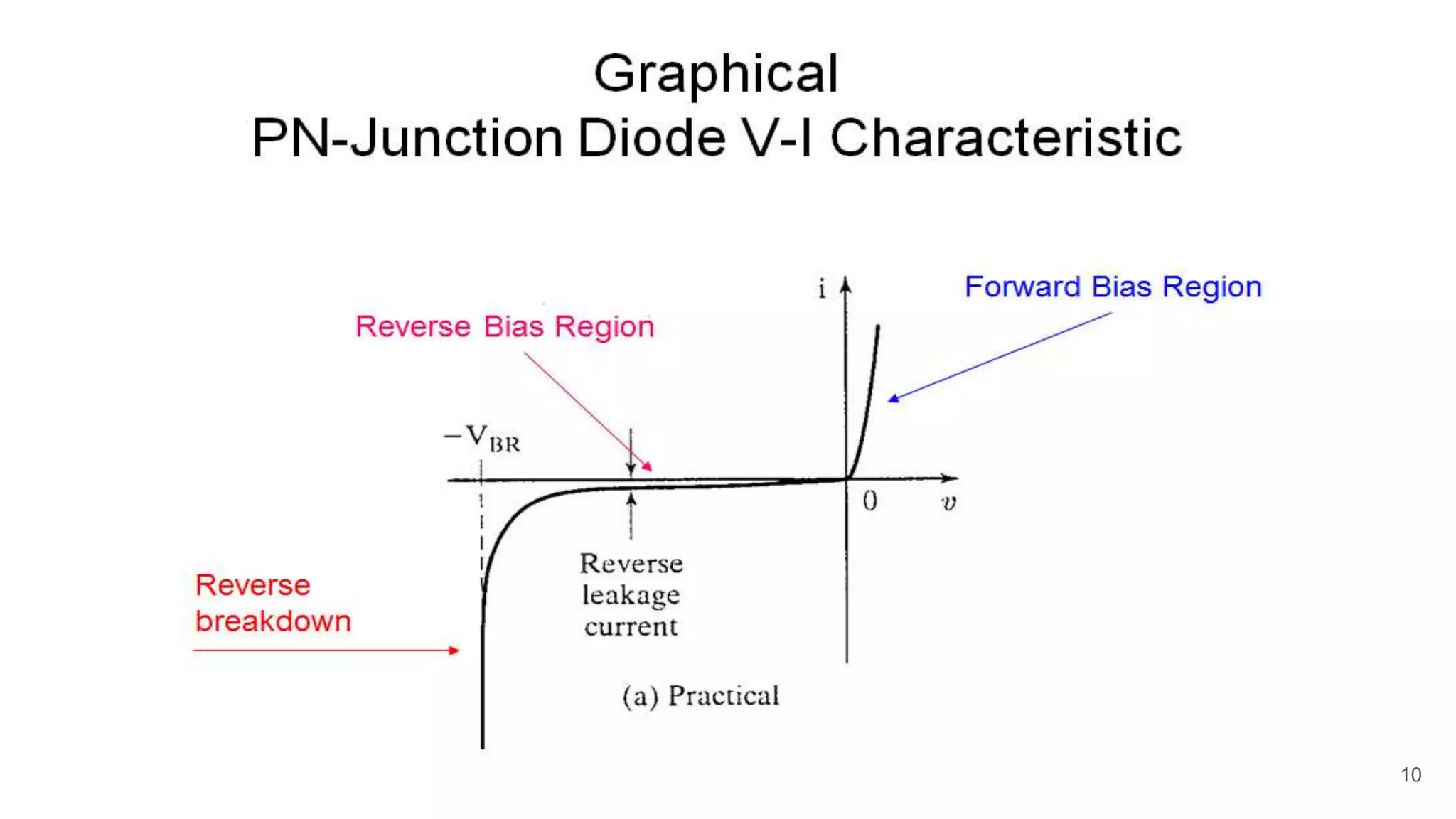
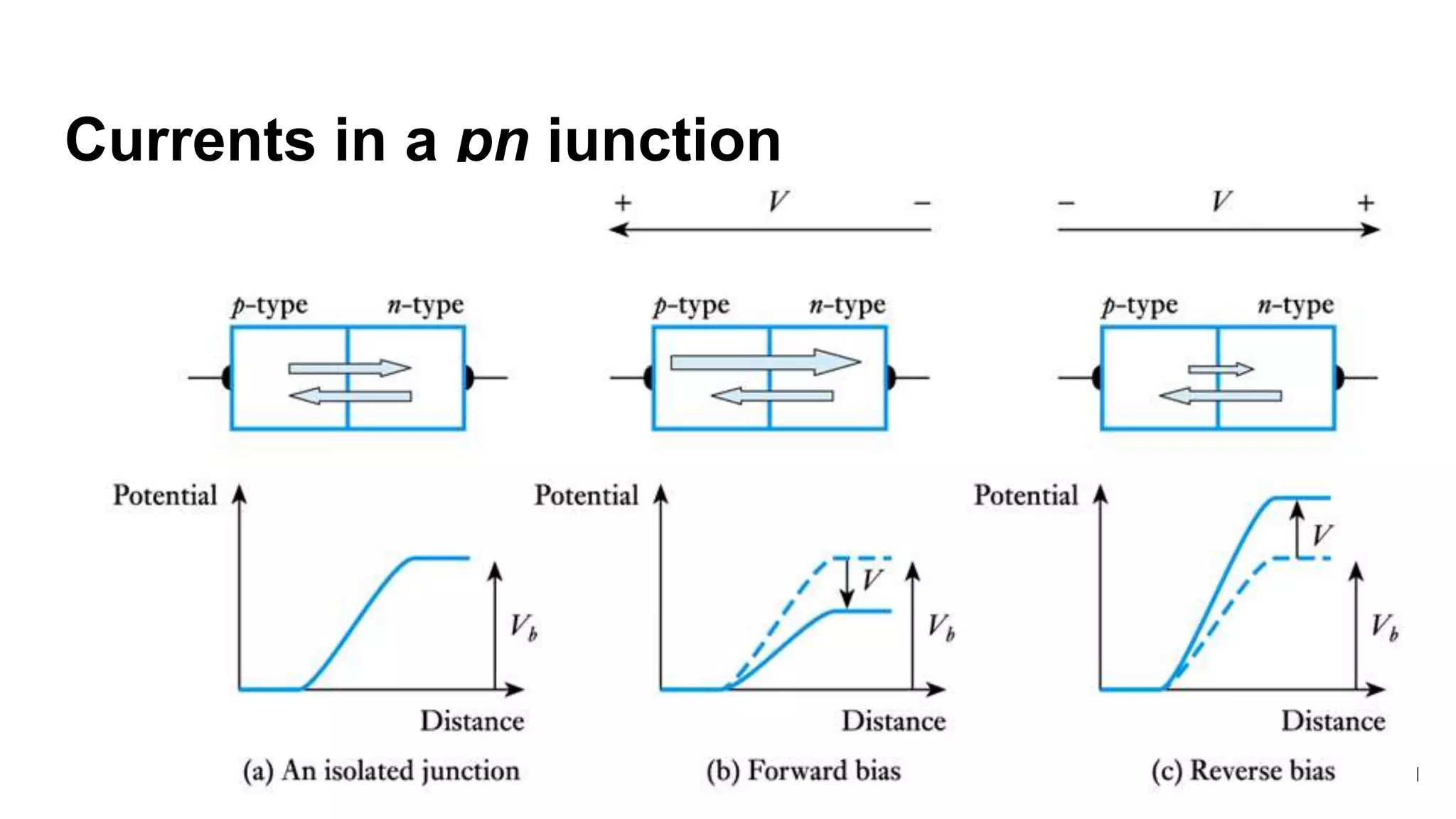
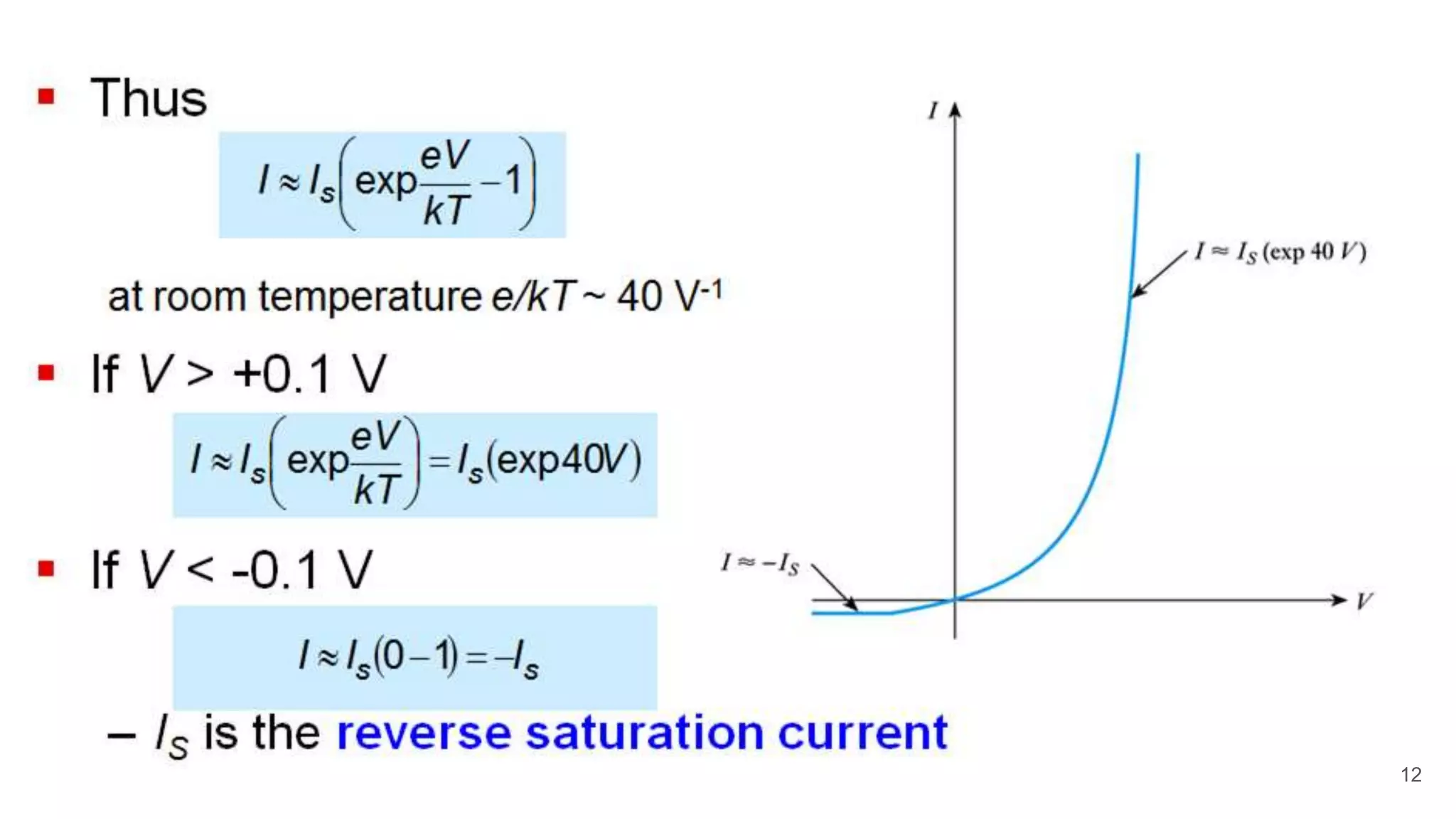
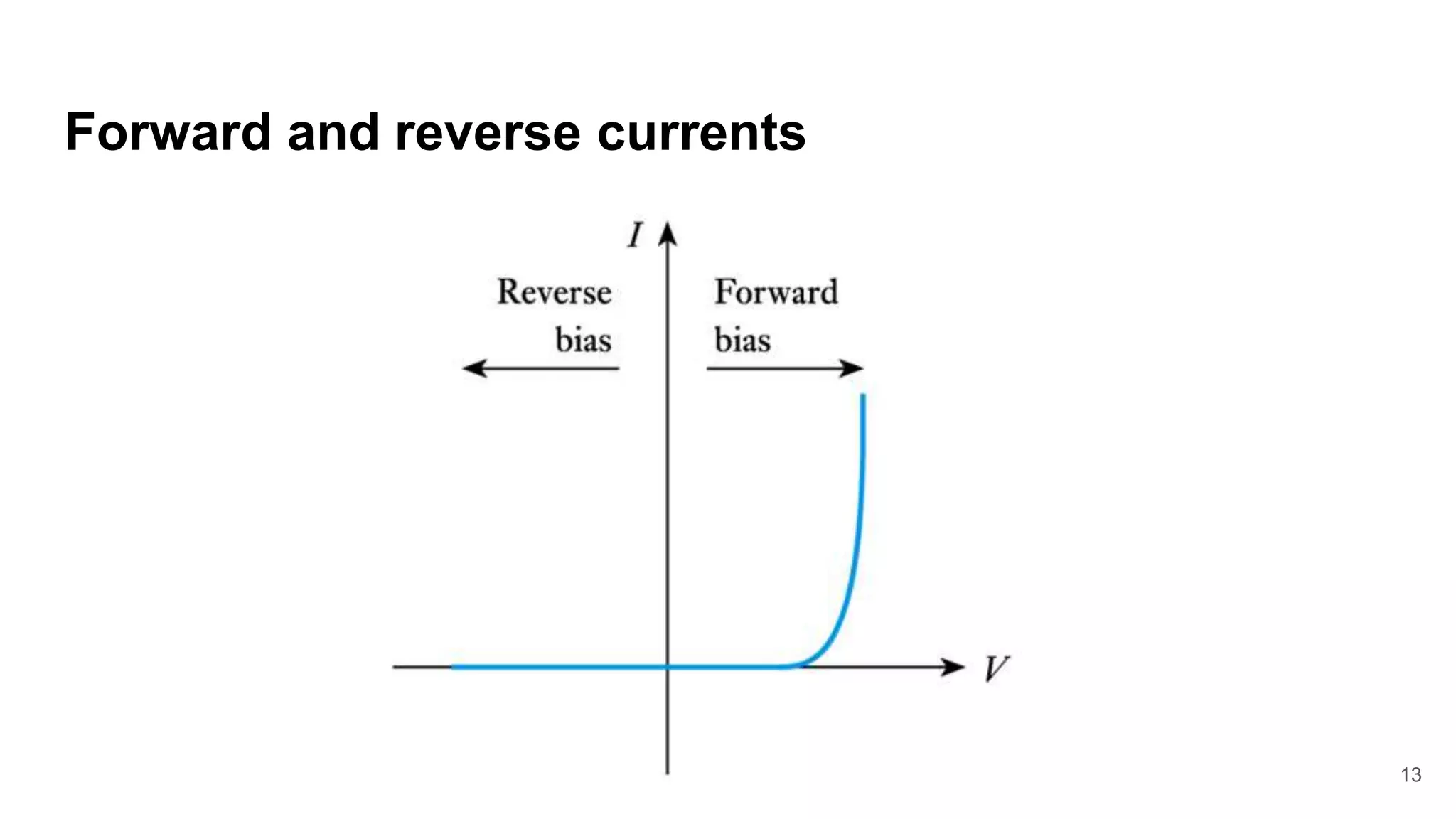
The document discusses the characteristics of diodes and pn junctions. It explains that a pn junction forms when p-type and n-type materials are joined, creating a depletion layer. When the junction is forward biased by making the p-type side positive, the potential barrier is reduced and more charge carriers can flow across, increasing the diffusion current. When reverse biased by making the p-type side negative, the barrier height increases, reducing the diffusion current to nearly zero while the drift current remains small, resulting in a negligible leakage current.