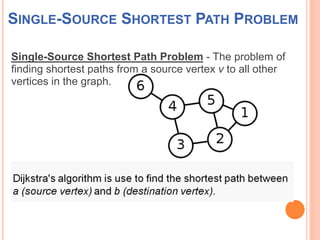
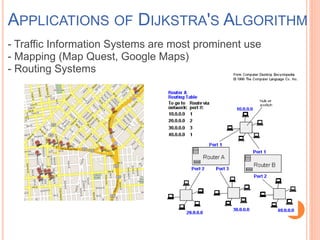
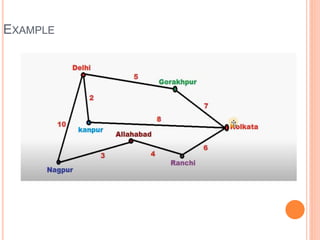
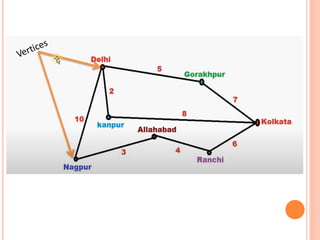
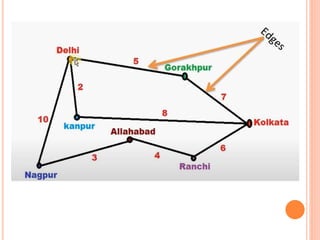
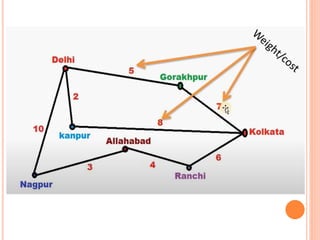
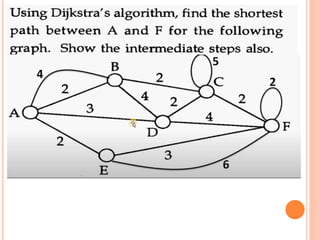
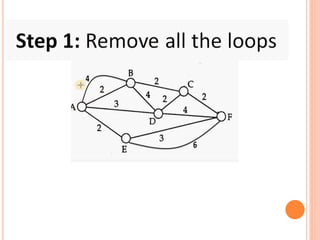
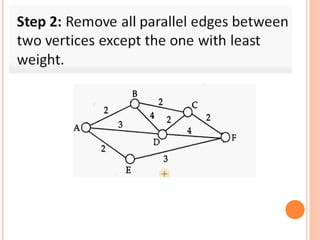
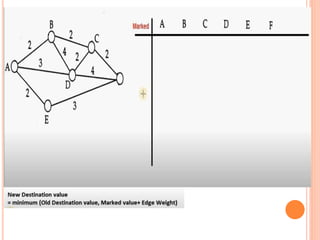
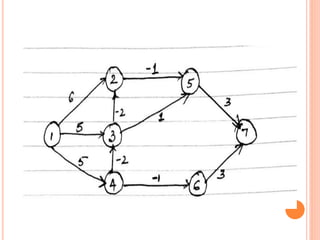
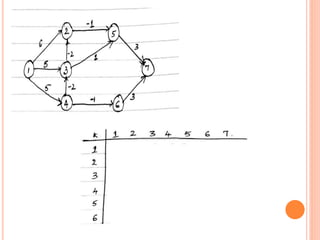
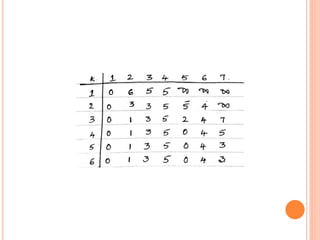
This document discusses Dijkstra's algorithm, which is a solution to the single-source shortest path problem in graph theory. It finds the shortest paths from a source vertex to all other vertices in a graph. Dijkstra's algorithm works for both directed and undirected graphs as long as all edge weights are non-negative. It uses a greedy approach to iteratively mark the vertex with the smallest distance from the source and update the distances of neighboring vertices. The document also notes that while Dijkstra's algorithm is computationally expensive, it can be used anytime the shortest path to another vertex is needed once the origin is determined. Applications include traffic information systems, mapping, and routing systems.