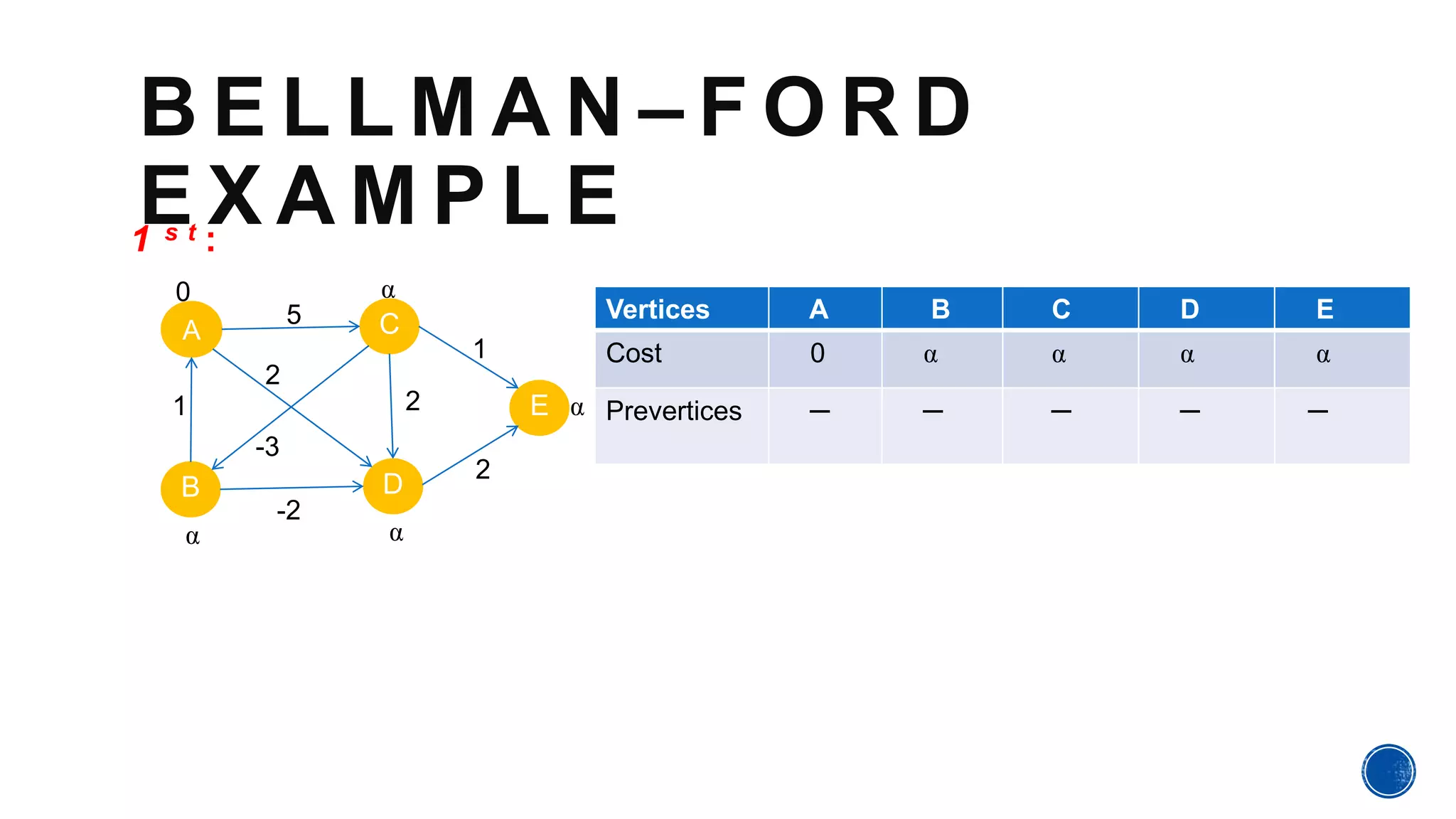
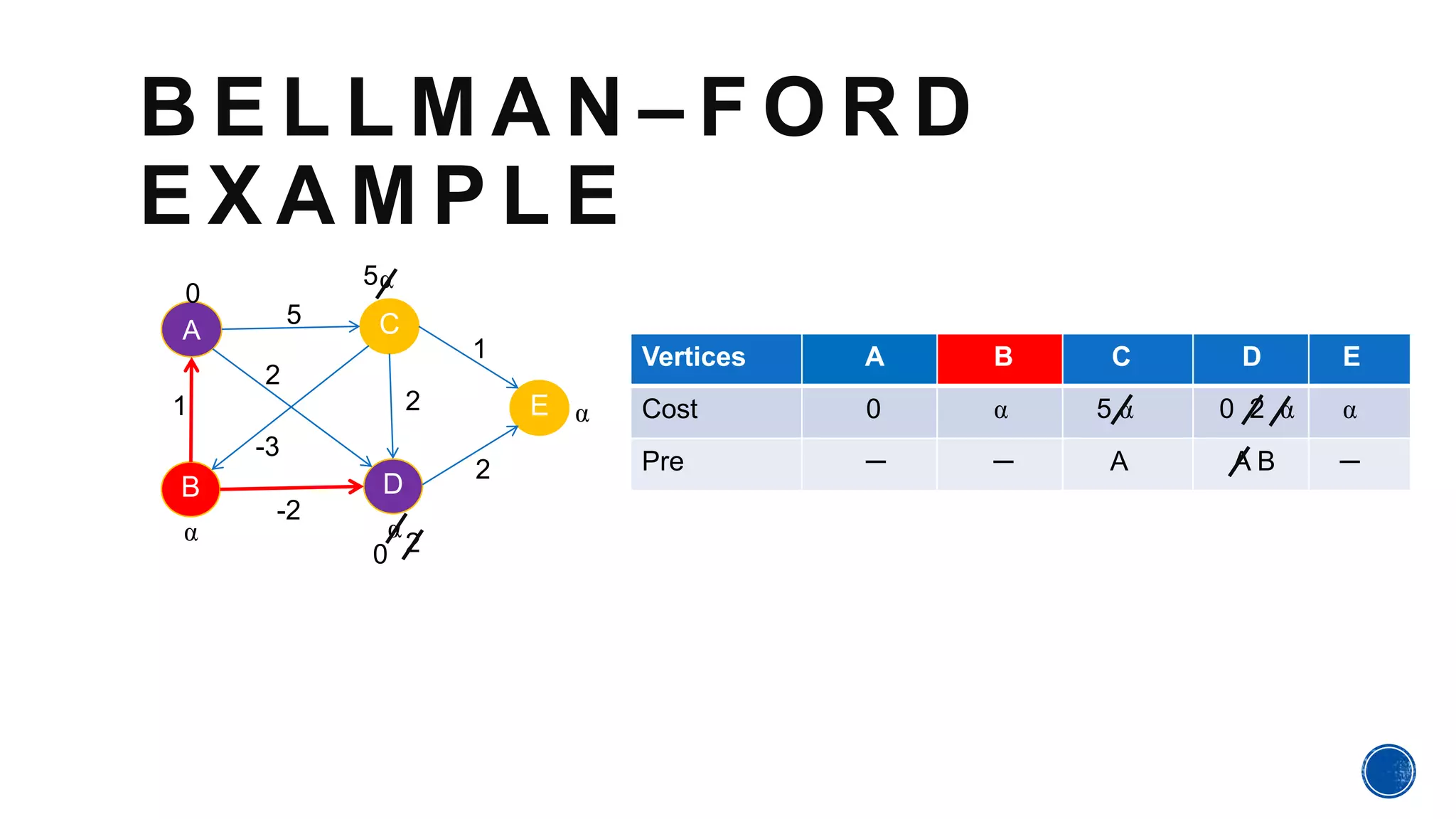
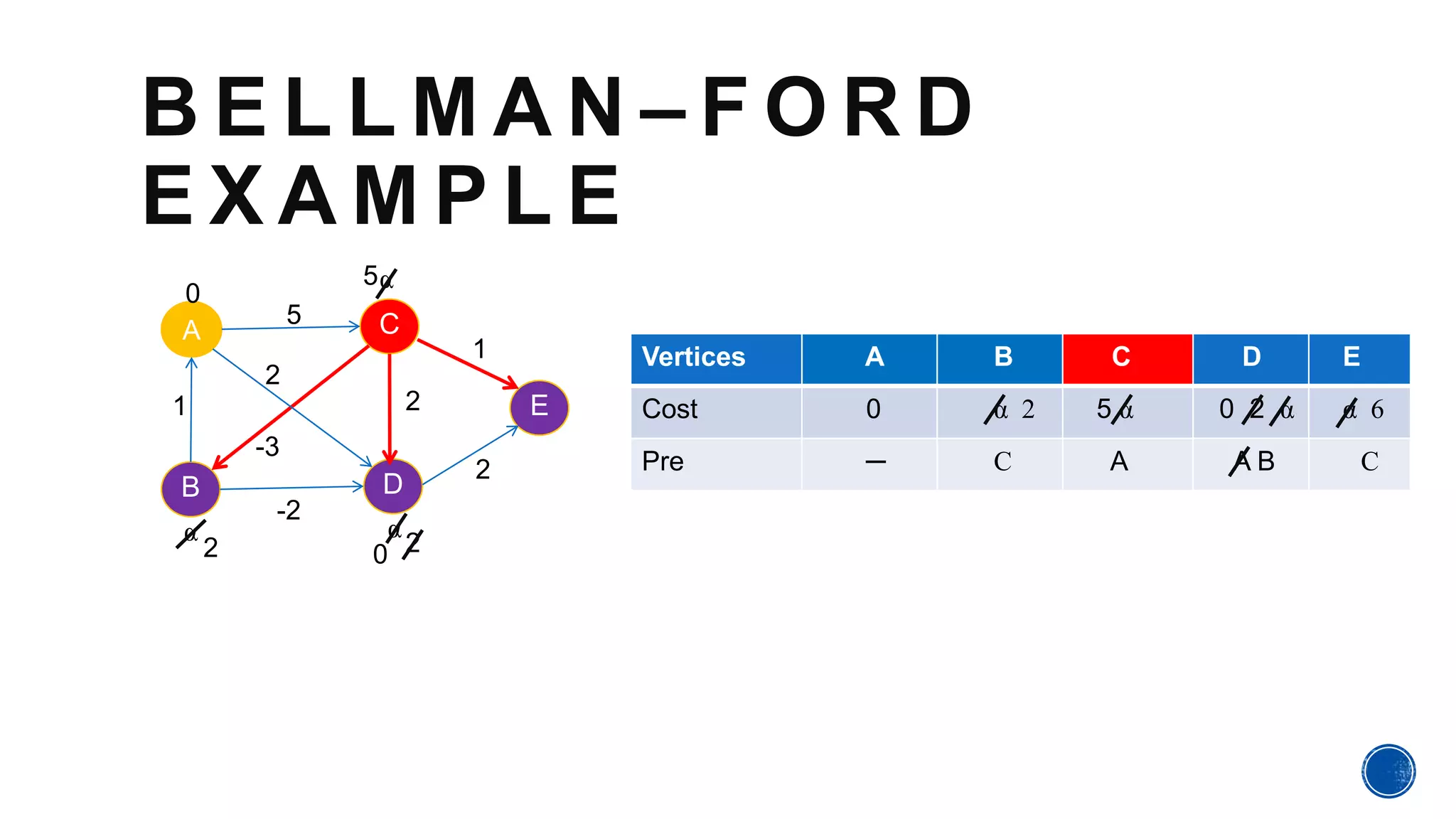
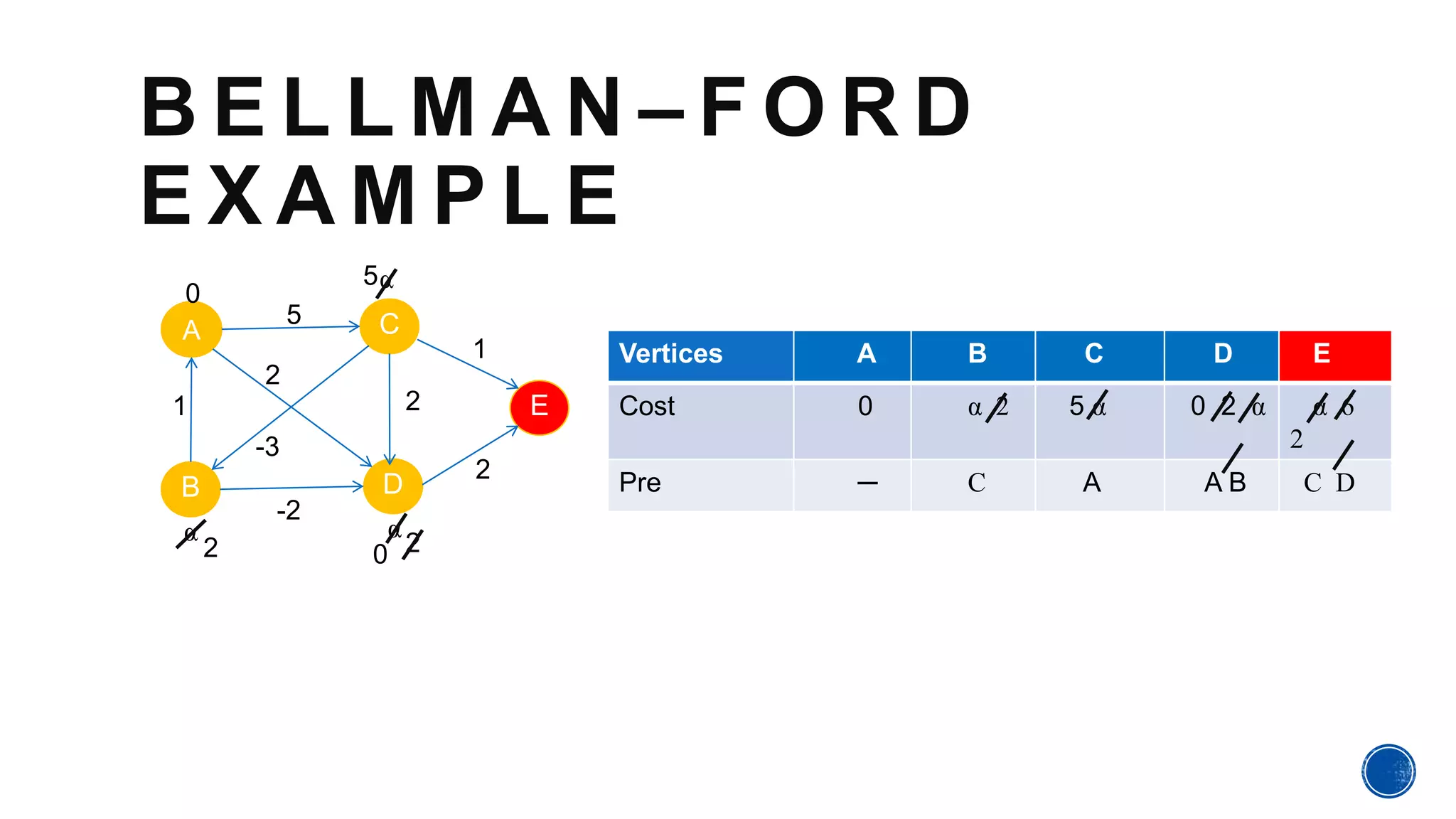
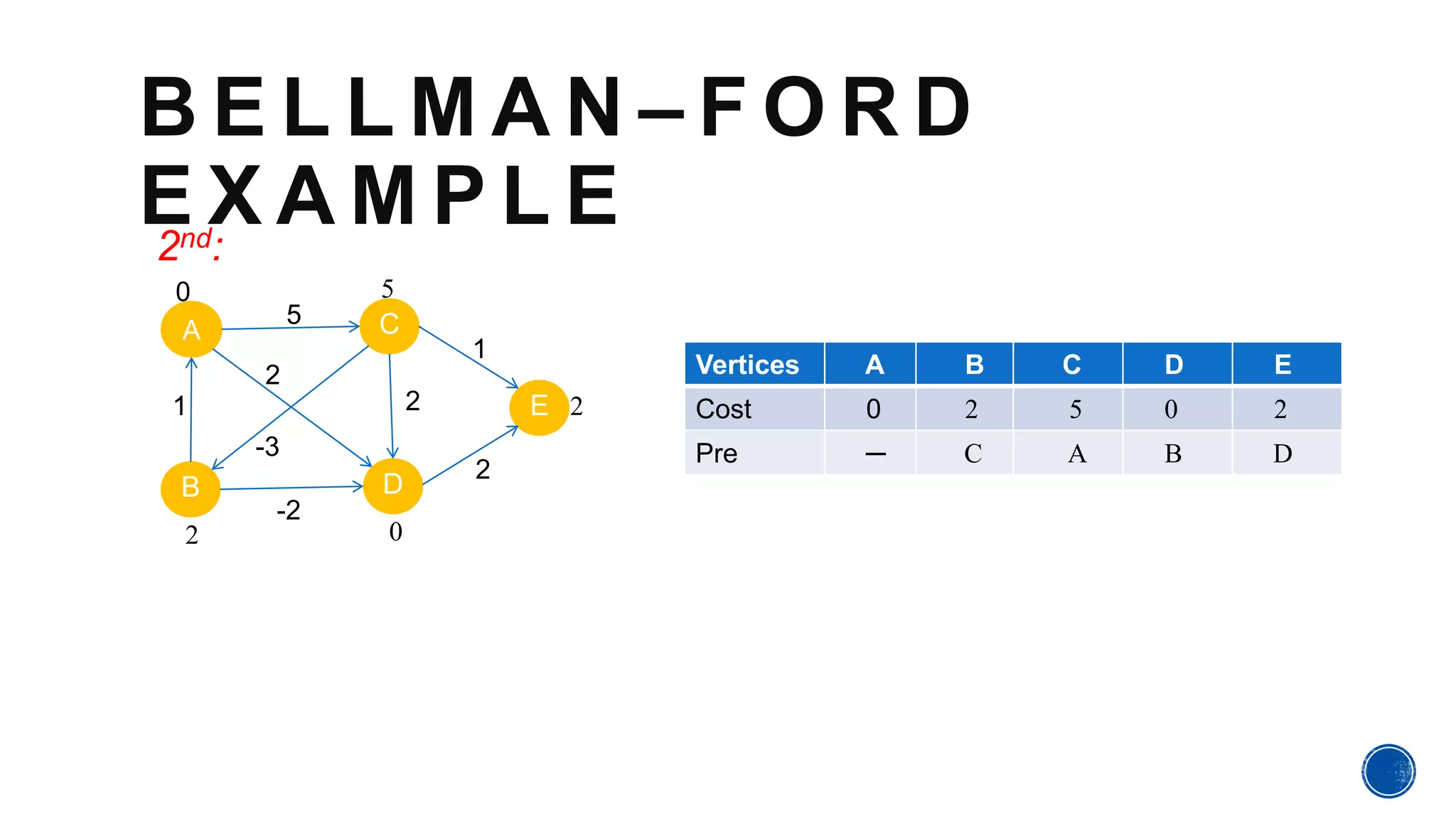
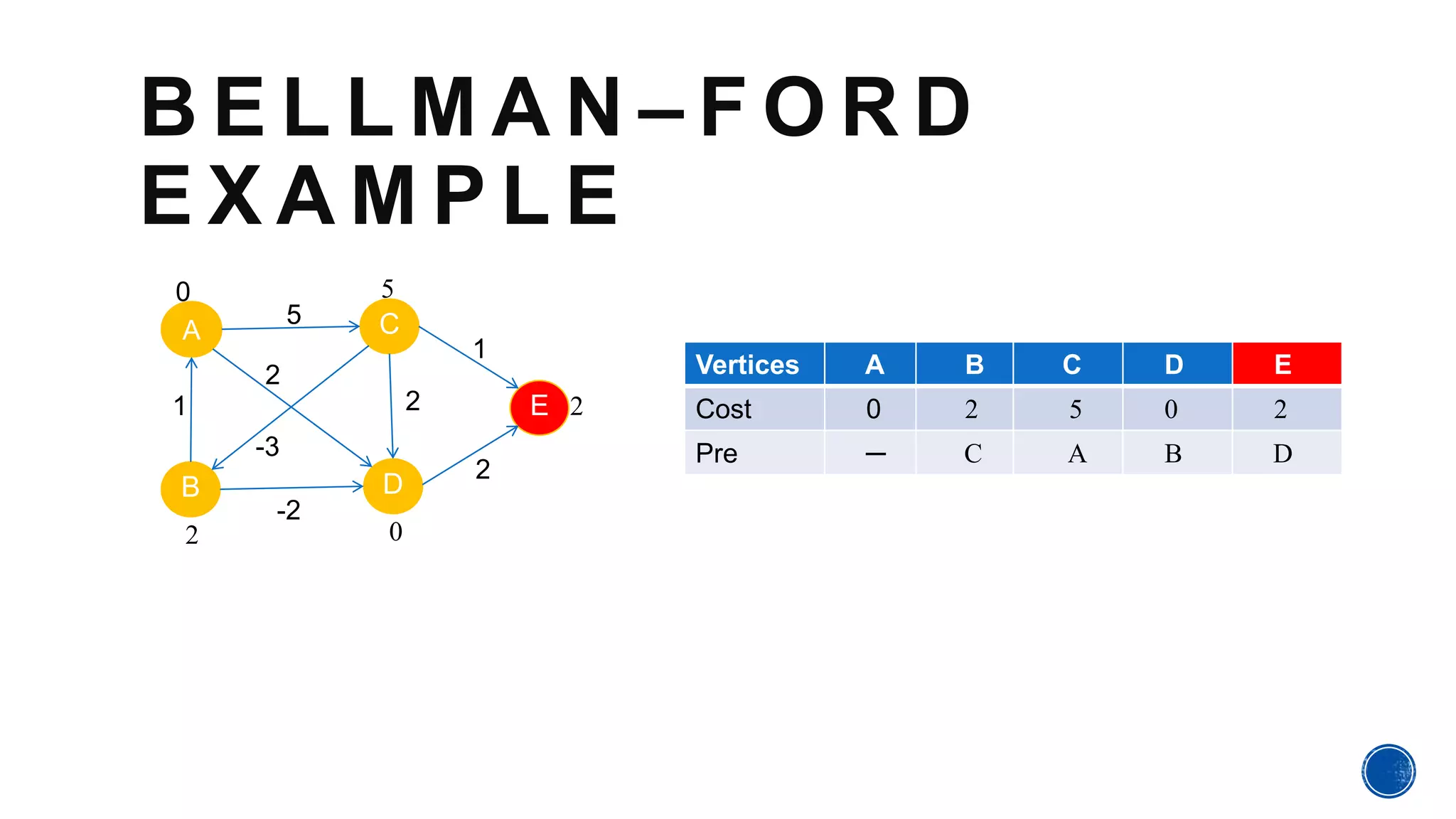
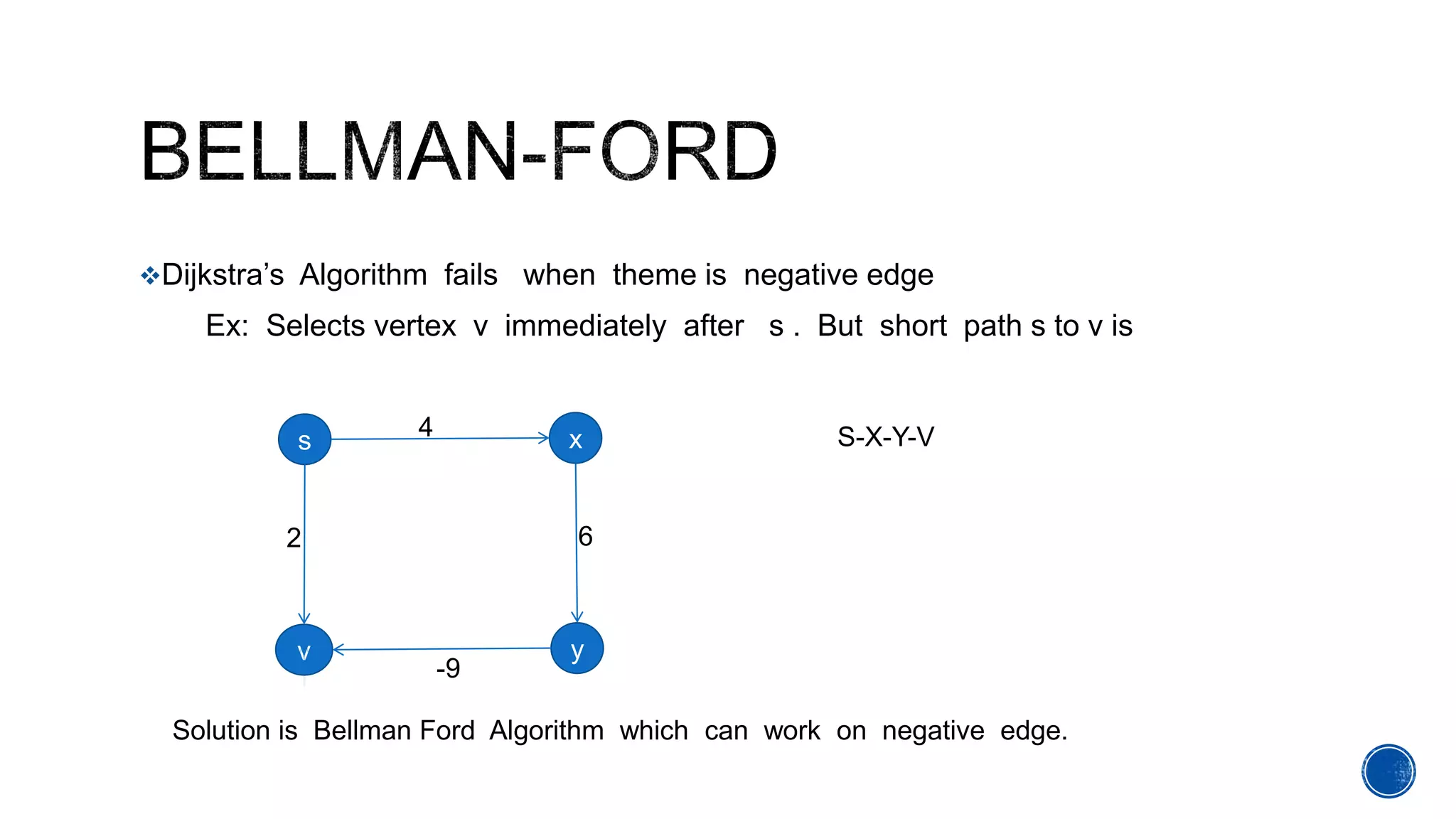
The Bellman-Ford algorithm, proposed by Richard Bellman and Lester Ford Jr., is designed to find the shortest paths in graphs that may contain negative edge weights. It can detect negative cycles, which can affect the existence of a shortest path, making it a valuable tool in various applications. The algorithm processes each edge iteratively to ensure accurate path cost calculations from a source to all other vertices.





![BELLMAN-FOR D ( G ,s )
INITIALIZE SINGLE – SOURCE ( G , s )
for i 1 to |V|-1 do computaion
for each edge ( u, v ) € G.E do
RELAX ( U , V )
for each edge ( u, v ) € E do
if d[V] > d[U] + W( U , V ) then check
return FALSE
return TRUE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/172-35-20882-180930142444/75/Bellman-ford-algorithm-7-2048.jpg)