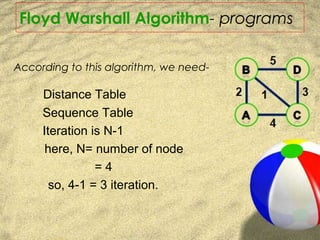
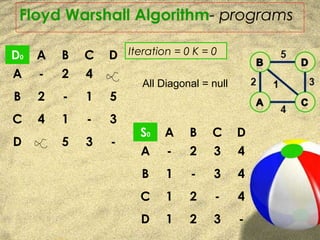
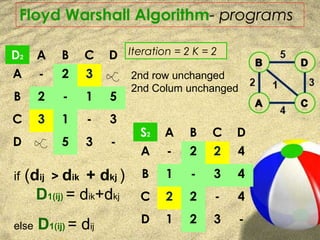
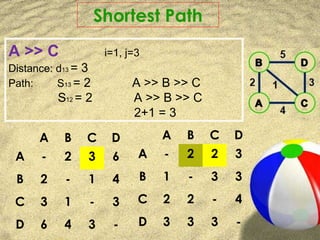
This document presents an overview of the Floyd-Warshall algorithm. It begins with an introduction to the algorithm, explaining that it finds shortest paths in a weighted graph with positive or negative edge weights. It then discusses the history and naming of the algorithm, attributed to researchers in the 1950s and 1960s. The document proceeds to provide an example of how the algorithm works, showing the distance and sequence tables that are updated over multiple iterations to find shortest paths between all pairs of vertices. It concludes with discussing the time and space complexity, applications, and references.