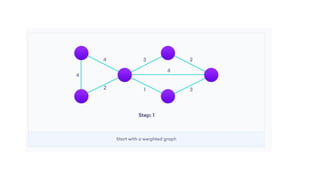
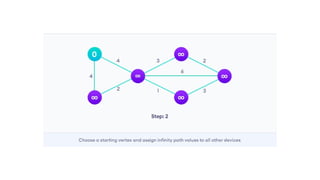
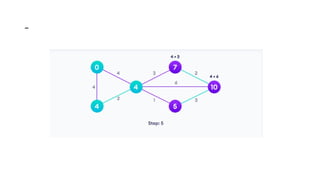
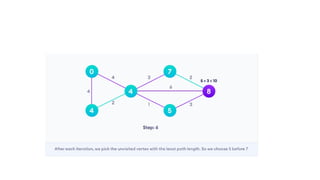
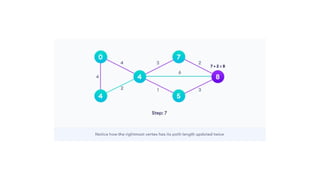
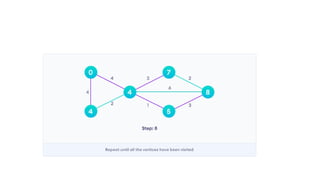
Dijkstra's algorithm is used to find the shortest paths from a source vertex to all other vertices in a graph by leveraging the property that any subpath of the shortest path is also the shortest. The algorithm iterates over vertices, updating distances and maintaining a priority queue, and has a time complexity of O(e log v) and space complexity of O(v). It is applicable in various domains, including social networking, telecommunications, and mapping.

![function dijkstra(G, S)
for each vertex V in G
distance[V] <- infinite
previous[V] <- NULL
If V != S, add V to Priority Queue Q
distance[S] <- 0
while Q IS NOT EMPTY
U <- Extract MIN from Q
for each unvisited neighbour V of U
tempDistance <- distance[U] + edge_weight(U, V)
if tempDistance < distance[V]
distance[V] <- tempDistance
previous[V] <- U
return distance[], previous[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dijkstrasalgorithm1-250210161736-f9c33025/85/Data-structures-and-algorithms-Dijkstra-s-Algorithm-1-pptx-2-320.jpg)