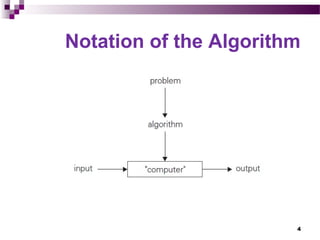
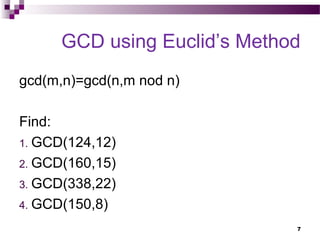
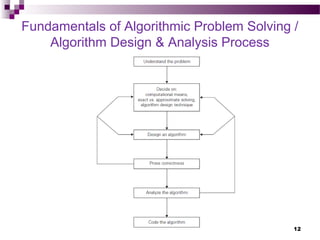
The document introduces algorithms, outlining their definition, design, and implementation steps while highlighting important problem types and fundamental data structures. It explains the concept of algorithms through examples like finding the greatest common divisor (gcd) and generating prime numbers. The document also touches on algorithm efficiency, correctness, and various problem-solving techniques.