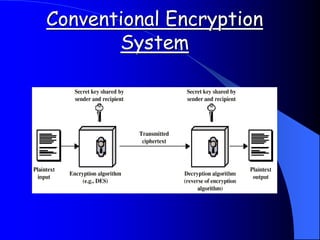
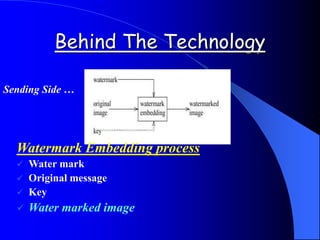
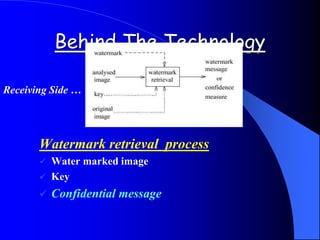
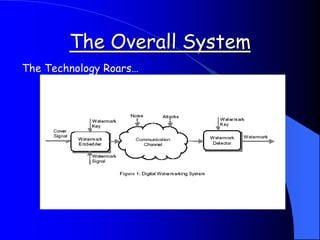
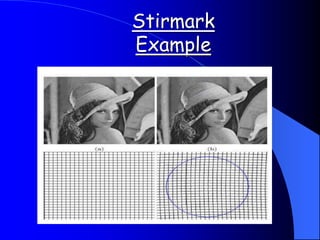
This document provides an overview of digital watermarking. It defines digital watermarking as a technique that embeds a low-energy signal or watermark imperceptibly into digital content. The document discusses different types of watermarking including robust, fragile, visible, and invisible watermarking. It also outlines various digital watermarking techniques and applications for copyright protection, content authentication, and metadata tagging. The document concludes that digital watermarking is an effective technique for protecting digital content and preventing illegal copying.