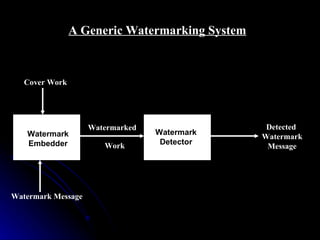
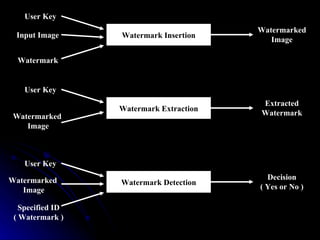
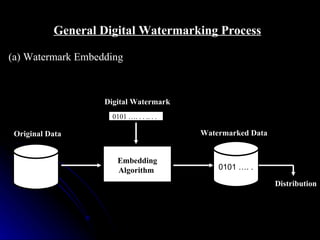
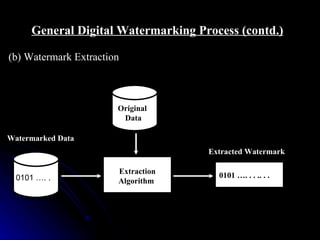
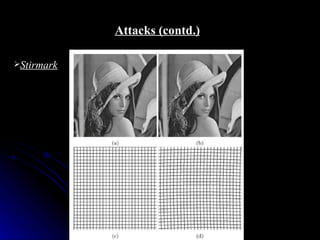
This document discusses digital watermarking (DWM), which involves hiding invisible signatures or visible logos in digital media like images, video and audio. DWM can be used for copyright protection, owner identification and content authentication. Watermarks are classified as perceptible or imperceptible, robust or fragile, and private or public depending on their visibility, ability to withstand modifications, and whether the original data is needed for detection. The document outlines the DWM process, common attacks, advantages, disadvantages and techniques like least significant bit encoding.