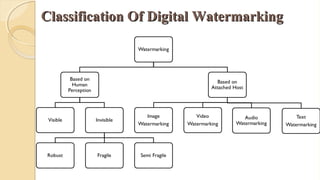
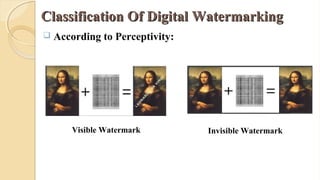
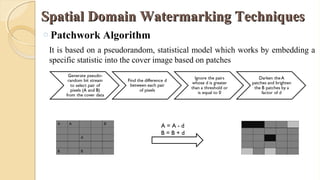
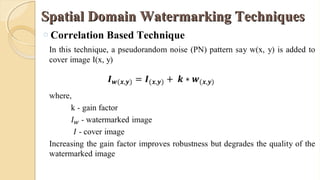
The document presents an in-depth overview of digital watermarking, describing its applications, classifications, techniques, and vulnerabilities to attacks. Digital watermarking embeds secret signals into digital media for purposes like copyright protection and content authentication, with various methods discussed, including spatial and frequency domain techniques. It concludes that while watermarking offers security benefits, challenges from various types of attacks must be addressed to ensure robustness and effectiveness.


















![[1] P. Singh and R. S. Chadha, “A Survey of Digital Watermarking Techniques, Applications and
Attacks,” International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology, vol. 2, no. 9, pp. 165-
175, 2013
[2] Voloshynovskiy, Sviatolsav, et al. "Attacks on digital watermarks: classification, estimation based
attacks, and benchmarks." IEEE communications Magazine 39.8 (2001): 118-126
[3] Potdar, Vidyasagar M., Song Han, and Elizabeth Chang. "A survey of digital image watermarking
techniques." Industrial Informatics, 2005. INDIN'05. 2005 3rd IEEE International Conference on.
IEEE, 2005
[4] Liu, Tong, and Zheng-ding Qiu. "The survey of digital watermarking-based image authentication
techniques." Signal Processing, 2002 6th International Conference on. Vol. 2. IEEE, 2002
[5] Lee, Sin-Joo, and Sung-Hwan Jung. "A survey of watermarking techniques applied to
multimedia." Industrial Electronics, 2001. Proceedings. ISIE 2001. IEEE International
Symposium on. Vol. 1. IEEE, 2001.
ReferencesReferences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalwatermarkingnaz1-180103062024/85/Digital-watermarking-Techniques-25-320.jpg)