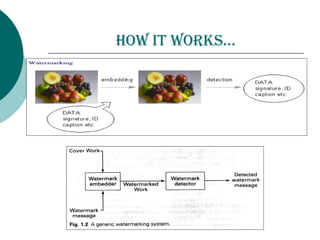
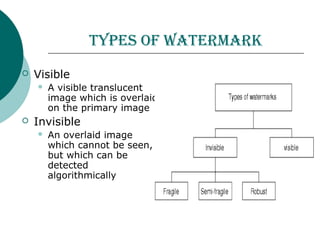
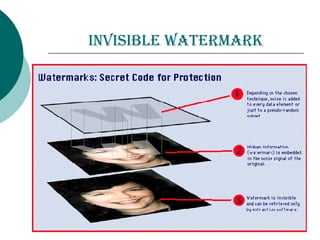
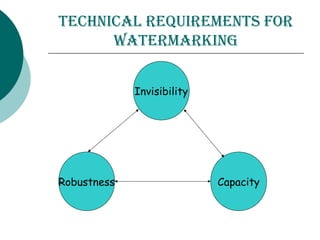
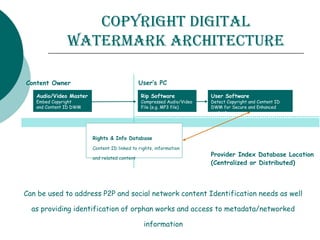
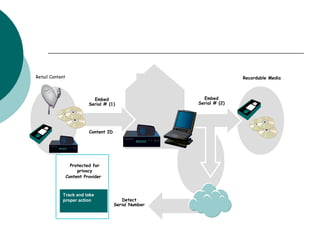
Digital watermarking involves hiding identification information within digital content like images, video and audio. It can be used to authenticate ownership and detect unauthorized copying. There are two main types - visible watermarks which can be seen overlaid on an image, and invisible watermarks which are imperceptible but can be detected algorithmically. Digital watermarking works by imperceptibly altering content to embed a message. It has applications in copyright protection, content management, and tracking of digital media. The embedded data, or watermark, must be invisible, inseparable from the content, and not increase the file size. The Digital Watermarking Alliance promotes standards for watermarking across different media types.