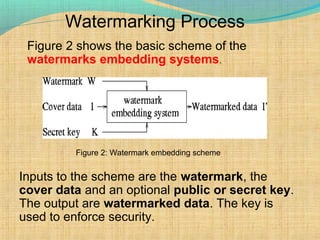
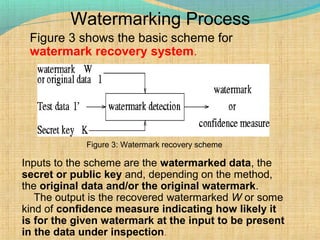
The document discusses information hiding, focusing on digital watermarking, which embeds distinguishing marks into digital media without compromising quality. Watermarking is characterized by transparency, robustness, efficiency, and independence, with applications including copyright protection, tamper proofing, and quality assessment. Additionally, it outlines various watermarking schemes and potential attack types against them, emphasizing the need for security in watermarking processes.