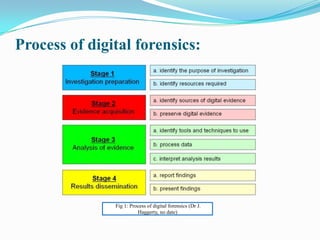
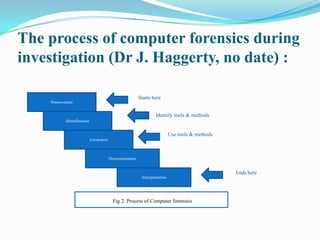
Digital forensics involves identifying evidence from digital sources using scientific tools and techniques to solve crimes. There are two criteria for evidence admission in court: relevance to the case and use of scientific methods. Errors in evidence gathering can result in meaningless evidence or penalties. The process involves preservation, identification, extraction, documentation, and interpretation of data. Tools like WetStone's Gargoyle and Niels Provos's stegdetect can detect hidden data. The reliability of found data must undergo a Daubert hearing to ensure the tools and methods are viable in court. Professional, ethical, and legal issues must be considered regarding an investigator's role, privacy concerns, and challenges from evolving technologies.





![References:
Fig 1: Dr J. Haggerty, no date. Digital forensics: Digital forensic process. Available
at: http://www.cse.salford.ac.uk/profiles/haggerty/forensics.php [Accessed on
16/10/2011]. Fig 3: Kessler, G. C., 2004. WetStone Technologies’ Gargoyle.
Available at:
<http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.90.8113&rep=rep1&typ
e=pdf > [Accessed on 16/10/2011].
Fig 4: Niels Provos, 2004. Niels Provos’s stegdetect. Available at:
<http://www.outguess.org/detection.php > [Accessed on 17/10/2011].
Carrier, B. (2002). Open Source Digital Forensics Tools. Citeseerx[Online paper].
Available at: : <http://www.digital-
evidence.org/papers/opensrc_legal.pdf>[Accessed on 16/10/2011]. Daniel J.R and
G. Shpantzer (2005). Legal Aspects of Digital Forensics. Available at:
http://euro.ecom.cmu.edu/program/law/08-732/Evidence/RyanShpantzer.pdf>
[Accessed on 17/10/2011]. Dr J. Haggerty(no date). Digital forensics. Available at:
http://www.cse.salford.ac.uk/profiles/haggerty/forensics.php [Accessed on
16/10/2011]. Digital Forensics Magazine(2010). Ethics in Computer Forensics.
Available at:
<http://www.digitalforensicsmagazine.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=a
rticle&id=540> [accessed on 17/10/2011].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalforensics-120503063829-phpapp02/85/Digital-forensics-8-320.jpg)
