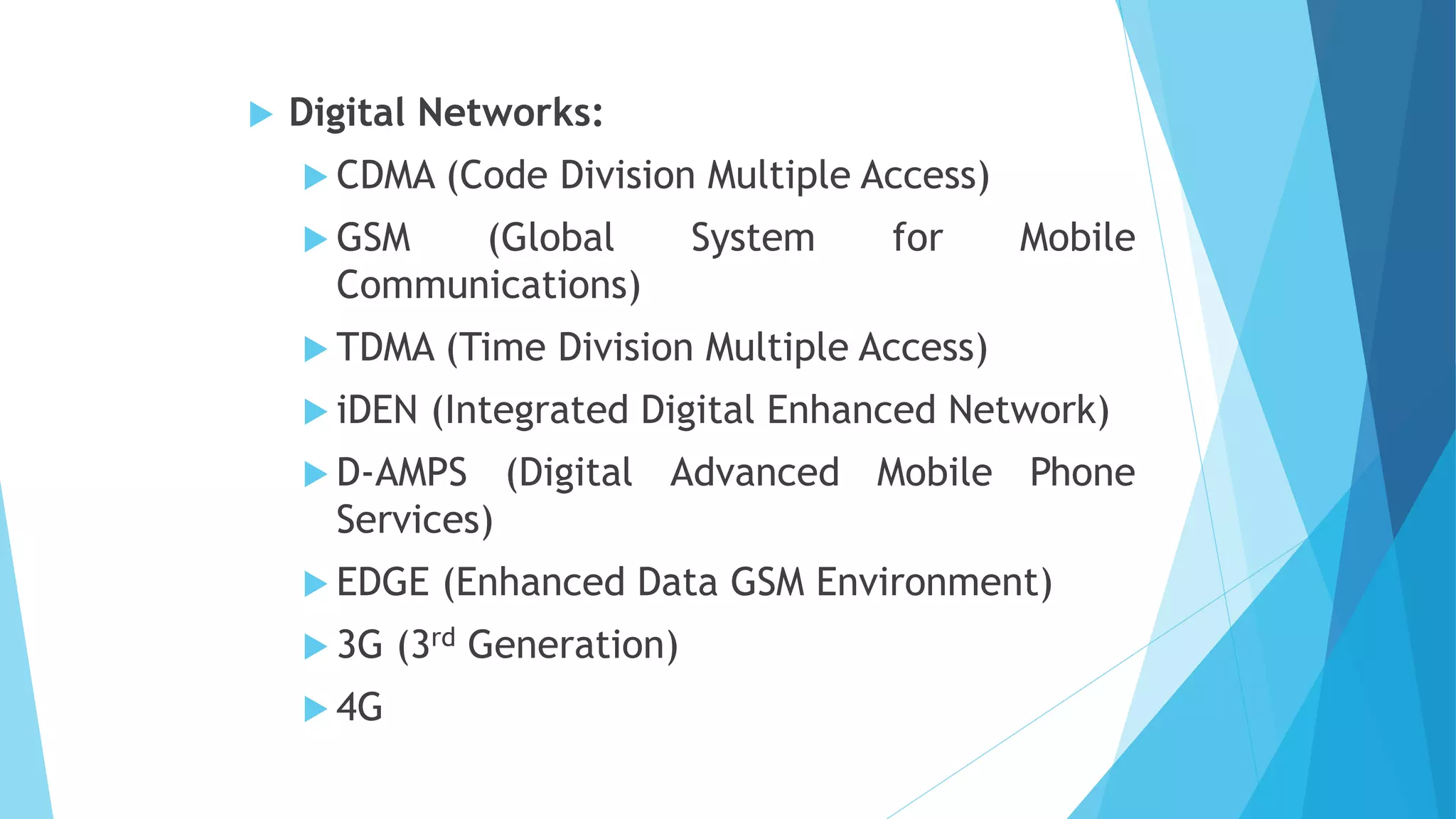
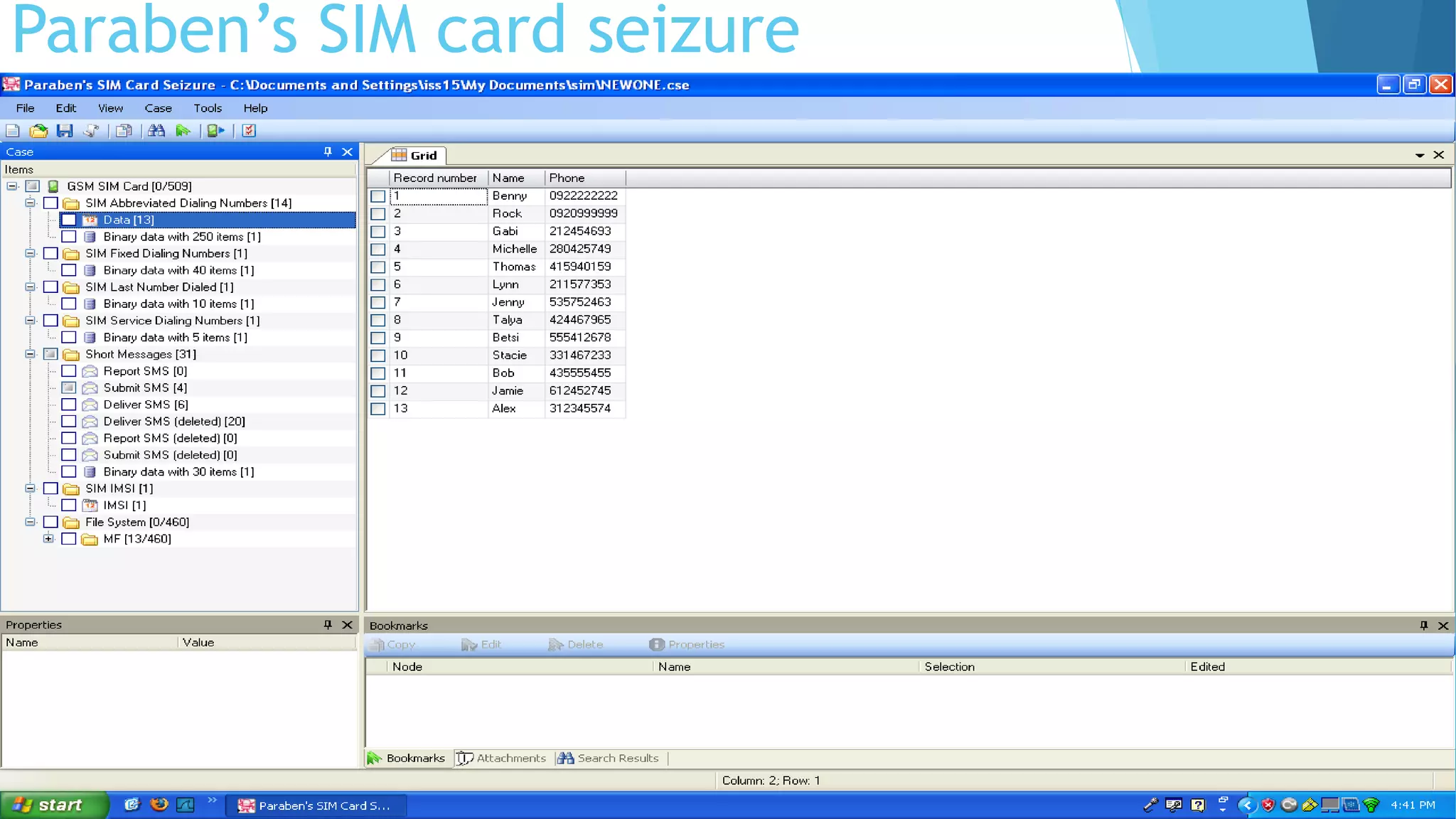
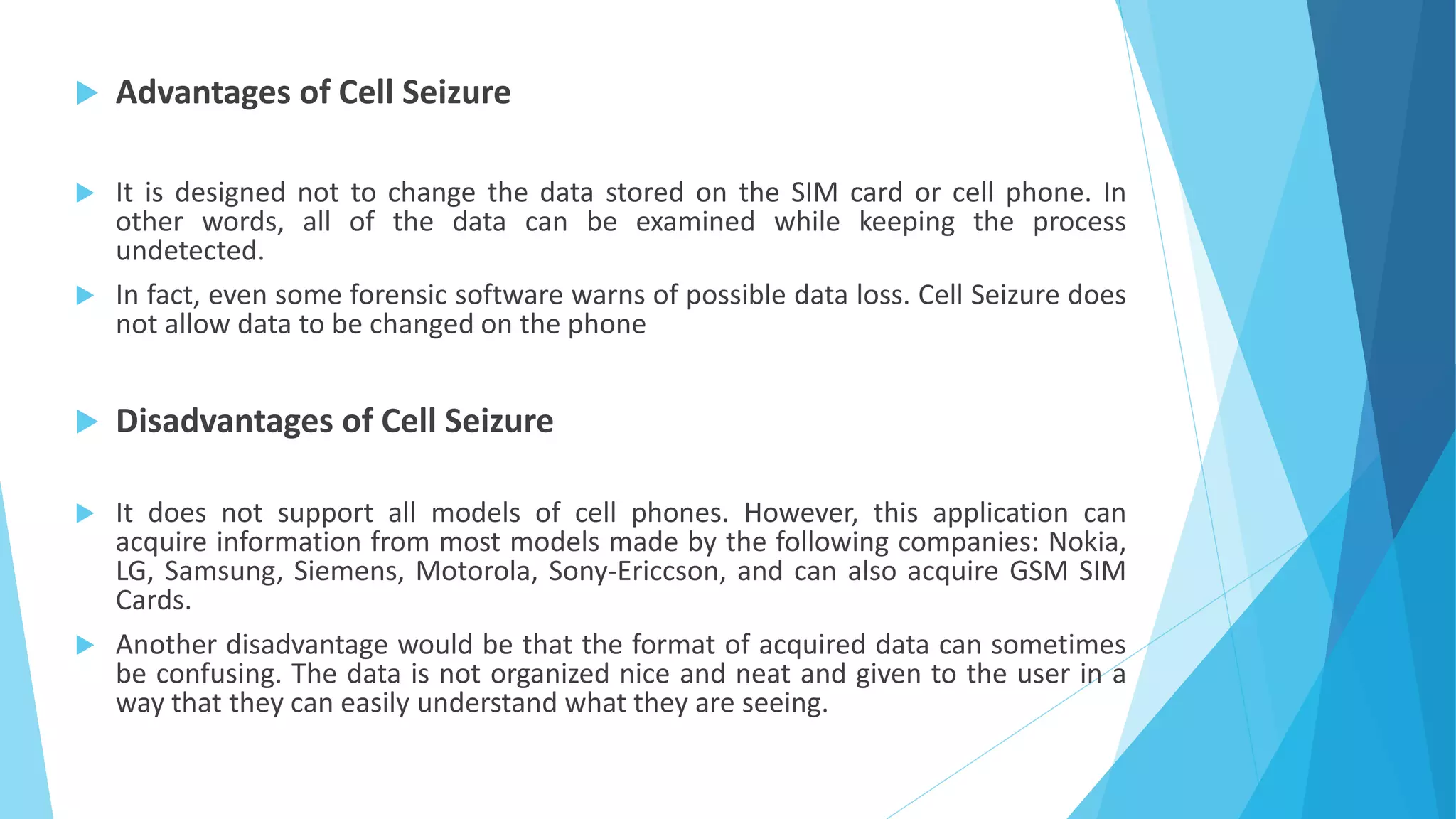
The document is a comprehensive guide to mobile phone seizure, covering topics from understanding mobile device forensics to specific forensic tools and equipment. It highlights the importance of securely handling and examining mobile devices to maintain the integrity of evidence and outlines the principles guiding digital evidence collection. Various mobile forensic tools and techniques for examining data stored on cell phones, including the challenges posed by different operating systems and device models, are also detailed.