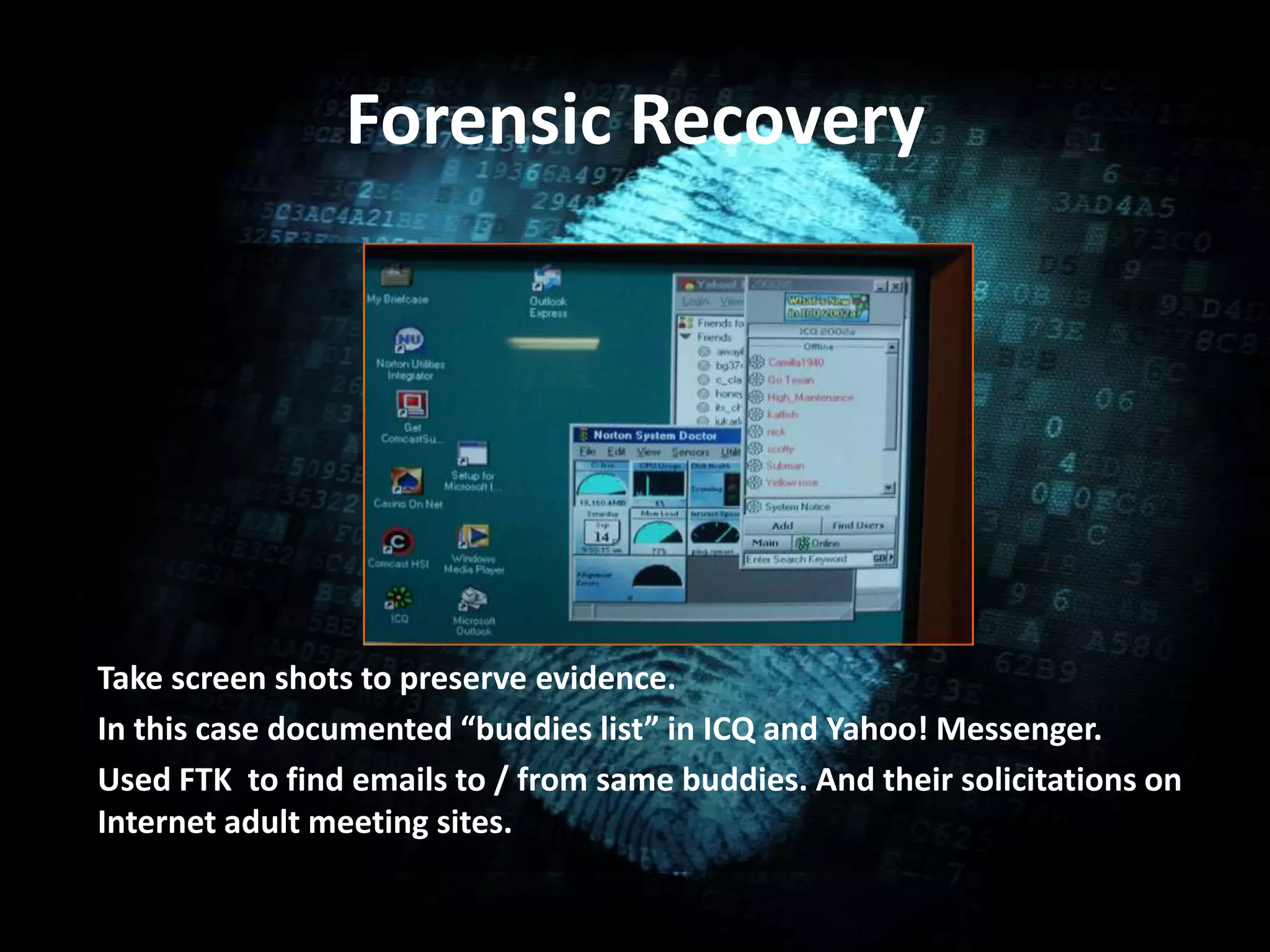
Computer forensics involves the legal acquisition, preservation, analysis and presentation of digital evidence found on computers and digital devices. It follows standard processes and guidelines to ensure evidence is collected properly and can be used in legal cases. The main steps are acquisition of evidence from devices, identification and evaluation of relevant data found, and proper presentation of findings. Computer forensics experts work in law enforcement, private companies, and other organizations to gather digital evidence for various crimes and disputes.