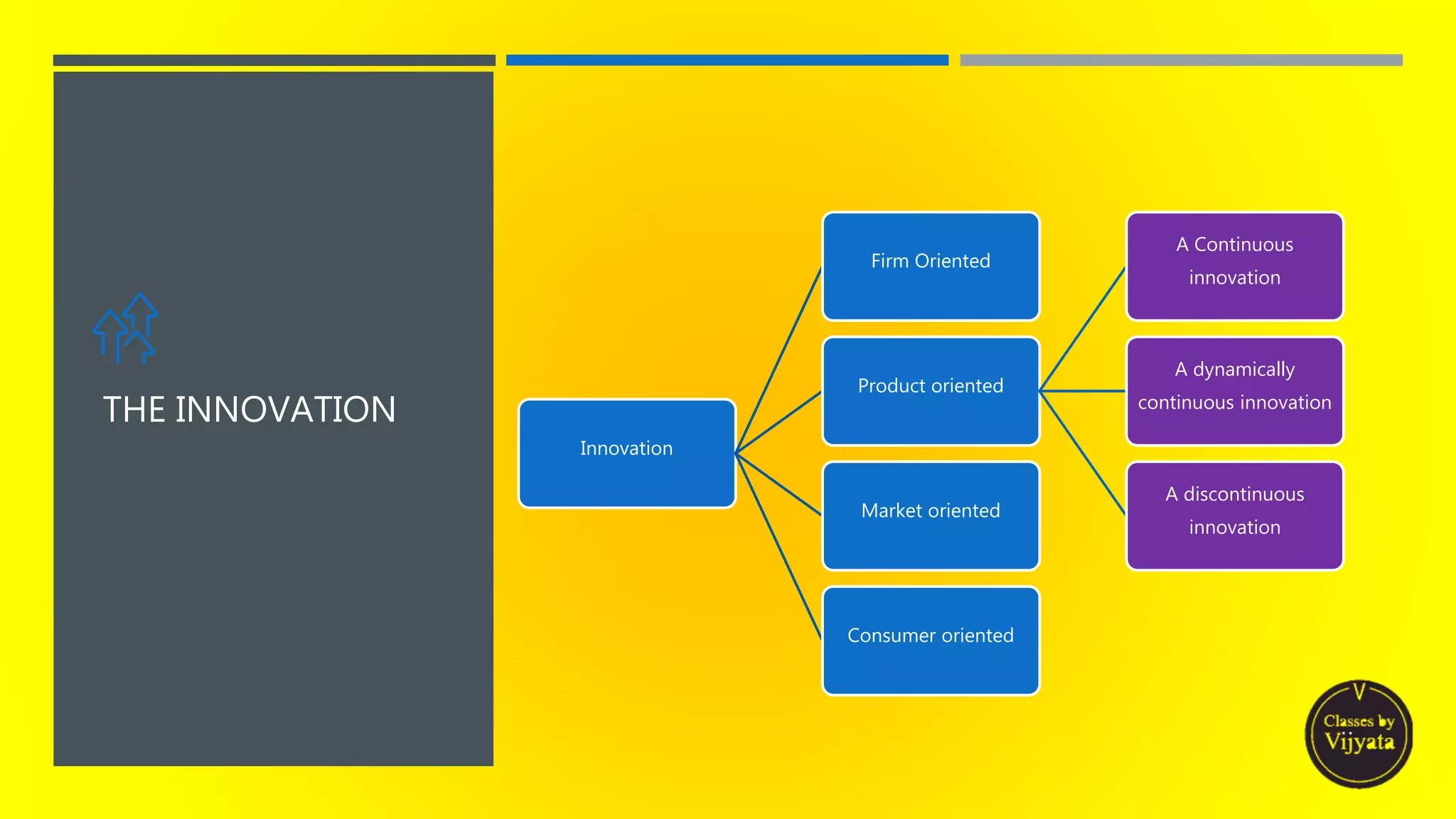
This document discusses the diffusion of innovation, which examines how new products, ideas or technologies are adopted by consumers over time. It outlines several key aspects of the diffusion process, including:
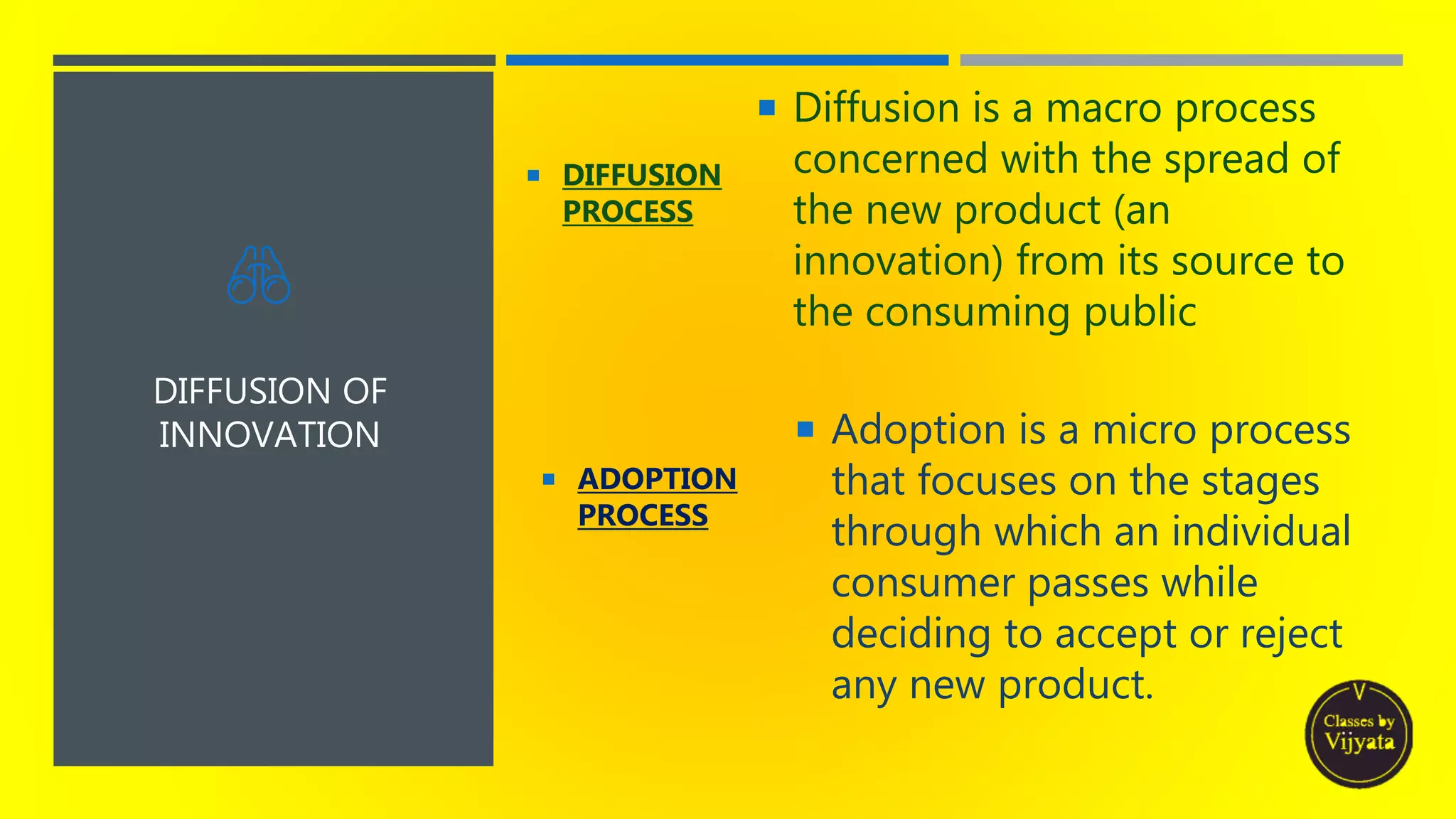
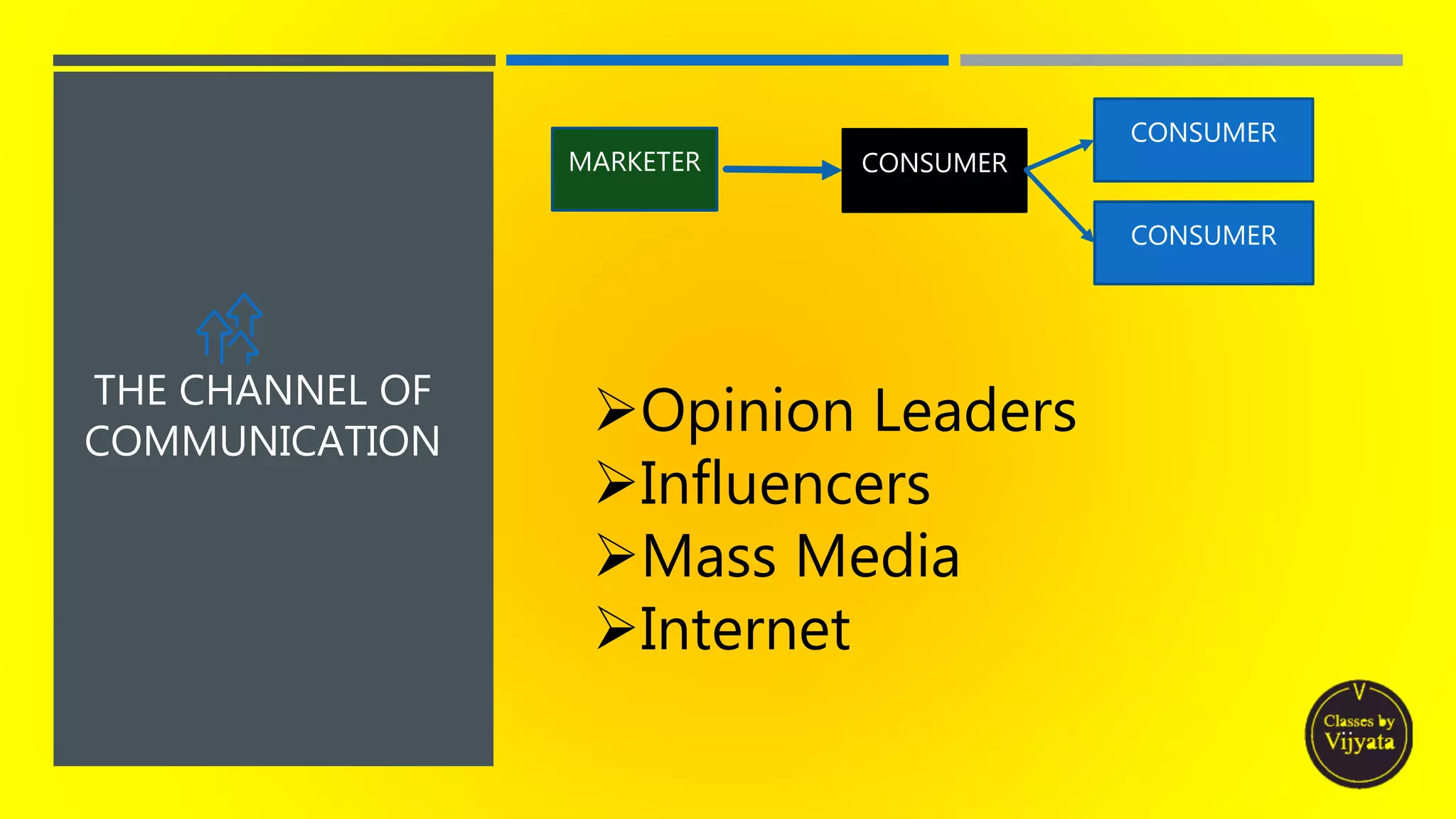
- The diffusion process itself, by which an innovation spreads via communication channels to members of a social system over periods of time.
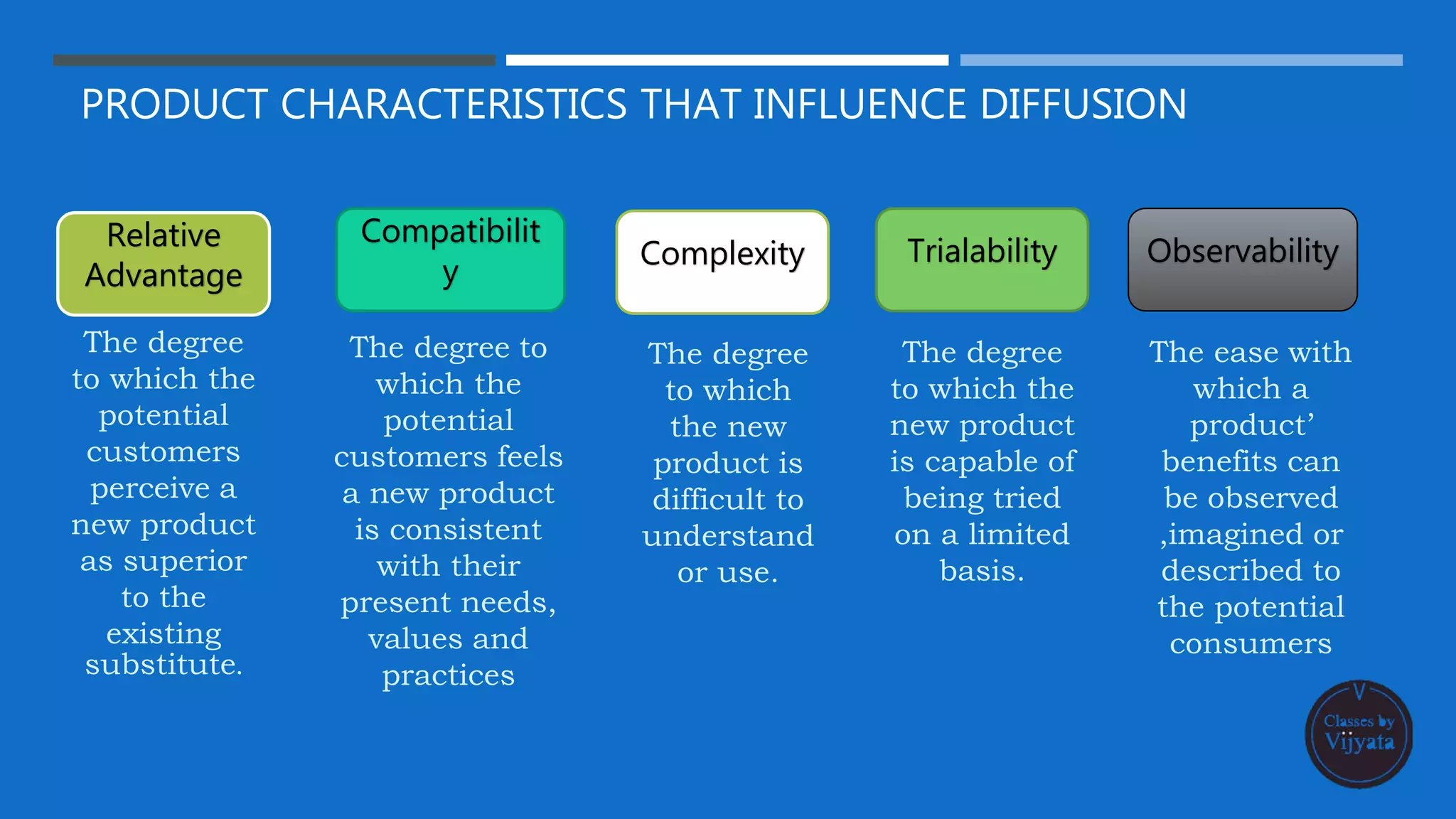
- The innovation characteristics that influence its rate of adoption, such as relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, trialability and observability.
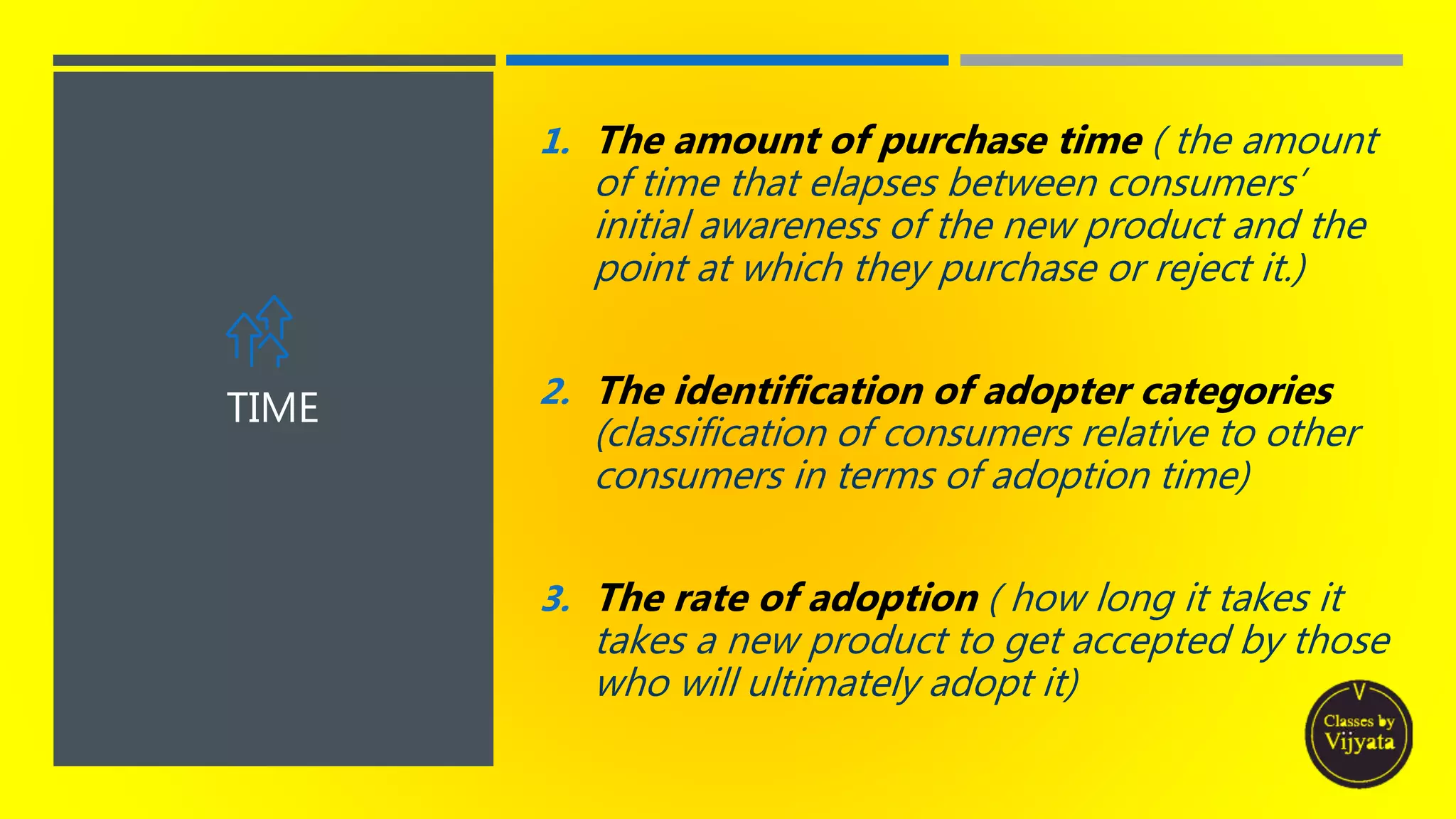
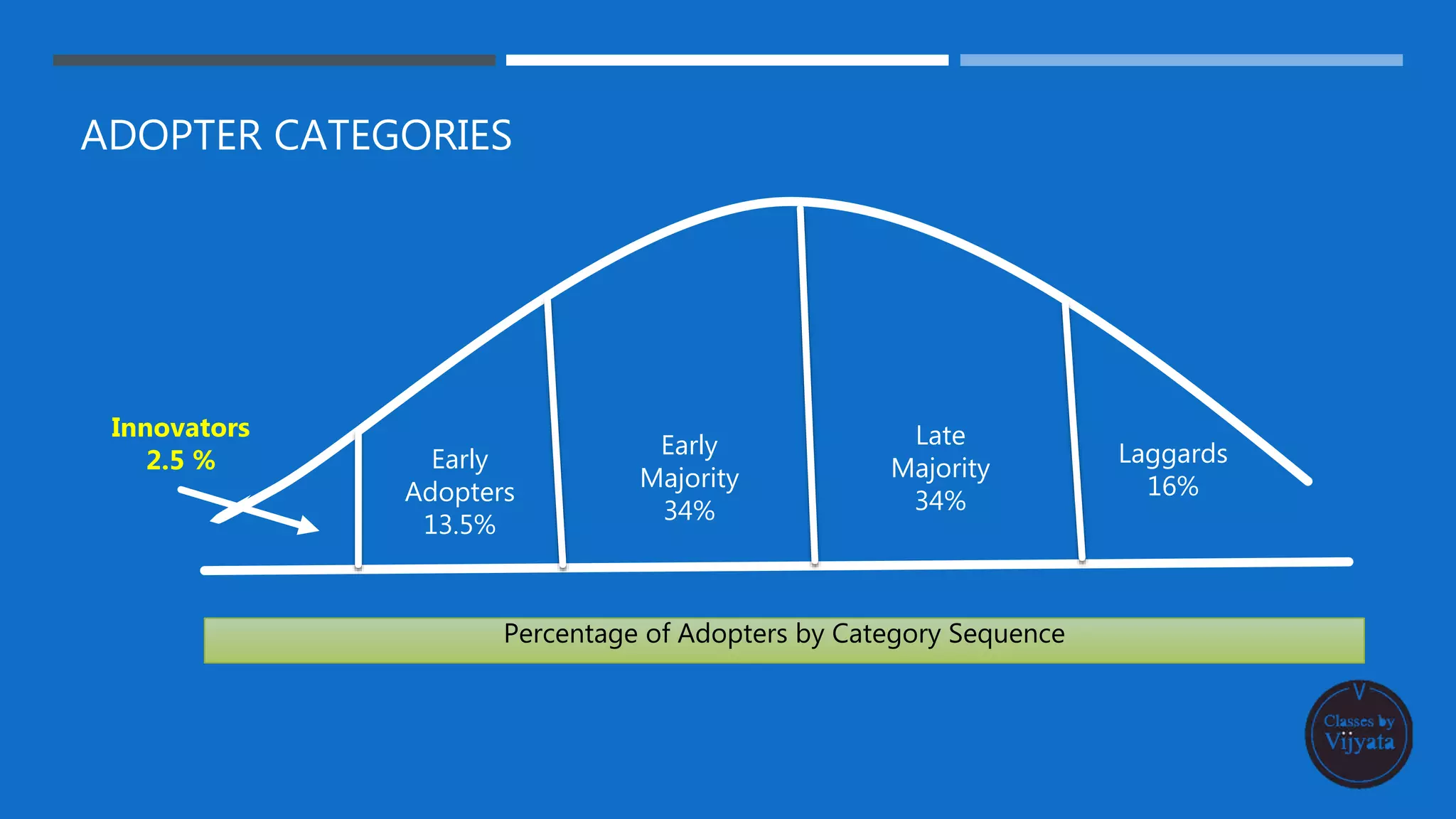
- Adopter categories that consumers fall into based on when they adopt - innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority and laggards.
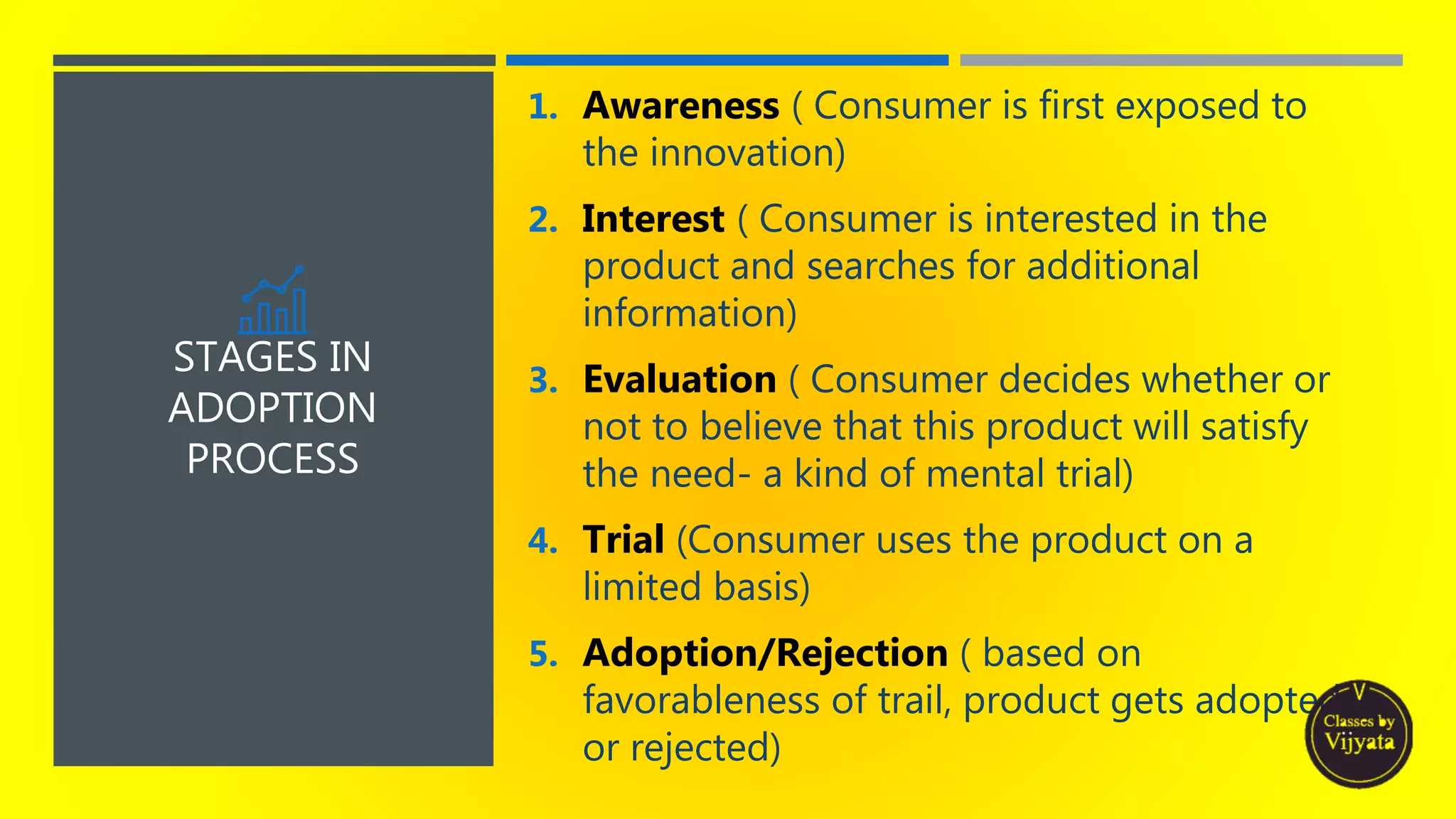
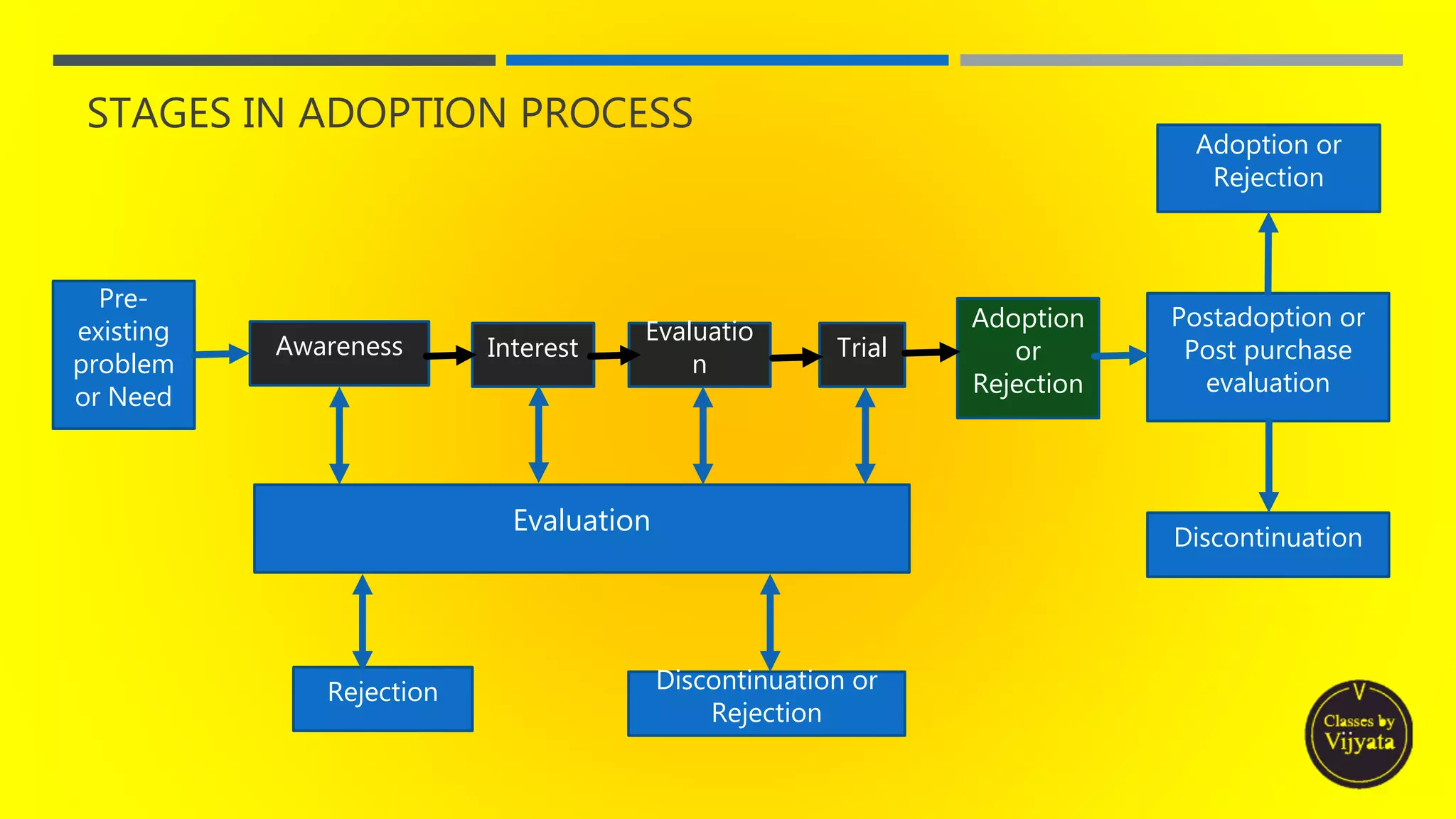
- The innovation adoption process individuals go through - awareness, interest, evaluation, trial and adoption/reject