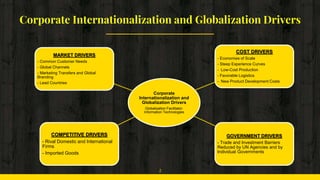
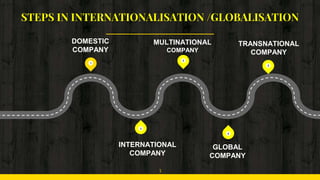
This document discusses the stages of internationalization that companies go through as they expand globally. It begins by outlining several drivers of corporate internationalization including cost drivers, government drivers, competitive drivers, and market drivers. It then describes 5 stages of internationalization that companies typically progress through: 1) Domestic Company, 2) International Company, 3) Multinational Company, 4) Global Company, and 5) Transnational Company. For each stage, it provides details on the company's strategy, view of world markets, orientation, key assets, and the role of country units. It concludes by summarizing the differences between each stage in a chart.