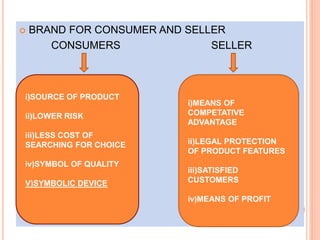
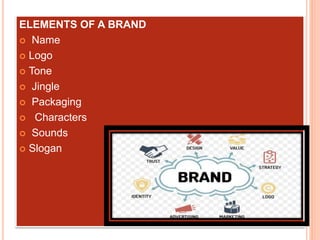
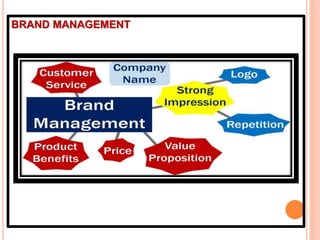
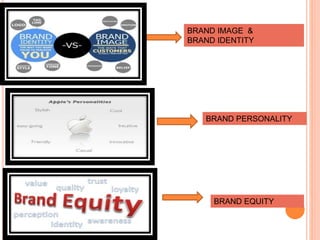
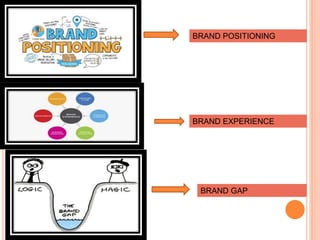
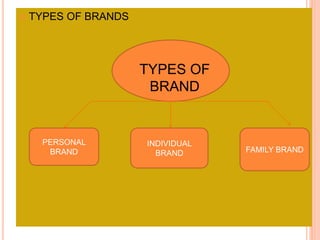
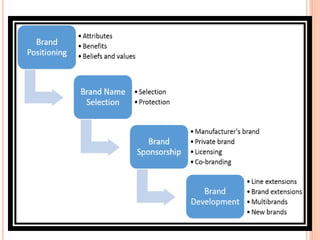
The document provides an in-depth overview of brand management, including its significance, functions, and elements. It covers key concepts such as brand identity, brand equity, and the various types of branding strategies like individual and family branding. Additionally, it explains the responsibilities of brand management and the importance of a brand name in establishing market presence and consumer recognition.