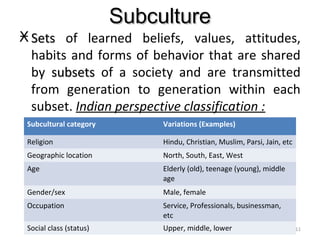
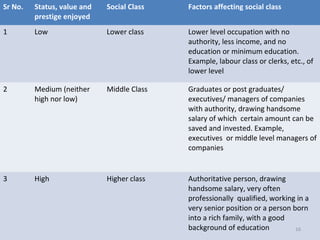
Core values define how products are used in societies and influence acceptable market relationships and behaviors. Culture includes learned beliefs, values, customs, and responses that direct consumer behavior. Cultural characteristics are learned and shared within groups. Marketers must understand how culture affects consumer pre-purchase activities like information search and post-purchase activities like product use. Culture also influences social classes that are hierarchical groups distinguished by factors like occupation, income, education, and prestige. Understanding differences in subcultures and cross-cultural groups is important for marketers to effectively target various national markets.