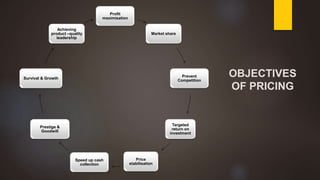
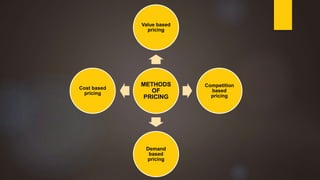
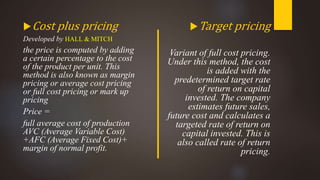
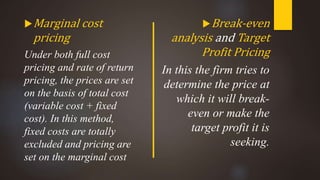
The document discusses pricing as the monetary value charged for products or services and outlines its objectives, including profit maximization and market share. It details various internal and external factors influencing pricing decisions and describes several pricing methods such as cost-based, demand-based, and competition-based pricing. Additionally, it explains concepts like price discrimination and value-based pricing, emphasizing the importance of perceived value in setting prices.