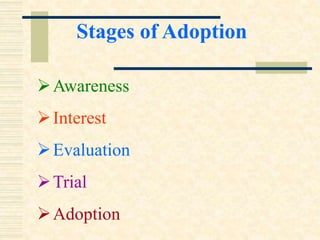
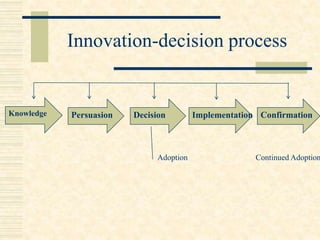
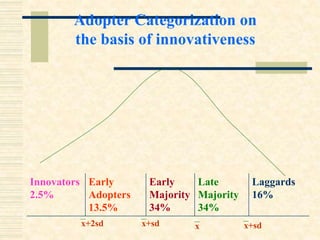
The document discusses the diffusion and adoption of innovations in agricultural development, outlining the processes through which new ideas are communicated and implemented among social systems. It details the stages of the adoption process, factors influencing adoption, and categorization of adopters based on innovativeness. Key elements affecting the decision to adopt innovations include personal, situational, and social factors.