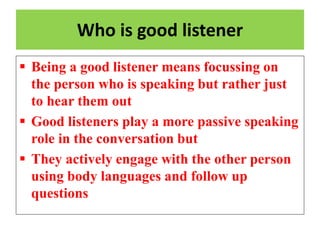
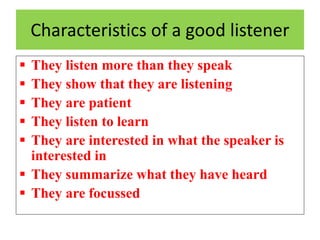
This document discusses feedback in communication and its importance. It provides definitions of feedback and notes that feedback helps enhance adoption rates and understanding by promoting free communication. It identifies some difficulties in obtaining feedback, such as limitations of communication channels, shyness of receivers, and socioeconomic barriers. The document recommends several methods for encouraging feedback, such as not getting defensive, updating knowledge, and ensuring feedback is timely. Overall, the document emphasizes that feedback is important for removing barriers, facilitating action, rectifying errors, and improving the communication process.