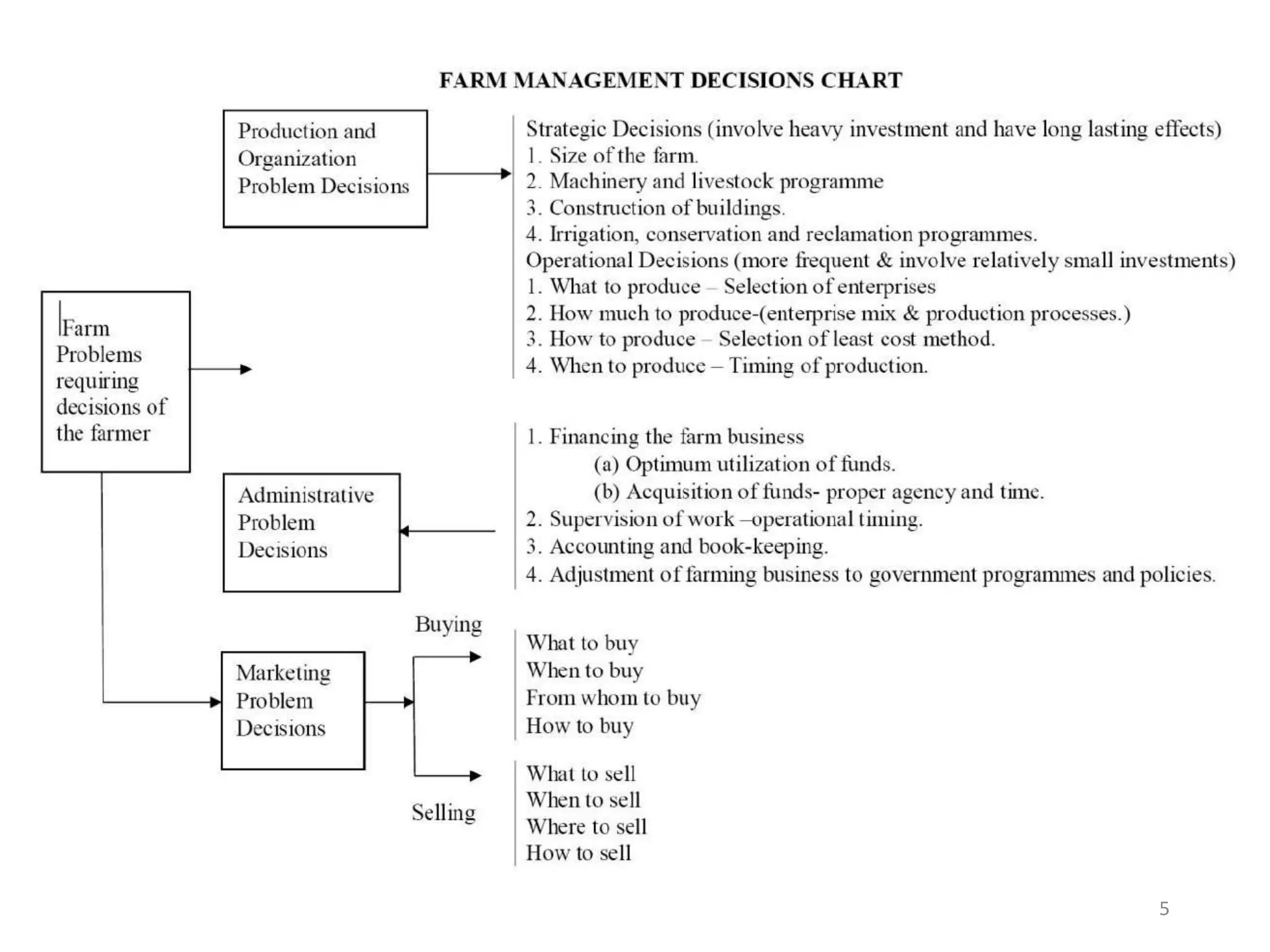
Farm management involves making strategic decisions about how to organize and operate a farm to maximize sustainable profits. There are three main types of farm management decisions: organizational decisions, which involve determining what and how much to produce, as well as strategic decisions about farm size and infrastructure; administrative decisions around financing, supervision, and record keeping; and marketing decisions regarding buying farm inputs and selling farm outputs, including when, where, and to whom to sell. Making good decisions is essential to the sustainable profitability and success of a farm business over time.