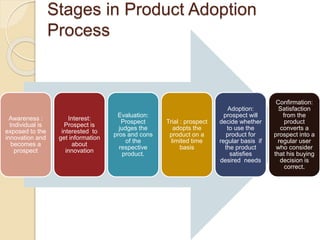
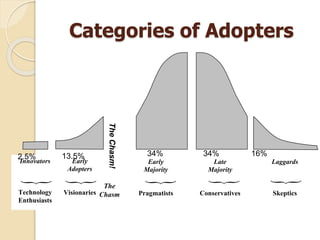
The document outlines the innovation adoption process, detailing five stages that individuals go through: awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption, with a focus on the factors influencing the rate of adoption such as relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, trialability, communicability, and observability. It categorizes adopters into different groups including innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards, each defined by their characteristics and willingness to adopt new technologies. The document emphasizes the importance of understanding these stages and categories for successful innovation diffusion.