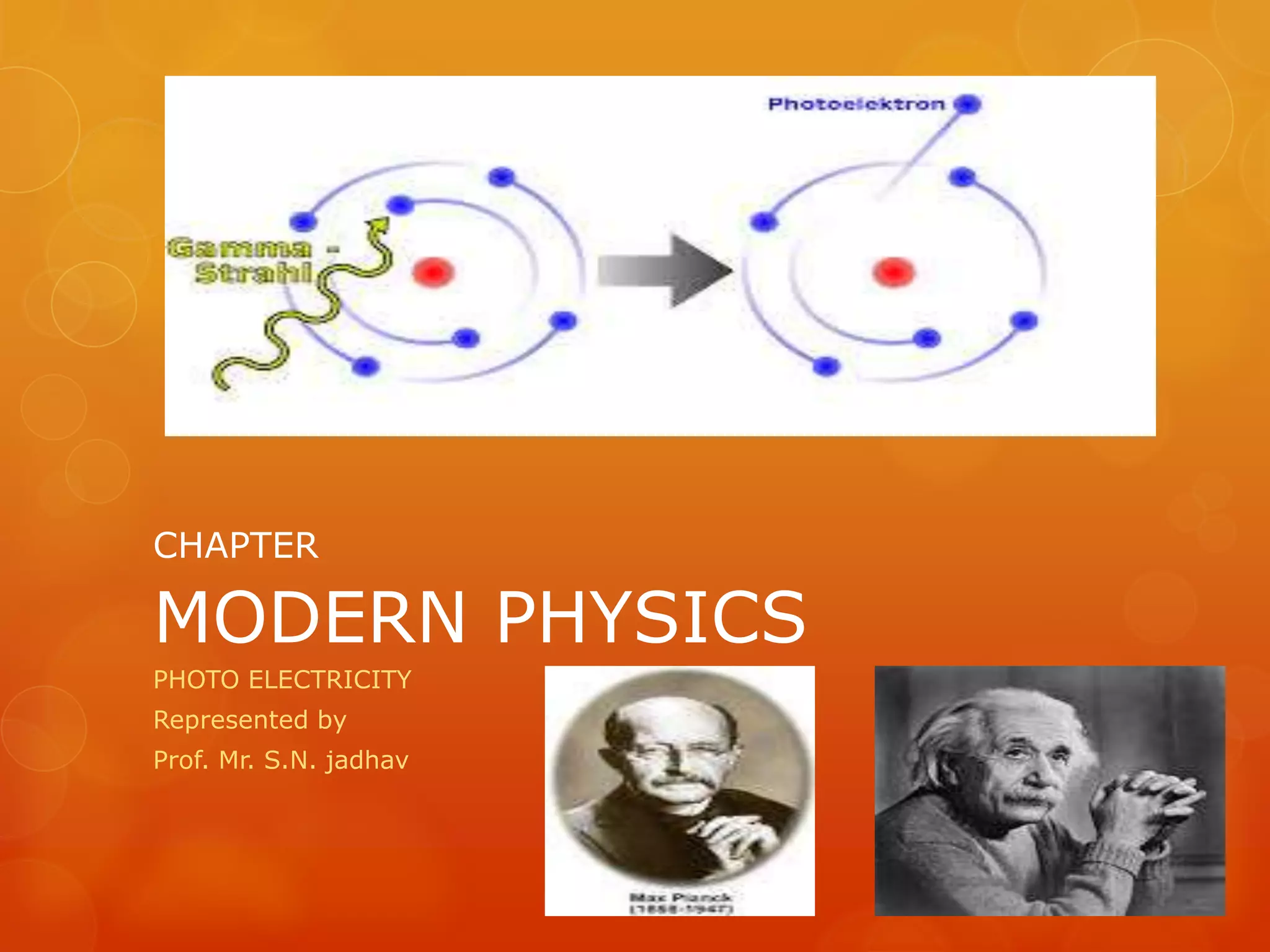
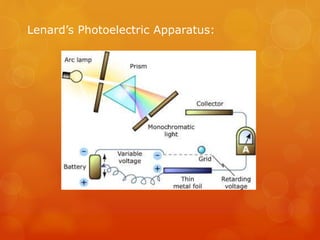
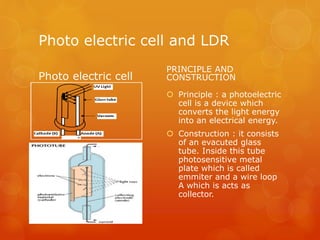
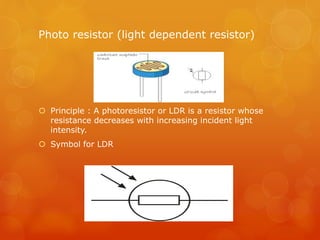
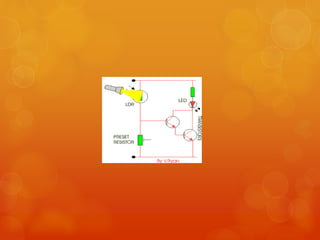
Einstein proposed that light is made up of discrete packets called photons. Each photon has an energy proportional to its frequency. Photons have no mass or charge and travel at the speed of light. The photoelectric effect occurs when photons of sufficient frequency eject electrons from metal surfaces. Experiments showed that the kinetic energy of ejected electrons depends on photon frequency, not intensity. Einstein explained this using a quantum model where photons transfer discrete units of energy. Photoelectric cells and light dependent resistors use this effect, finding applications in cameras, alarms, and other devices.