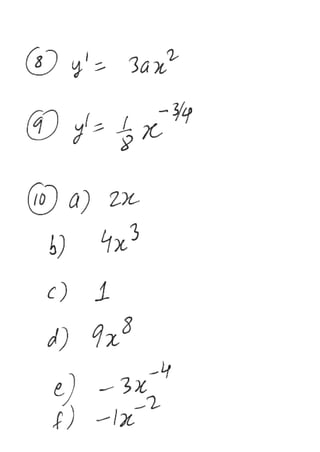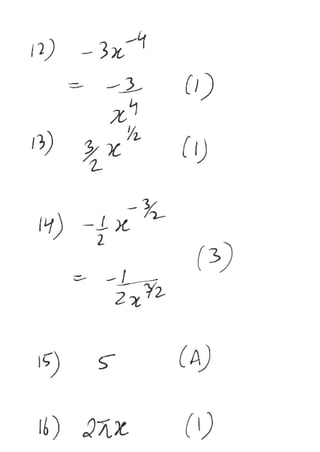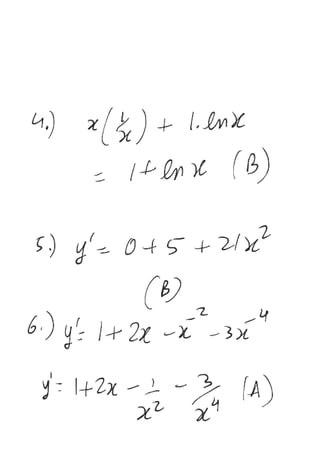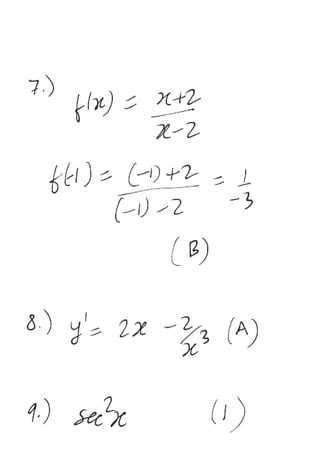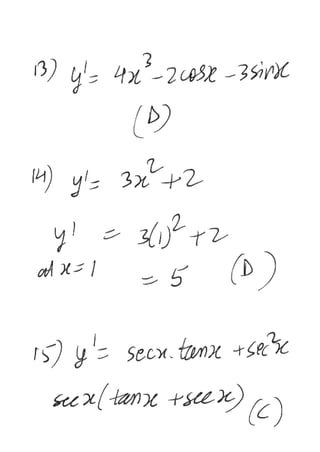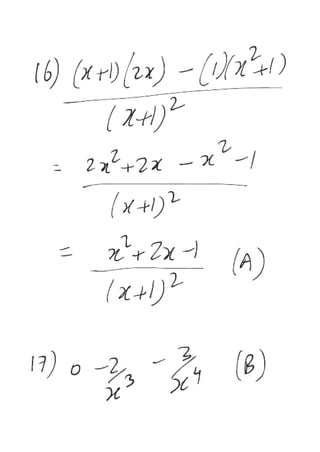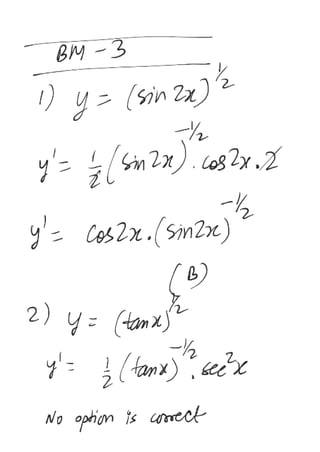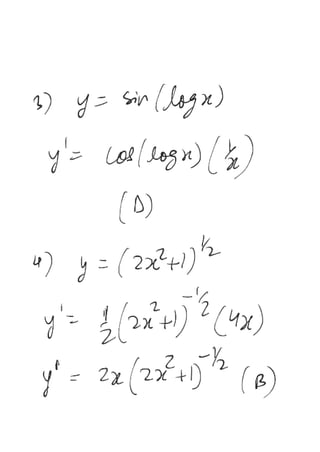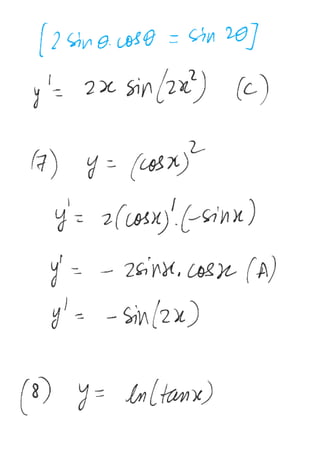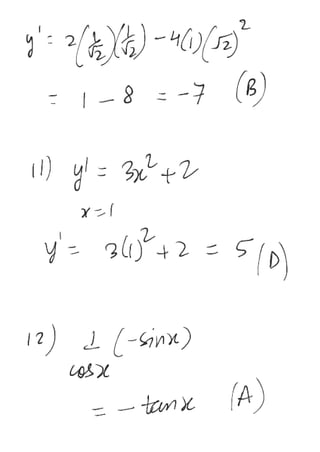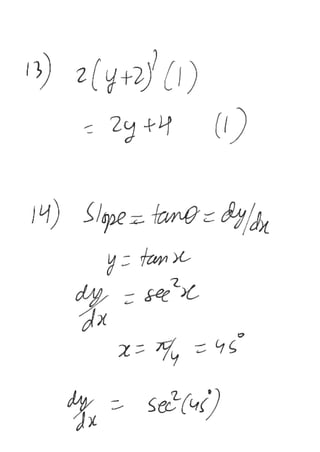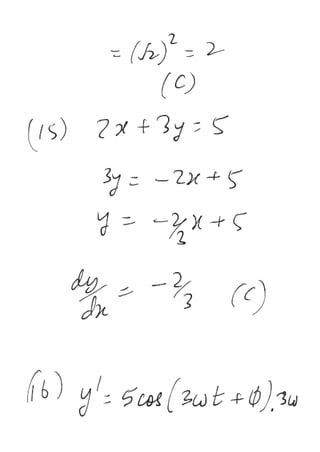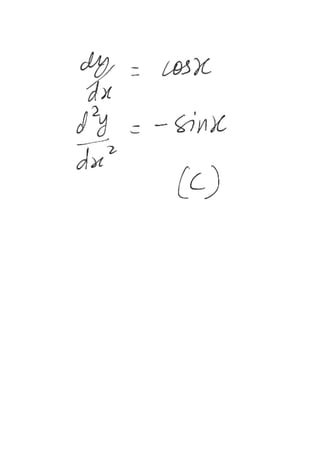The document provides a series of exercises focused on differentiating various mathematical functions with respect to x. It includes examples with polynomial, trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions, along with multiple-choice questions about their derivatives. It also addresses the concepts of slope and double differentiation.

![1. If y = x
3
+ 2x
2
+ 7x + 8 then
dx
dy
will be -
(A) 3x2
+ 2x + 15 (B) 3x2
+ 4x + 7 (C) x
3
+ 2x
2
+ 15 (D) x
3
+ 4x + 7
2. If y = x2
sin x , then
dx
dy will be -
(A) x2
cos x + 2x sin x (B) 2x sin x (C) x
2
cos x (D) 2 x cos x
3. If y = ex
. cot x then
dx
dy will be
(A) ex
cot x – cosec2
x (B) e
x
cosec2
x (C) e
x
[cot x – cosec2
x]
(D) e
x
cot x
dx
dy
will be
4. If y = x nx then
(A) nx + x (B) 1 + n x (C) nx (D) 1
dx
dy
5. y = 4 + 5x + 7x3
. Find
(A) 5 - 21x
2
(B) 5 + 21x2
(C) 9 + 7x
2
(D) 5 + 21x
x3
1
x
1
Find
dx
dy
6. y = x +x
2
. +
(A)1 + 2x –
x4
2
3
x
1
(B) 1 + 2x – 4
2
x
(C) 1 – 2x – 4
3
x
(D) 1 + 2x – 3
3
x
7. If f(x) =
x 2
x 2
The value f (–1) is
(A)
3
1
(B)
3
1
(C) 3 (D) –3
8. y = x2
+
x
1
2
.Find
dx
dy
(A) 2x –
x3
2
(B) 2x – 4
2
x
(C) 2x +
x3
2
(D) None of these
2
x
1
2
x
1
2
x
1
Lakshya Educare
PHYSICS
Turtle Tutorials, Marris Road, Aligarh, PH 7617733555 | www.turtletutorials.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/differentiationassignment-240503043235-1014934d/85/differentiation-assignment-pdf-for-class-11th-2-320.jpg)


![Q.10 If y = sin2
x – 2 tan2
x , then
dx
dy
at x =
4
π
is -
(A) – 11 (B) – 7 (C) – 13 (D) – 15
Q.11 If y = x3
+ 2x + 1 then
dx
dy
at x = 1 is -
(A) 6 (B) 7 (C) 8 (D) 5)
Q.12
dx
d
[log(cosx)] is :
(1) –tan x (2) tan x (3) cot x (4) –cot x
Q.13
dy
d
(y + 2)2
is equal to
(1) 2y + 4 (2) 2y – 4 (3) 4 + y2
(4) 2(y + 1)
14. Slope of graph y = tanx drawn between y and x, at x = is :
4
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D)
2
1
15. Equation of straight line is 2x + 3y = 5. Slope of the straight line is :
(B) 2/3 (C) –2/3 (D) –3/2
(A) 3/2
dt
dy
16. y = 5sin (3 t + )
where and are constant
Find
(A) 15 cos (3 t + )
(C) 15 cos (3 t + )
(B) 15 cos (3 t)
(D) 5 cos (3 t + )
dt
17. If y = e
kt
then
dy
will be
(A) ekt
(B) ekt
/ k (C) tekt
(D) ke
kt
ss
18. Differentiation of sin(x
2
) w.r.t. x is -
(A) cos (x
2
) (B) 2x cos(x
2
) (C) x
2
cos(x
2
) (D) – cos (2x)
19. Double differentiation of displacement w.r.t. time is :
(A) acceleration (B) velocity (C) force (D) none
2
dx
2
If y = x3
then
d y is -
20.
(A) 6x
2
(B) 6x (C) 3x
2
(D) 3x
dx2
d2
y
will be :
21. If y = sinx, then
(A) cos x (B) sin x (C) – sin x (D) sin x + C
Lakshya Educare
Turtle Tutorials, Marris Road, Aligarh, PH 7617733555 | www.turtletutorials.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/differentiationassignment-240503043235-1014934d/85/differentiation-assignment-pdf-for-class-11th-5-320.jpg)