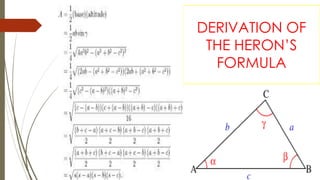
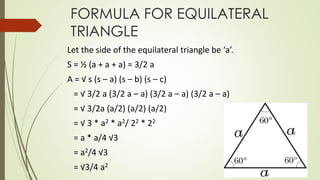
Heron's formula provides a way to calculate the area of a triangle when only the lengths of the three sides are known. It was derived by the Greek mathematician Heron of Alexandria around 10 AD. The formula expresses the area of a triangle in terms of its semiperimeter (s = (a + b + c)/2) and the lengths of its three sides (a, b, c). It can be written as: A = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c), where A is the area of the triangle. The document provides an example of using Heron's formula to find the area of an equilateral triangle and discusses applications of the formula.