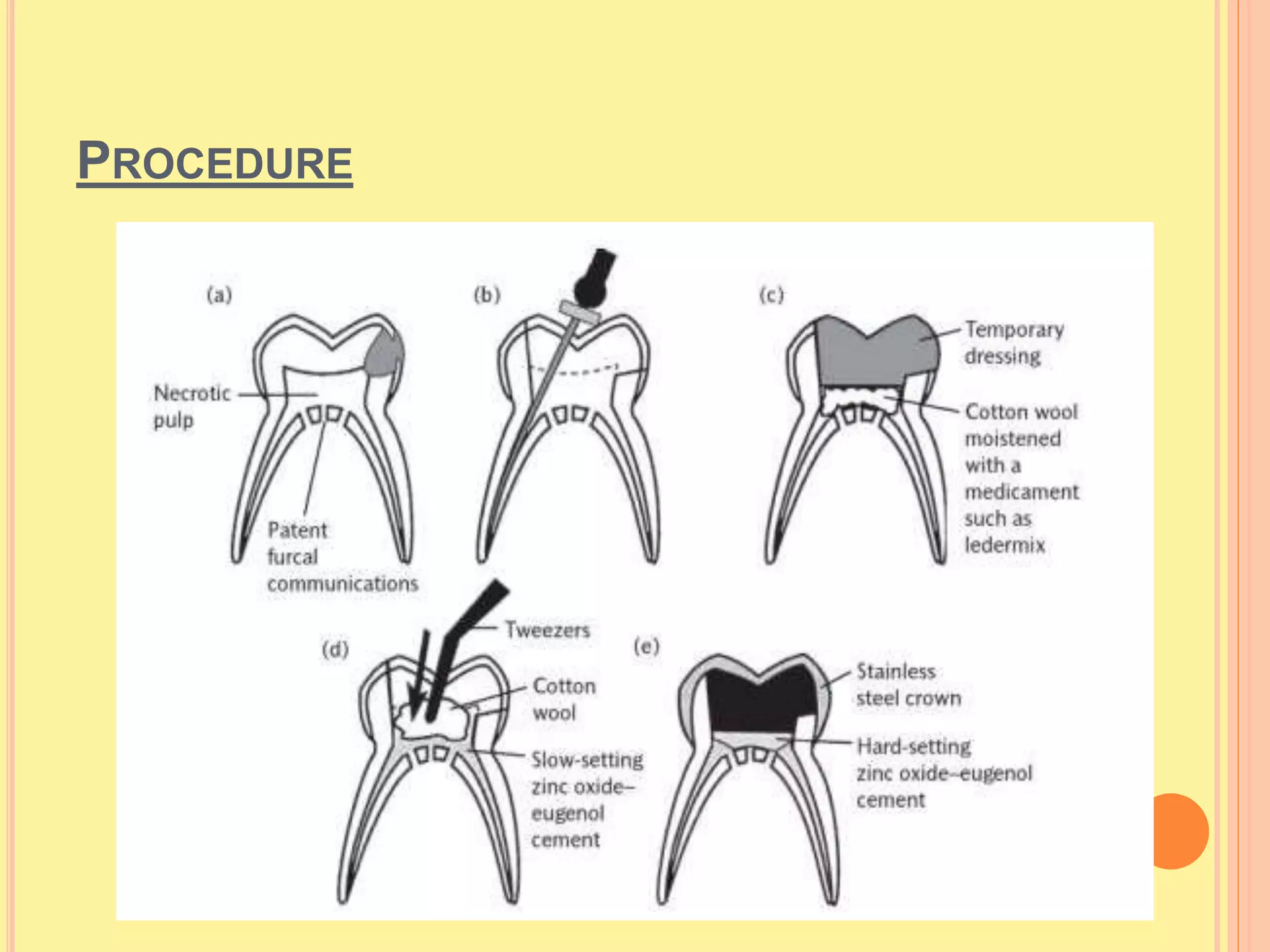
Pulpotomy involves removing the coronal portion of the pulp and placing a medicament, indicated for large carious lesions involving the marginal ridge in a vital tooth with no pain or infection. Pulpectomy removes all pulp tissue from the chamber and root canals, indicated for teeth with irreversible pulpitis throughout the pulp or abscessed primary teeth. Contraindications for both procedures include the presence of infection, bone loss, or non-restorable teeth.