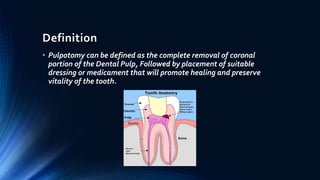
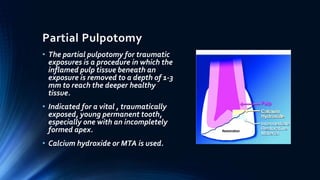
This document defines and discusses pulpotomy procedures. It defines pulpotomy as the removal of the coronal portion of the dental pulp followed by placement of a dressing to promote healing and preserve vitality. It lists indications such as carious exposure in primary teeth and contraindications like evidence of internal resorption. It classifies pulpotomy techniques as vital or non-vital and describes partial pulpotomy and non-vital pulpotomy procedures. The objective of pulpotomy is to remove infected pulp, neutralize infection, and preserve radicular pulp vitality.