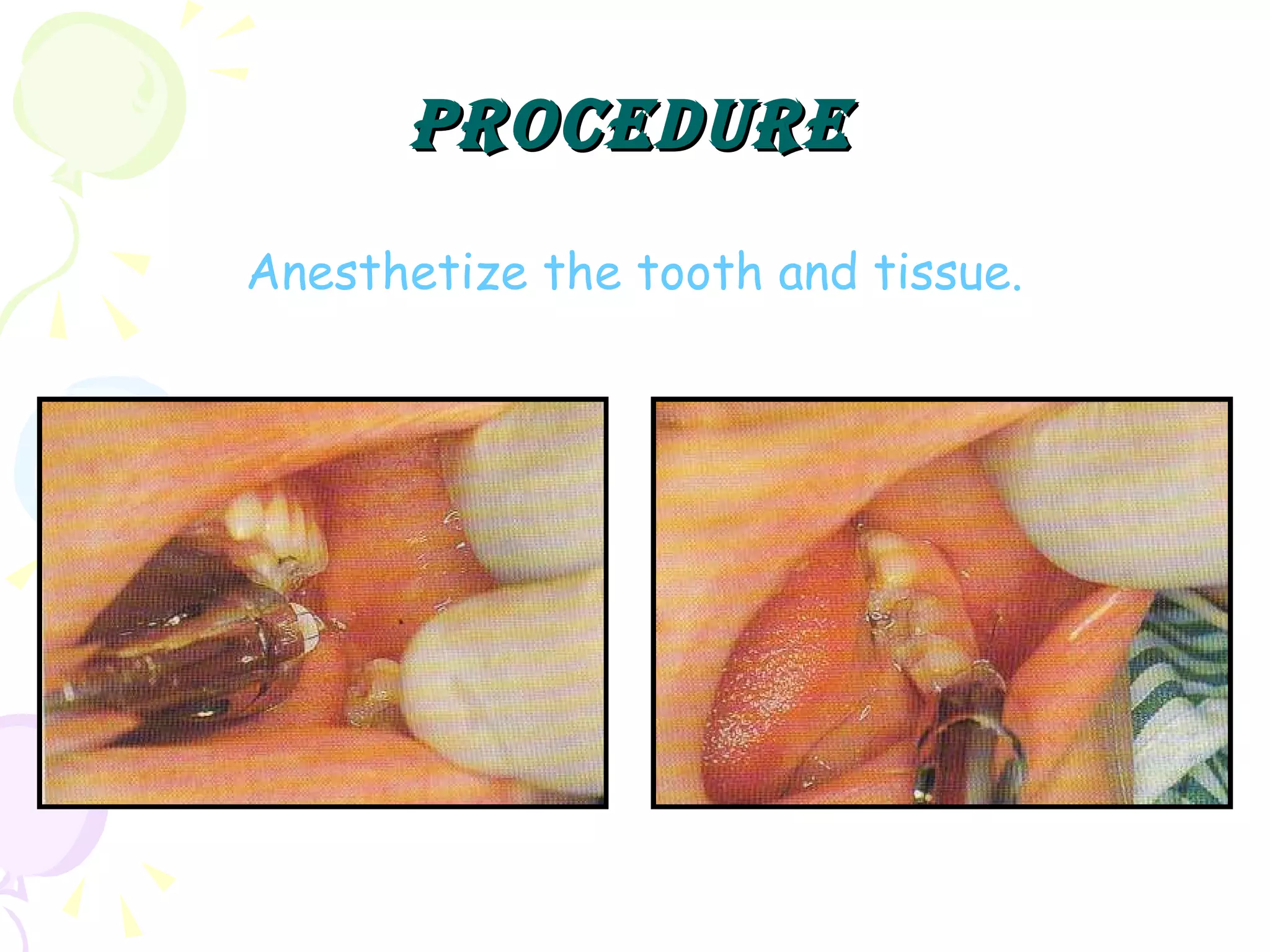
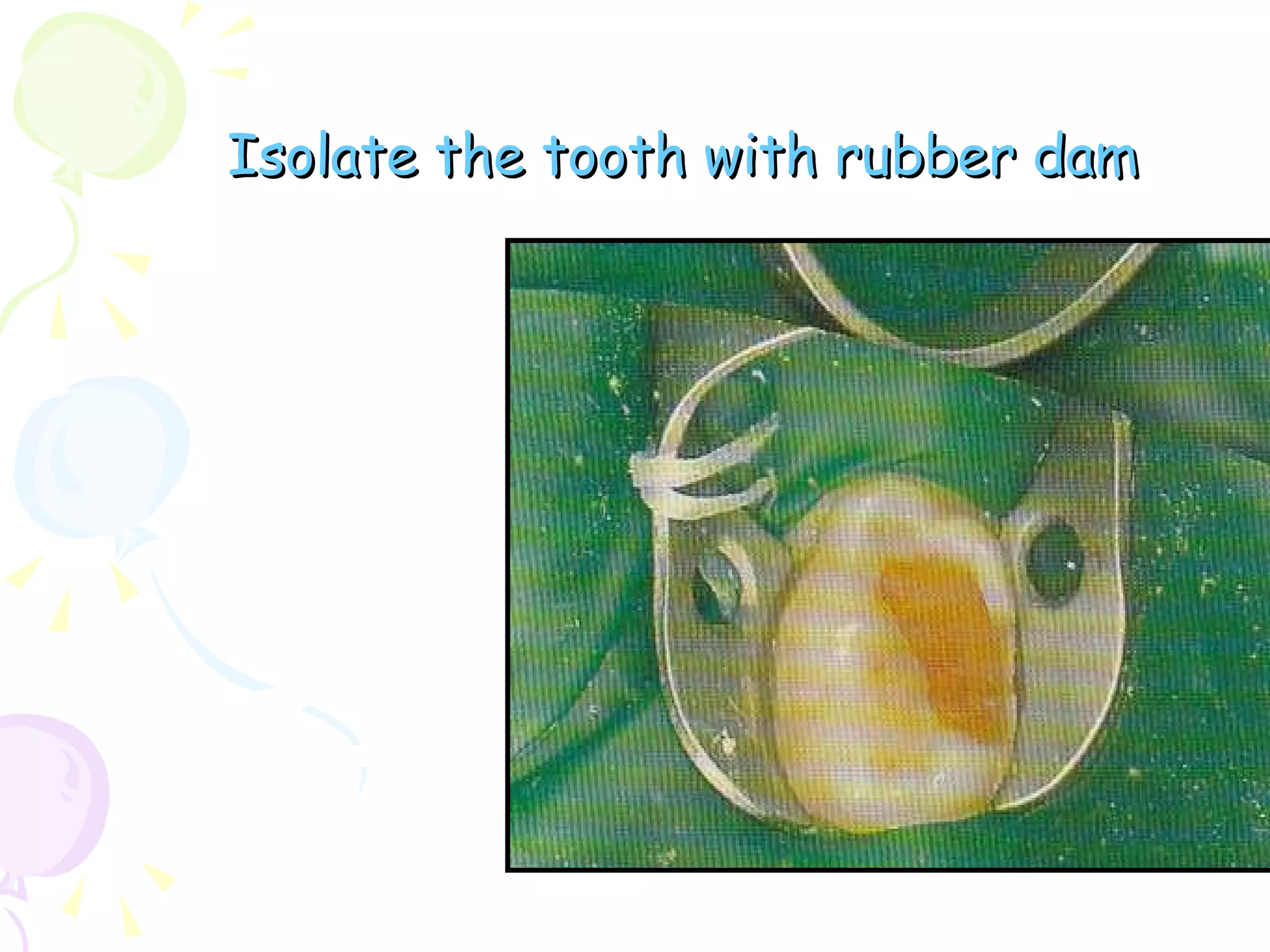
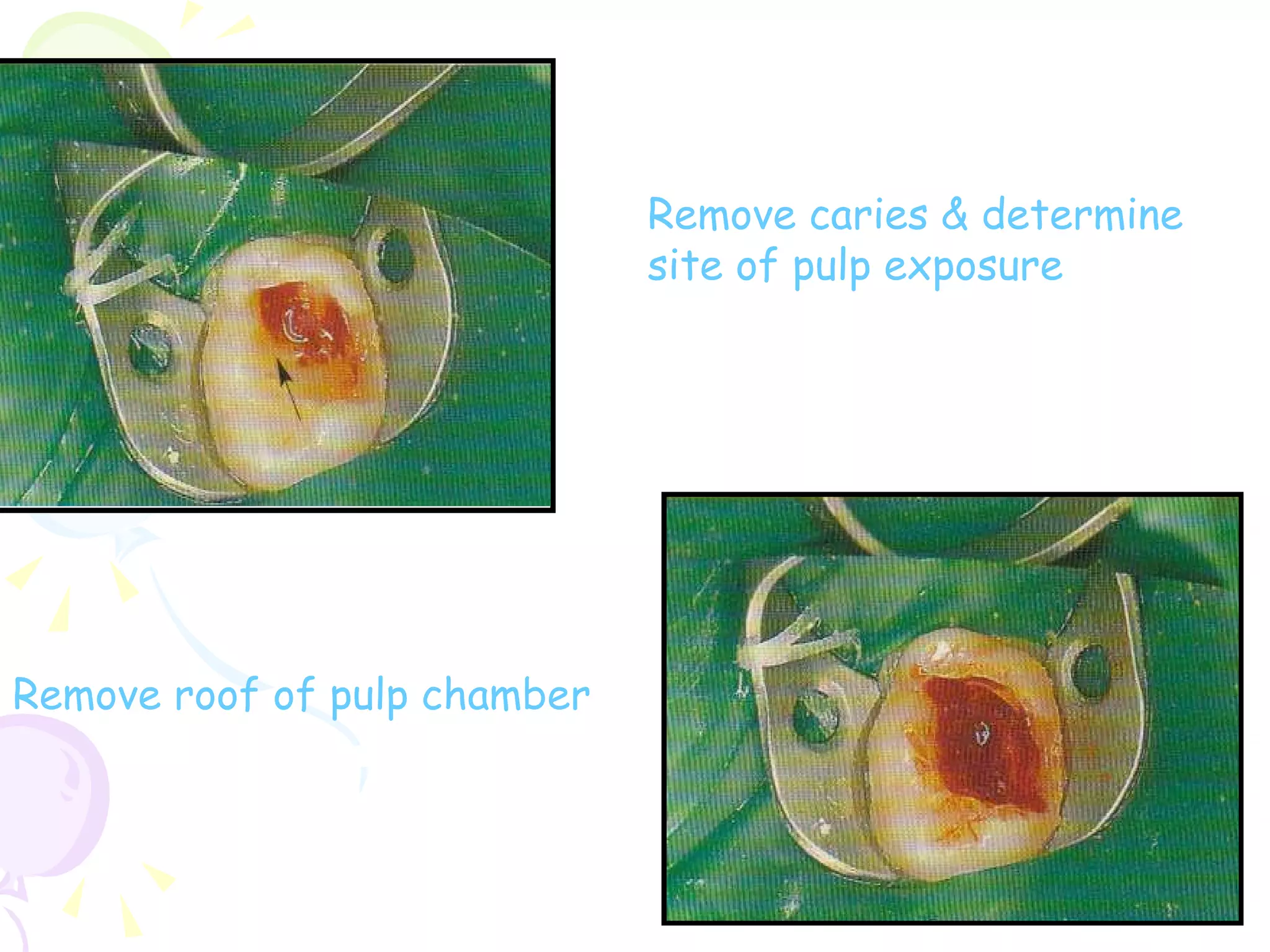
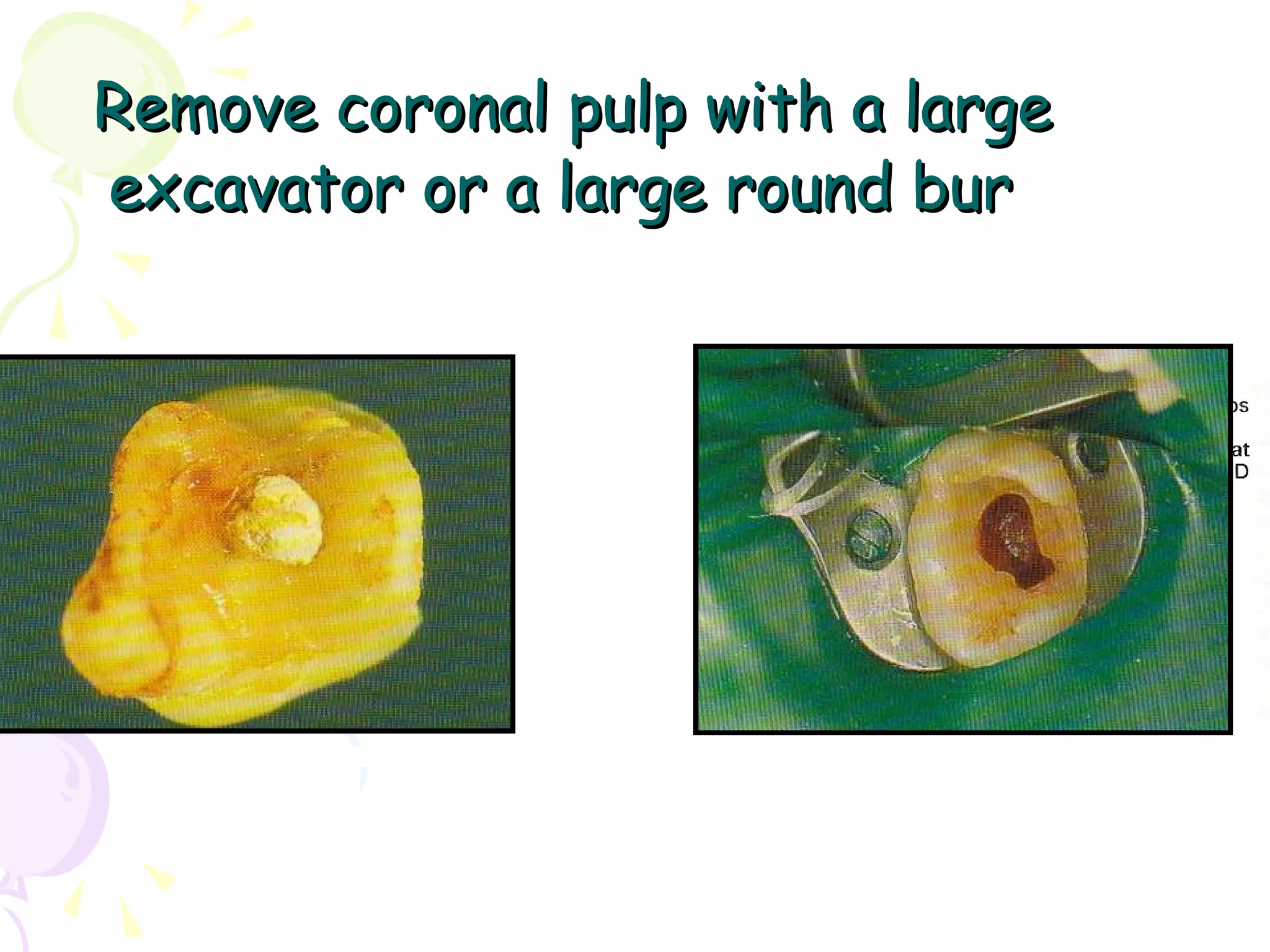
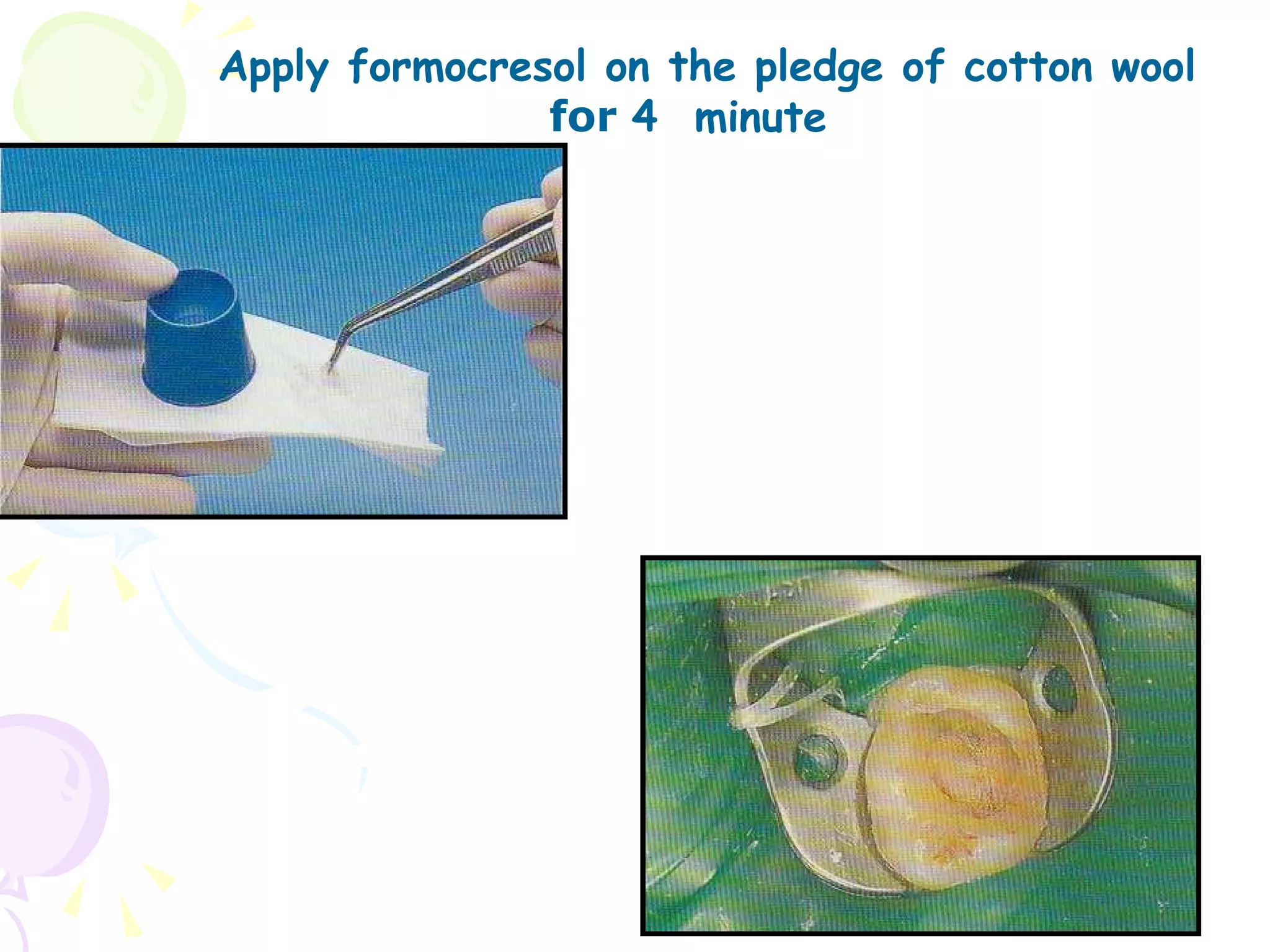
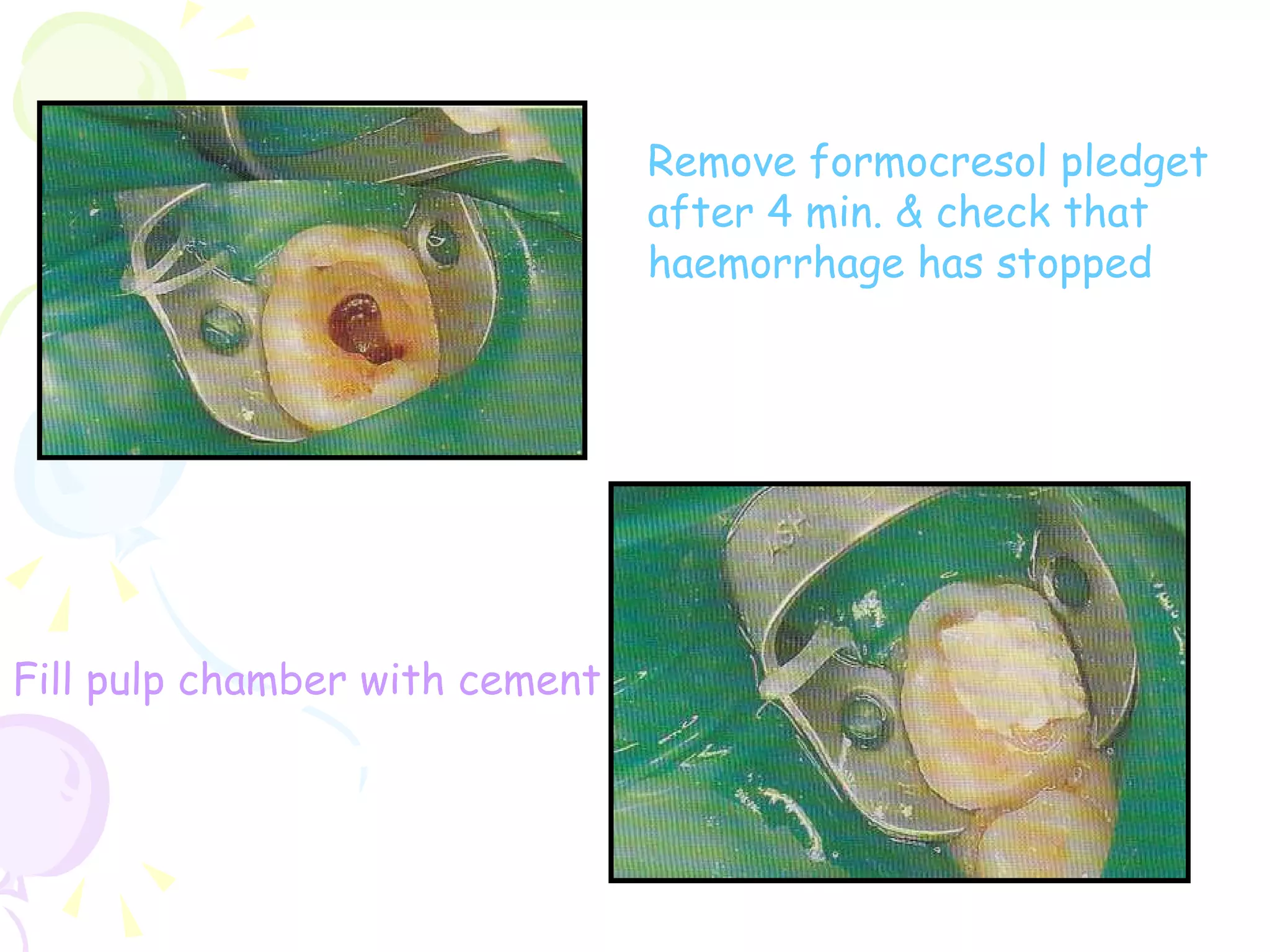
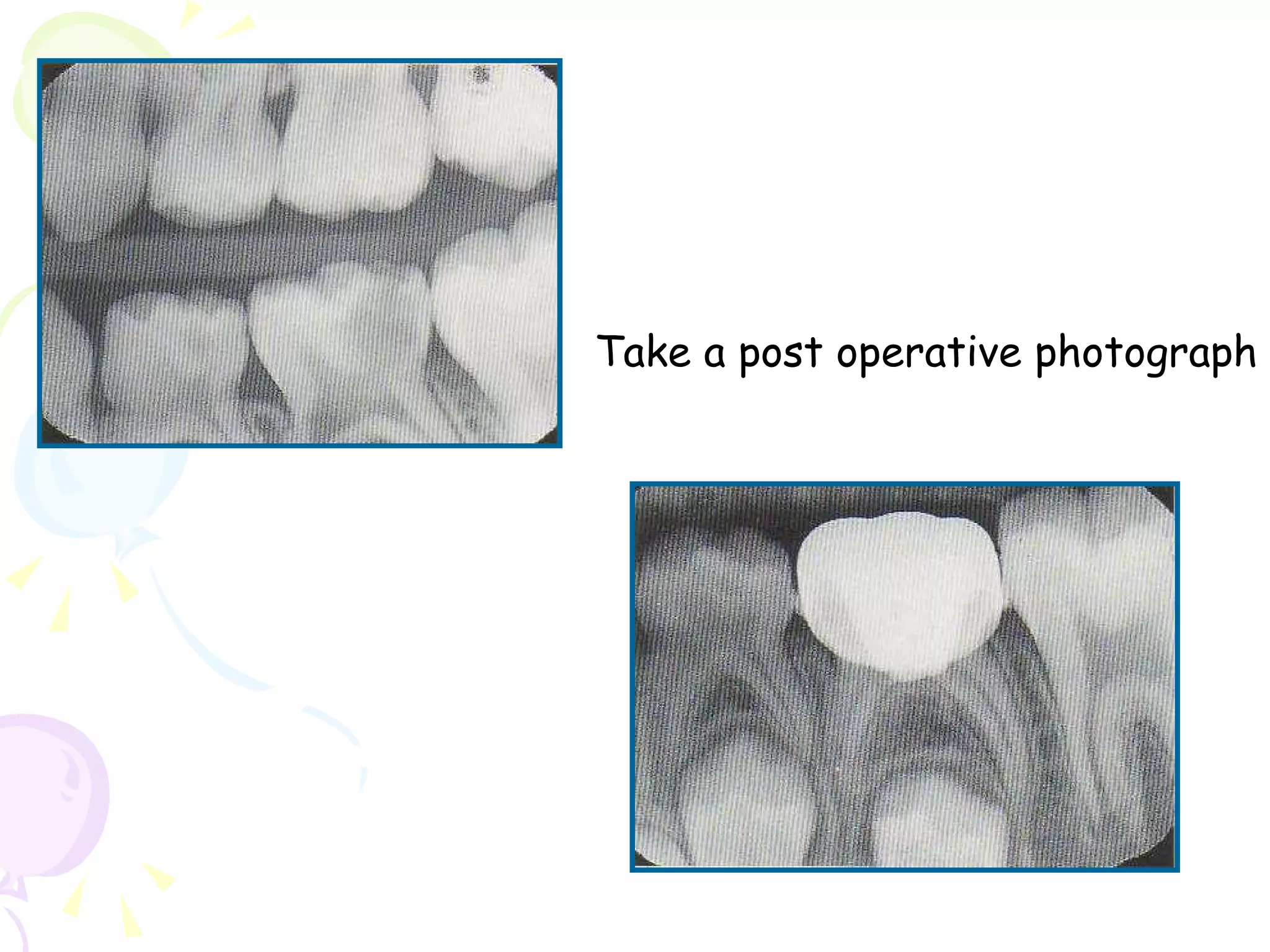
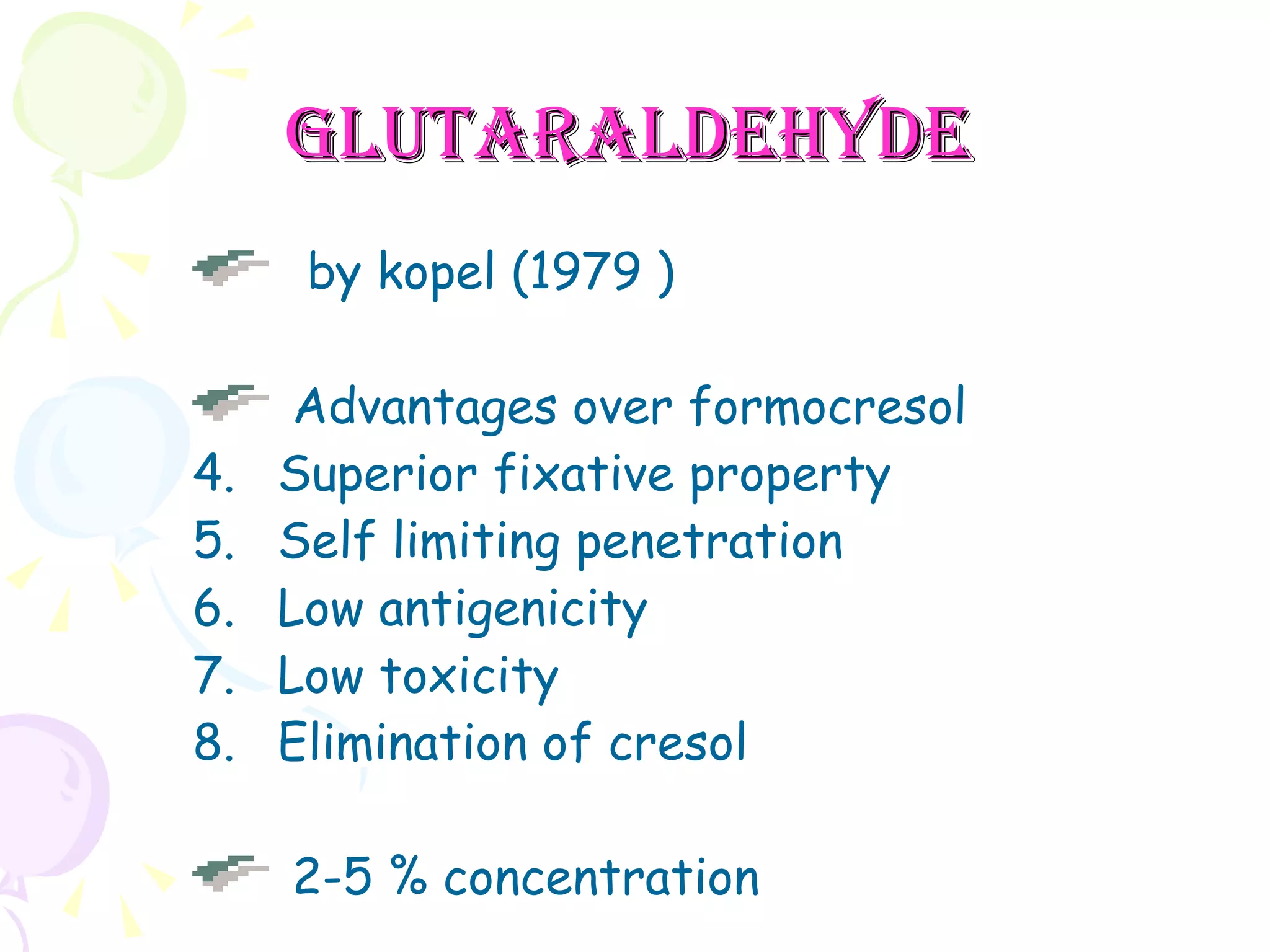
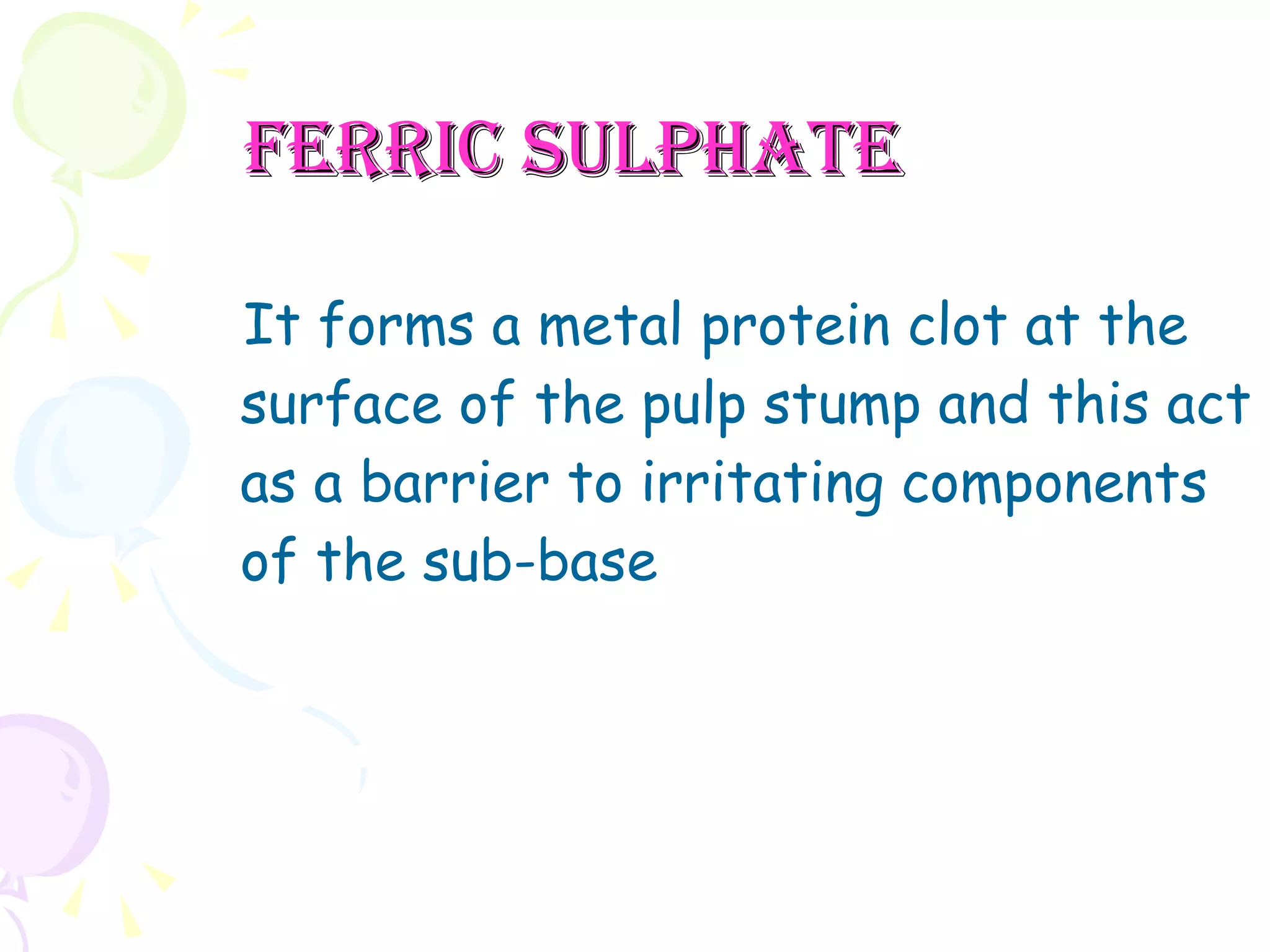
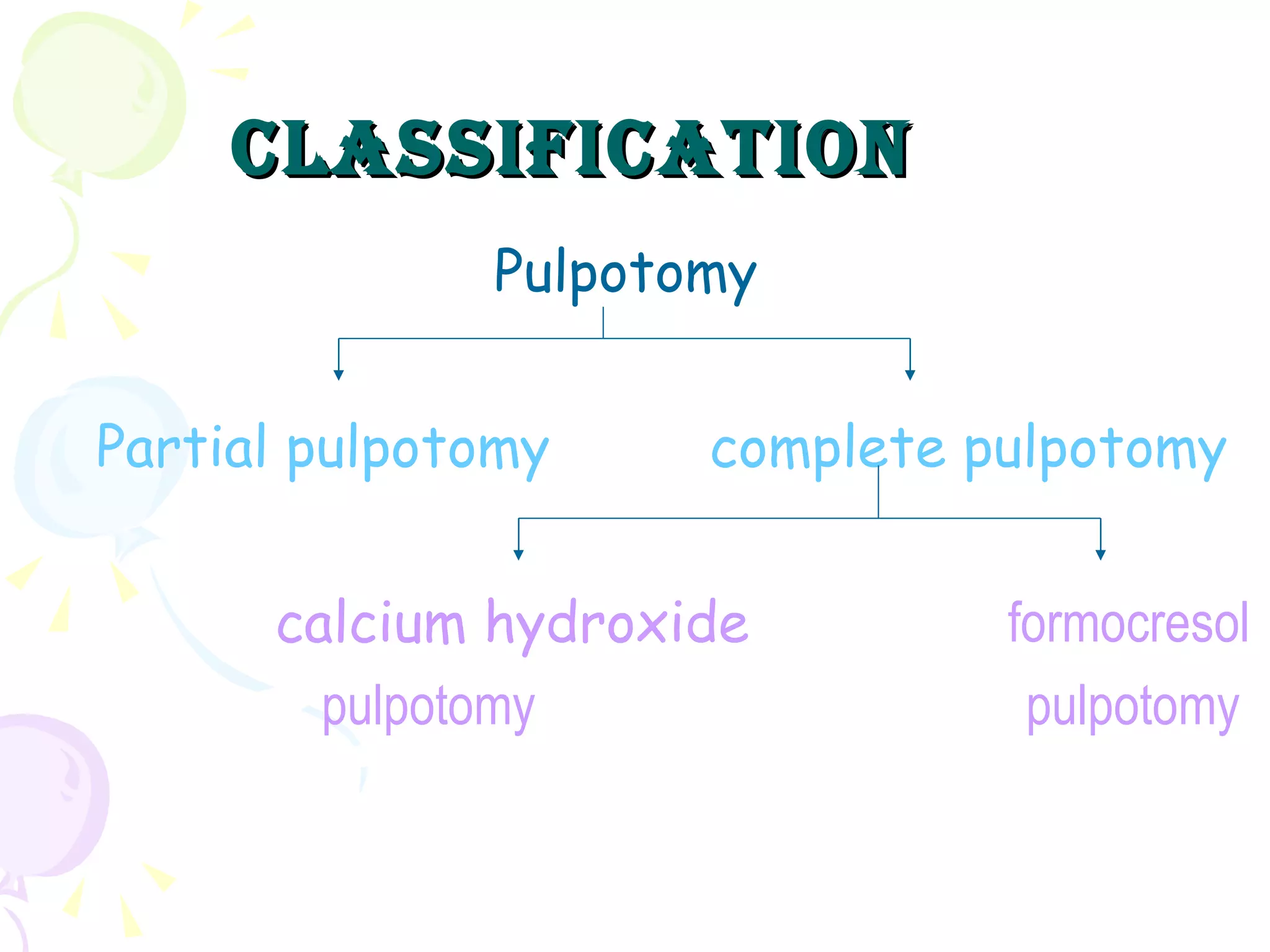
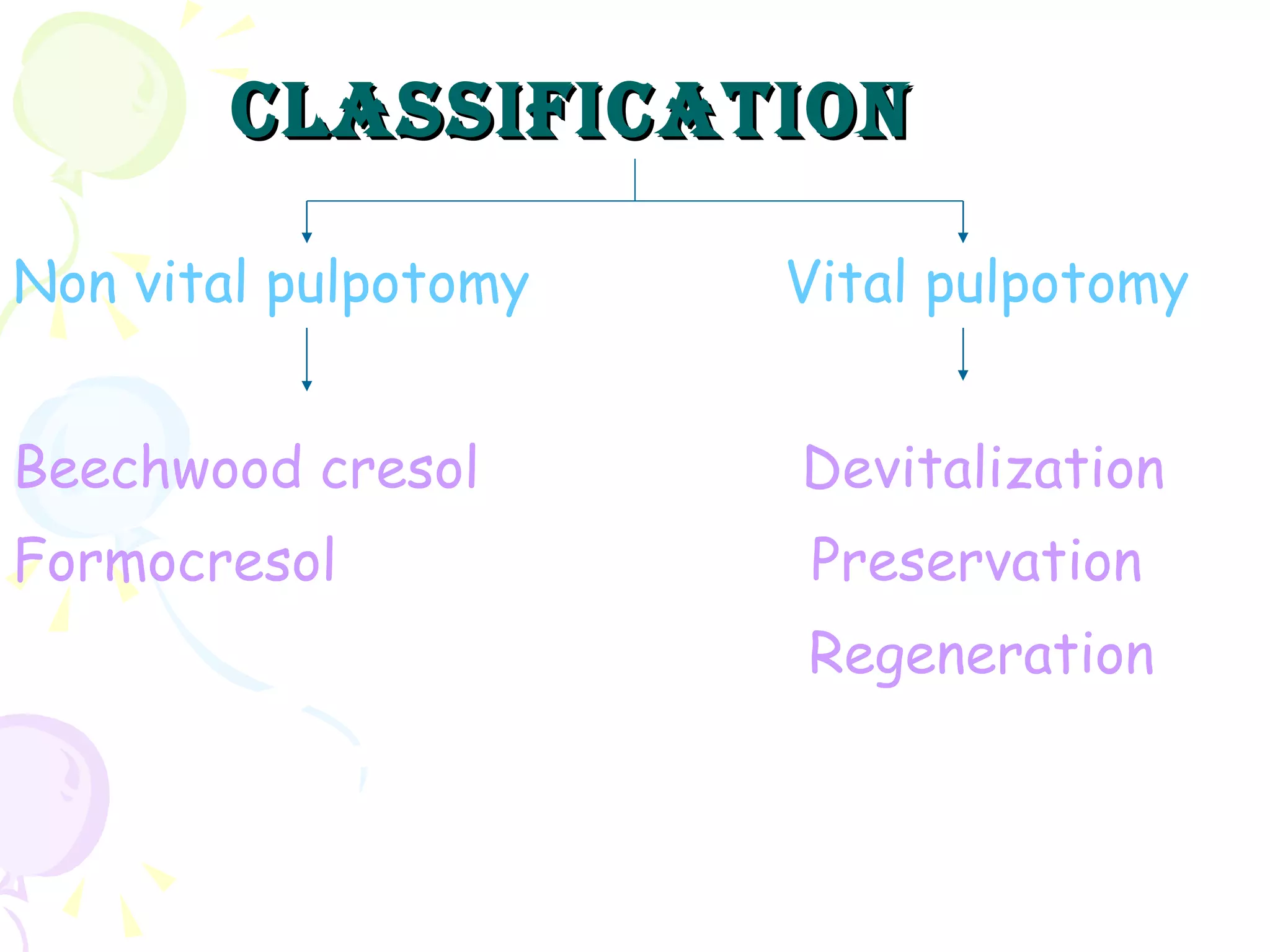
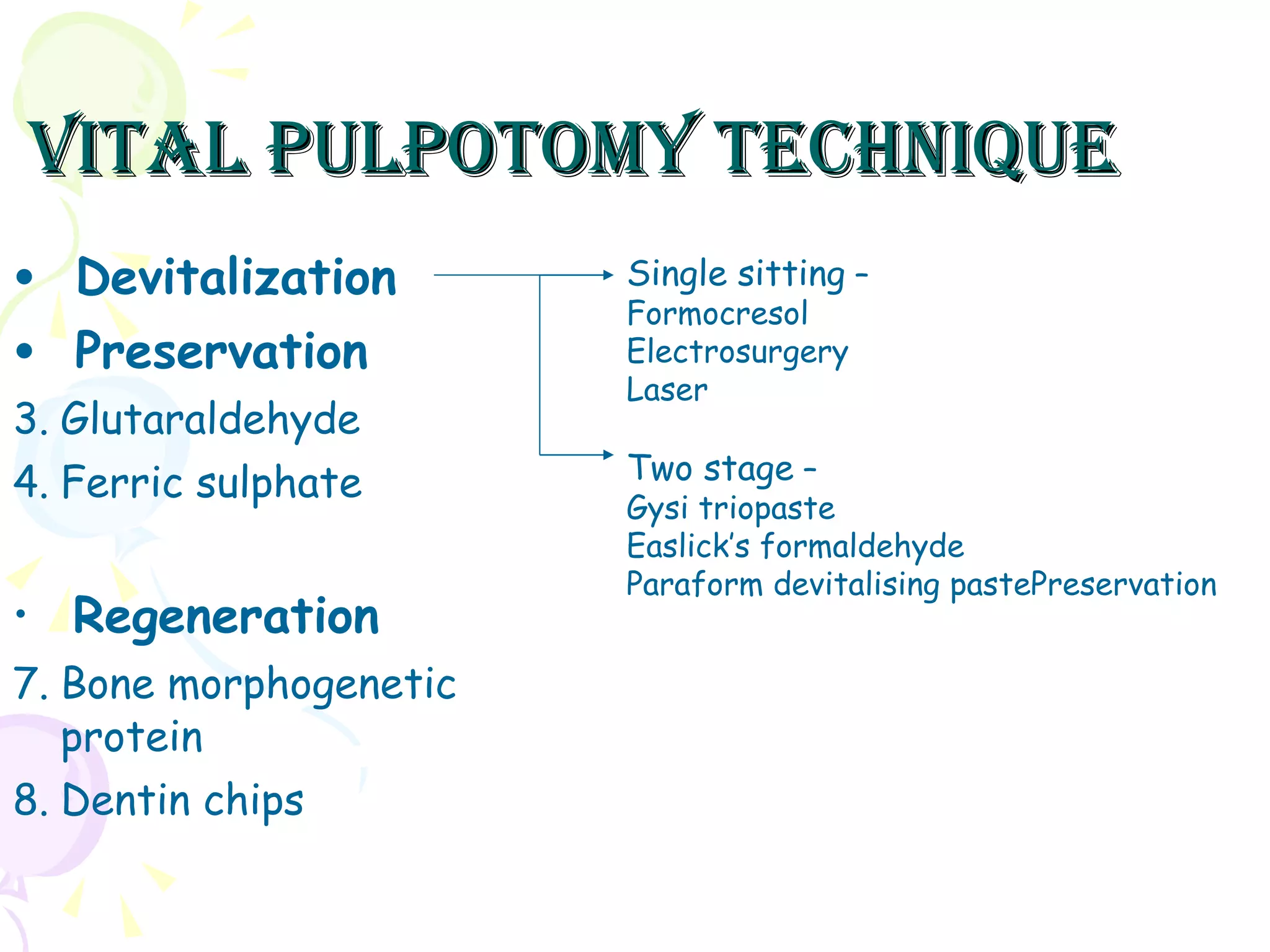
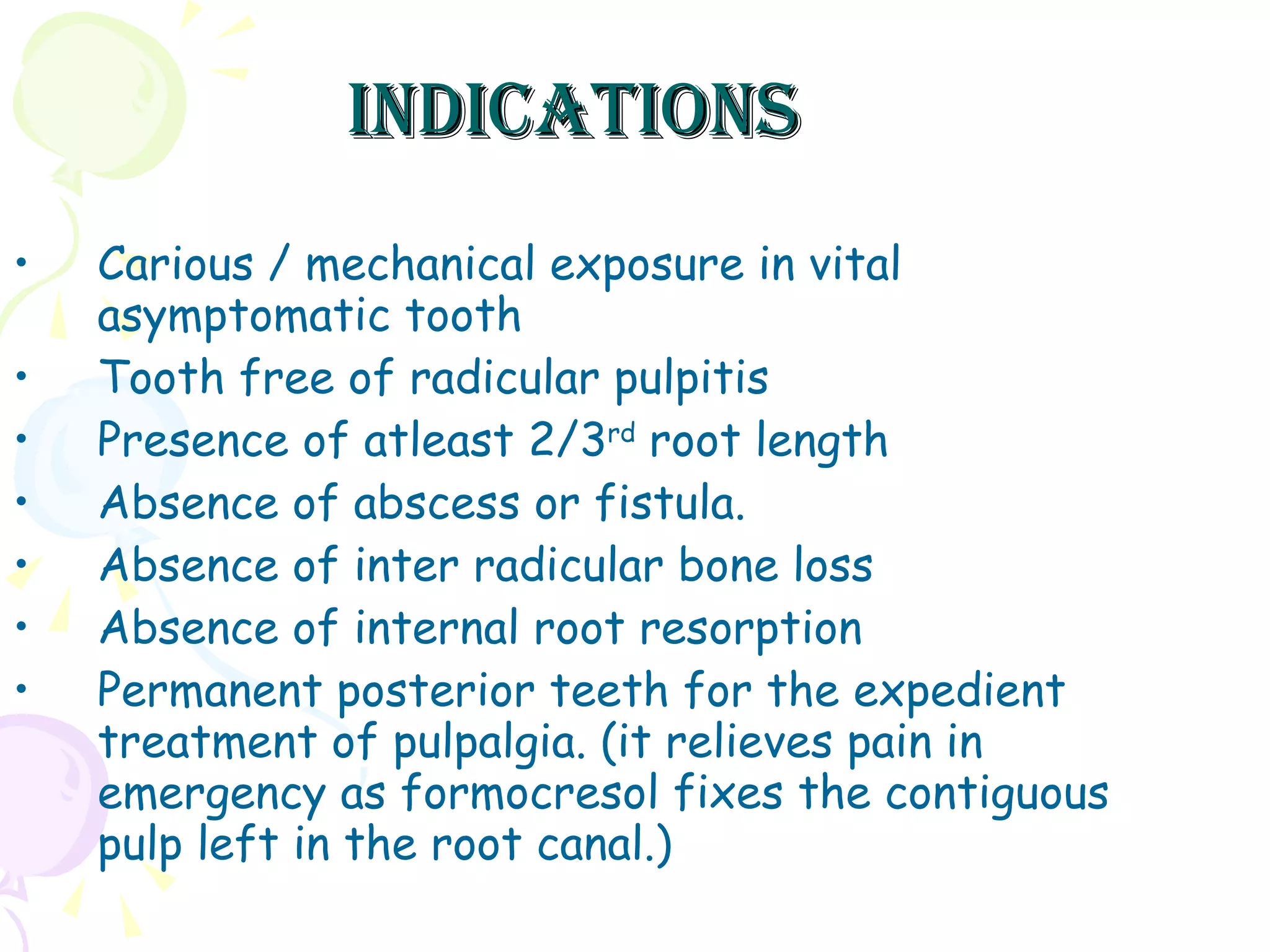
A pulpotomy involves removing the inflamed coronal pulp while leaving the healthy radicular pulp intact. The aim is to relieve pain and allow for root development. Formocresol pulpotomy is commonly used and involves applying formocresol to the exposed pulp stump to fix tissues and eliminate microorganisms. It is performed using either a single-stage or two-stage technique. Other materials used include calcium hydroxide, glutaraldehyde and ferric sulfate. Success rates depend on strict case selection and technique.




![TECHNIQUE The formocresol pulpotomy technique was first advocated by SWEET [1930] He used a multiple sitting technique, which has been subsequently modified to either a single or two stage technique. FORMULA :- 19% Formaldehyde 35% cresol 15% Glycerin & Water To prepare 1.5%concentration of this formula, first mix 3 parts of glycerin with 1 part of distilled water , then add 4 parts of this preparation to 1 part buckley’s formocresol , and throughly mix again.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32310019-pulpotomy-procedures-in-primary-dentition-pedo-120119232230-phpapp02/75/pulpotomy-procedures-in-primary-dentition-10-2048.jpg)