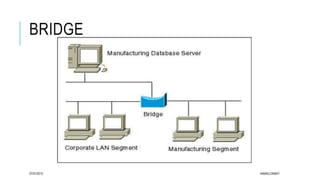
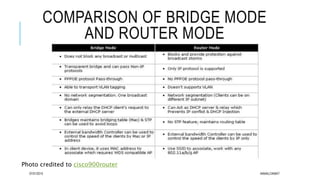
The document explains the differences between hubs, bridges, switches, and routers in networking. Hubs are simple devices that broadcast data to all connected ports, while bridges connect two LANs using the same protocol and filter traffic based on MAC addresses. Switches, which are more advanced, filter and forward packets efficiently based on both MAC and IP addresses, whereas routers operate at a higher level, forwarding data between different networks using IP addresses.