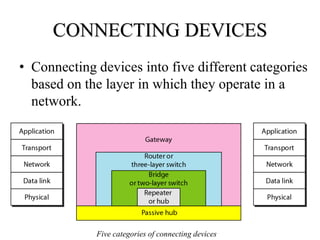
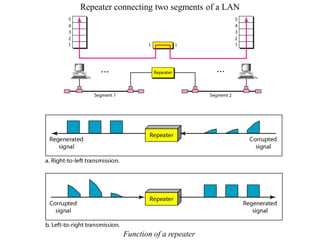
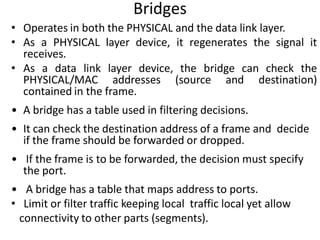
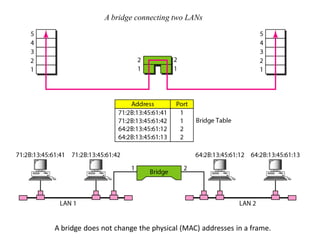
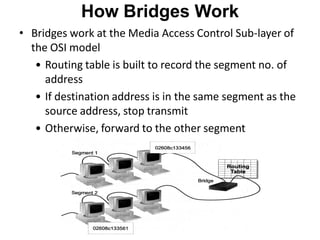
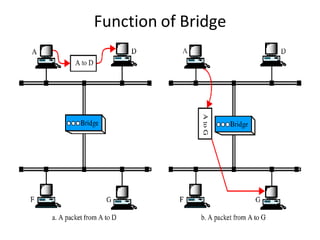
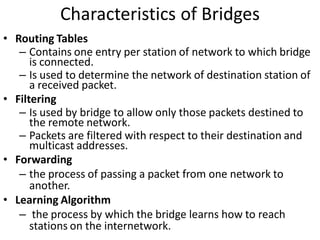
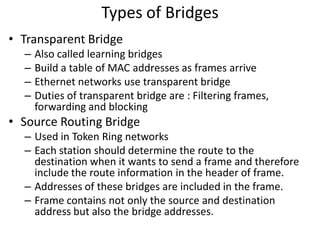
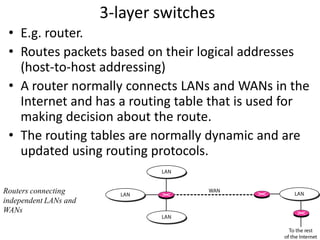
Networking devices can be categorized into five groups based on the OSI layer in which they operate: hubs, repeaters, bridges, routers, and gateways. Hubs and repeaters operate at the physical layer, bridges operate at the data link layer, and routers and gateways operate at the network layer or above. Bridges connect local area networks (LANs) by filtering and forwarding traffic between them based on MAC addresses, while routers connect LANs and wide area networks by routing packets based on logical network layer addresses.