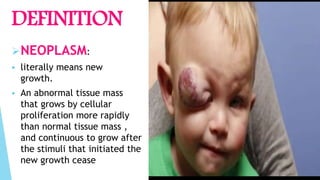
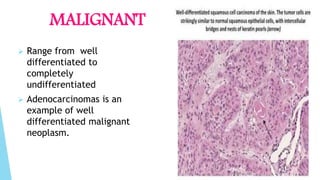
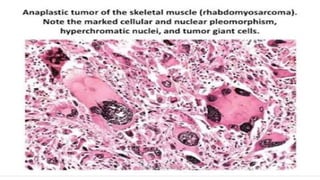
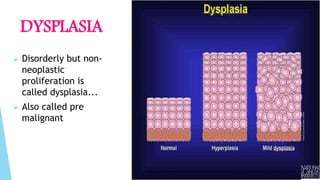
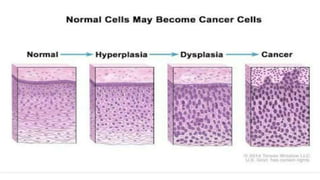
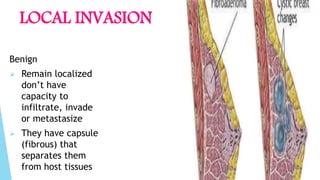
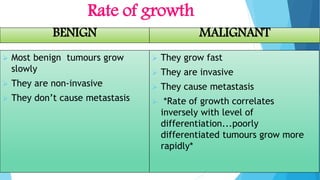
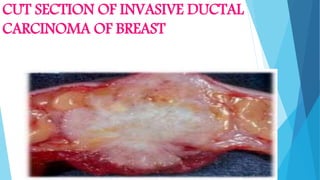
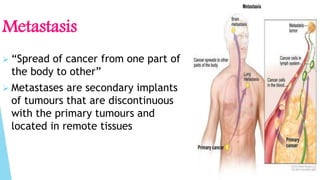
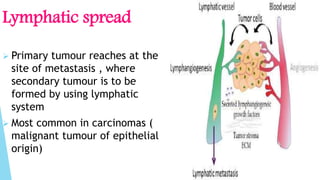
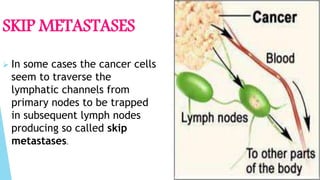
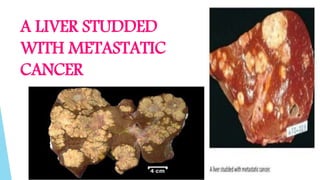
Benign and malignant neoplasms can be differentiated based on four features: differentiation and anaplasia, rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Benign tumors are well differentiated, slow-growing, localized, and often encapsulated, while malignant tumors can be undifferentiated, fast-growing, invasive, and have a tendency to metastasize. The document discusses the characteristics of both types of tumors and provides details on mechanisms of metastasis.