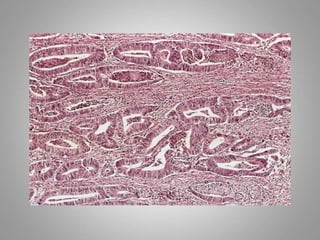
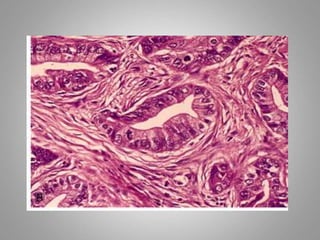
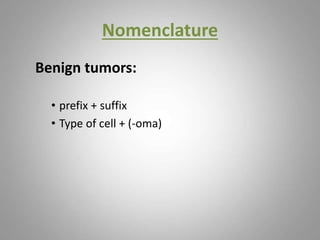
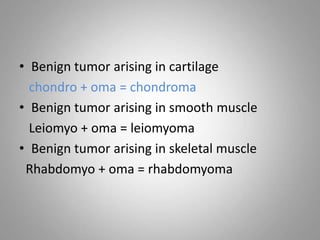
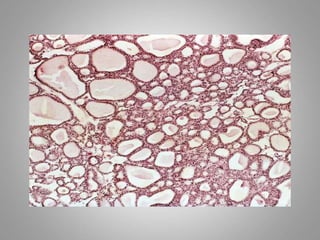
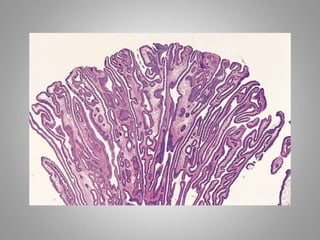
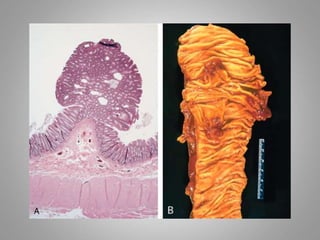
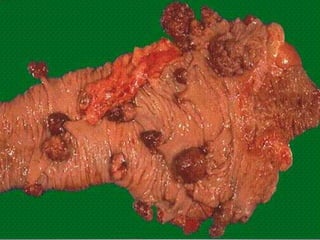
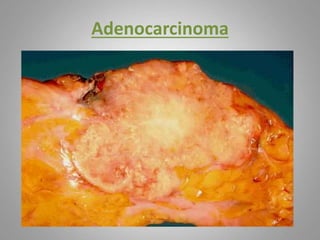
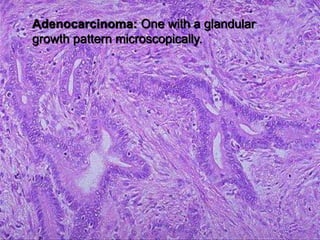
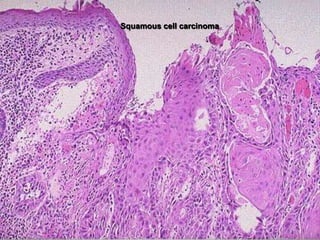
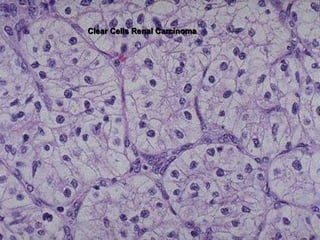
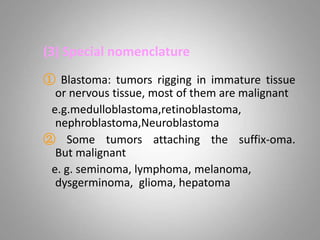
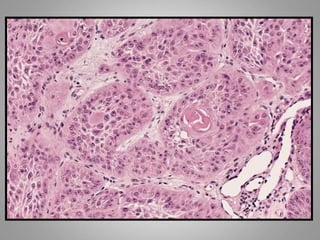
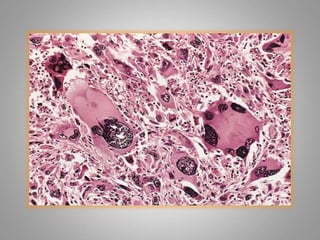
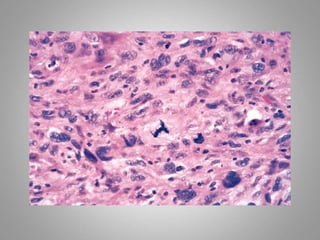
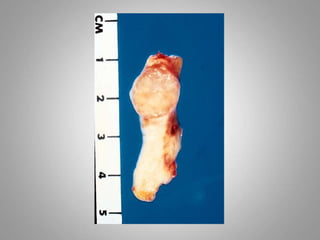
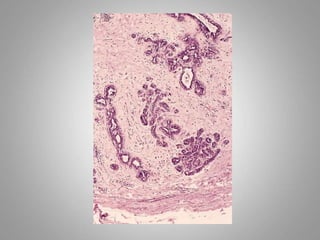
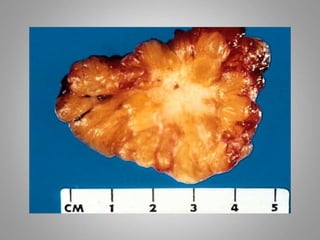
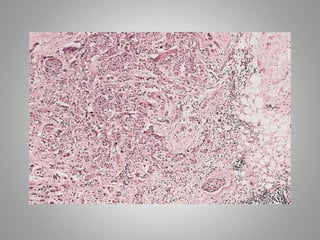
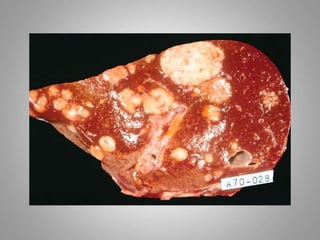
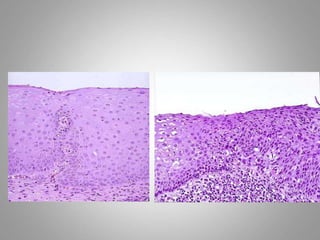
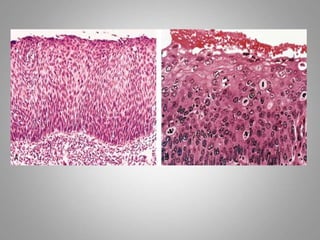
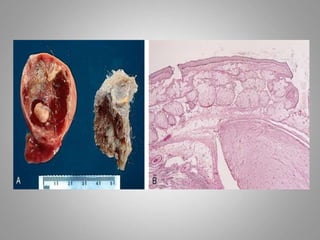
This document provides an overview of neoplasia (new abnormal growths or tumors). It defines neoplasia and discusses the classification of tumors as benign or malignant based on characteristics like differentiation, growth rate, invasion and metastasis potential. It also covers tumor nomenclature, risk factors for cancer like age, environment, heredity and pre-existing conditions. The document summarizes key concepts around epidemiology, molecular basis of cancer development, and laboratory diagnosis of tumors.